Patents
Literature
31results about How to "The preparation process is clear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
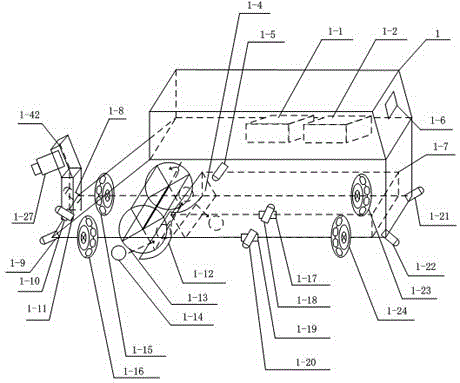
Intelligent ball picking system based on visual identification and multi-sensor data fusion
InactiveCN103341255AStrong execution efficiencyImprove execution efficiencyBall sportsManipulatorControl systemVision based
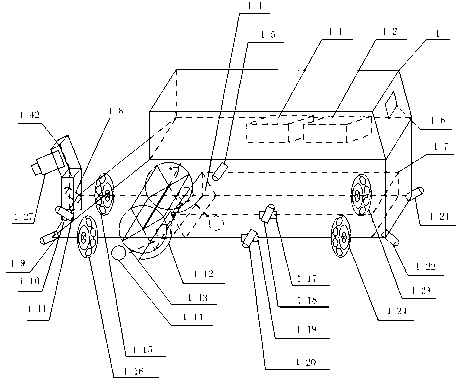
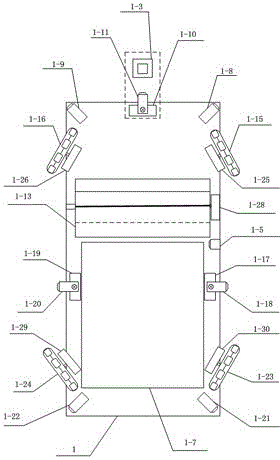
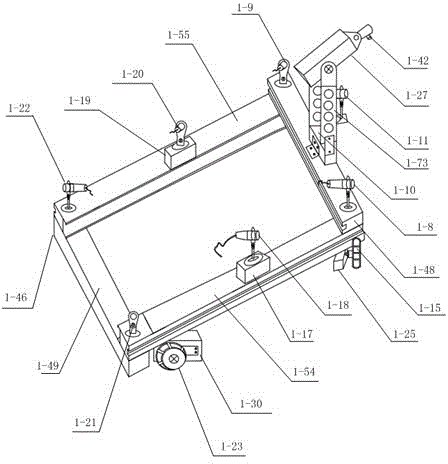
The invention discloses an intelligent ball picking system based on visual identification and multi-sensor data fusion. A multi-sensor data fusion method is adopted. A first infrared sensor (1-8), a second infrared sensor (1-21), a third infrared sensor (1-22) and a fourth infrared sensor (1-9) are four sensors at fixed positions and can detect barriers at the top corners of an intelligent ball picking device (1). A fifth infrared sensor (1-11) controlled by a fifth steering engine (1-10), a sixth infrared sensor (1-18) controlled by a sixth steering engine (1-17) and a seventh infrared sensor (1-20) controlled by a seventh steering engine (1-19) form three sets of sensors which can swing at angles, the sensors transmit collected data to a control system in real time and detect the barriers in front, on the left side and on the right side after the data are processed by the control system, and the barrier avoidance function is achieved. An infrared counting sensor (1-5) transmits collected information of the number of ball bodies to the control system for processing, and the counting function is achieved.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing double-wall-layer fresh ginger volatile oil microcapsules
ActiveCN105815784AImprove stabilityImprove bioavailabilityFood shapingNatural extract food ingredientsChemistryGingerol
The invention relates to a method for preparing double-wall fresh ginger volatile oil microcapsules.The method includes the steps that fresh ginger volatile oil is dispersed in an inner layer wall material and homogenized at normal temperature and high pressure, and a primary suspension is prepared; secondly, the primary suspension is dispersed in an outer layer wall material, emulsifier is added, the primary suspension is homogenized at normal temperature and high pressure, and a secondary suspension is obtained; thirdly, the secondary suspension is dried, and the double-wall fresh ginger volatile oil microcapsules are obtained.The embedding rate of the prepared fresh ginger microcapsules is 81-98%, in the preparation process, the technology that fresh ginger volatile oil is supercritically extracted and normal-temperature double-layer embedding, high-pressure homogenization and freezing or spray drying are conducted is adopted, so that the product embedding rate is high, the embedding effect is good, flowability is good, stability of effective components of the fresh ginger volatile oil can be improved, bioavailability is high, and the method is used in the food and health-care product field.
Owner:李洪清
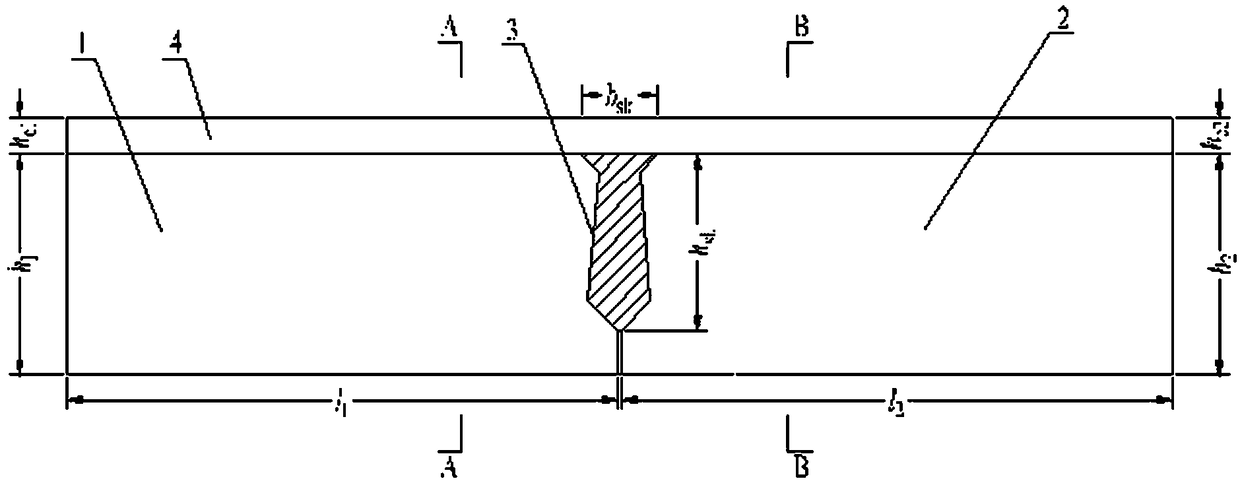
A hollow-slab-bridge hinge joint bearing capacity test piece, a manufacturing method thereof and a test method of the test piece
ActiveCN105842046AEasy to makeThe preparation process is clearPreparing sample for investigationStrength propertiesExperimental researchConcrete beams
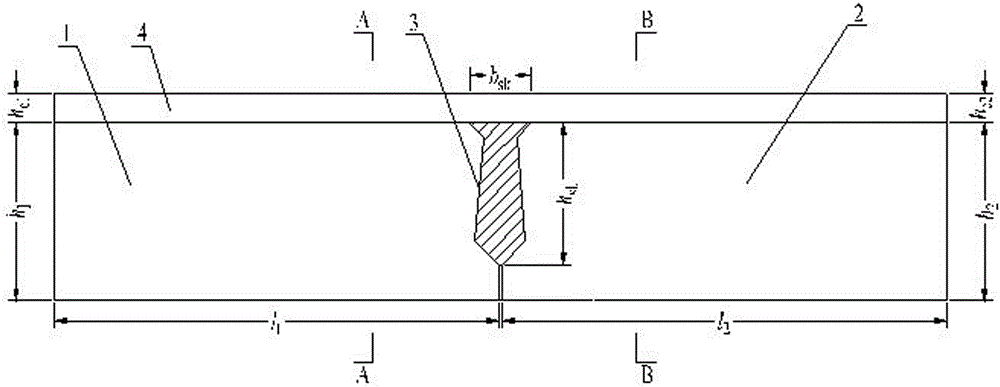
The invention relates to a hollow-slab-bridge hinge joint bearing capacity test piece, a manufacturing method thereof and a test method of the test piece. The test piece includes a first concrete beam and a second concrete beam. Reinforcing steel bars are disposed in the first and second concrete beams. Forms of the reinforcing steel bars and stirrups in the first concrete beam are same as those of the reinforcing steel bars and stirrups at corresponding positions in the first concrete beam. A hinge joint is disposed between the first and second concrete beams. A whole concrete pavement layer is disposed on the first and second concrete beams. The strength grade of the first concrete beam and the strength grade of the second concrete beam are same as the strength grade of a hollow slab bridge to be tested. The test piece is simple to manufacture, strong in operationality, convenient in experiment research of hinge joint stress performance and small in volume, can conveniently perform static force and fatigue tests, and can overcome the technical difficulty, namely rapid measurement of hinge joint stress performance.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Manufacturing method and applications of otolith cross section grinding sheet of mandarin fish
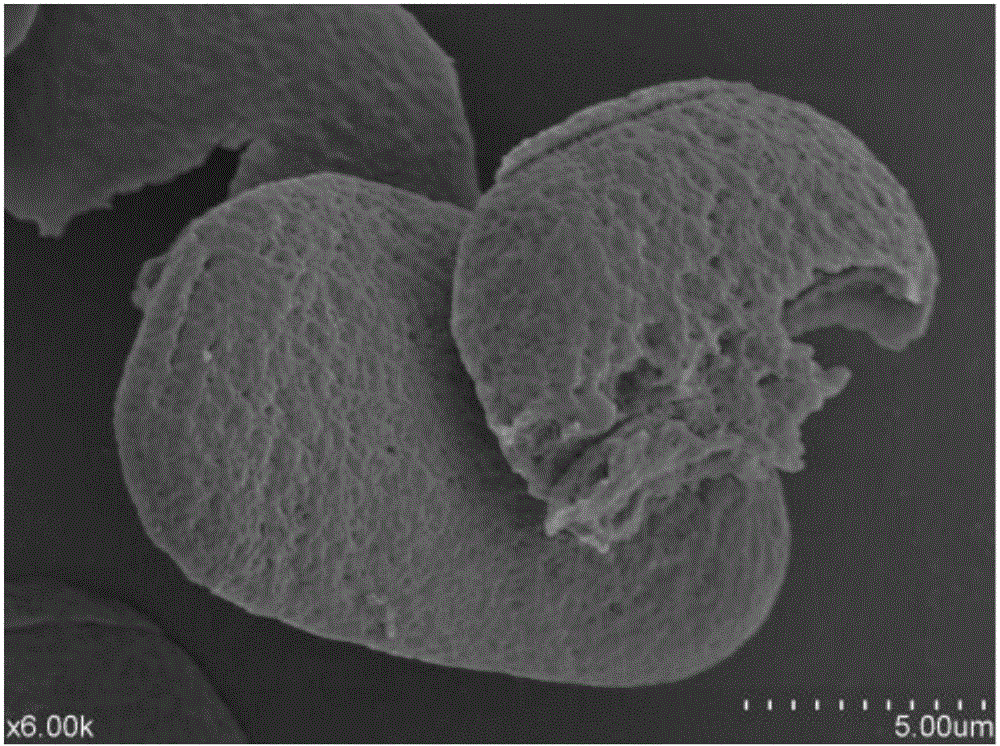
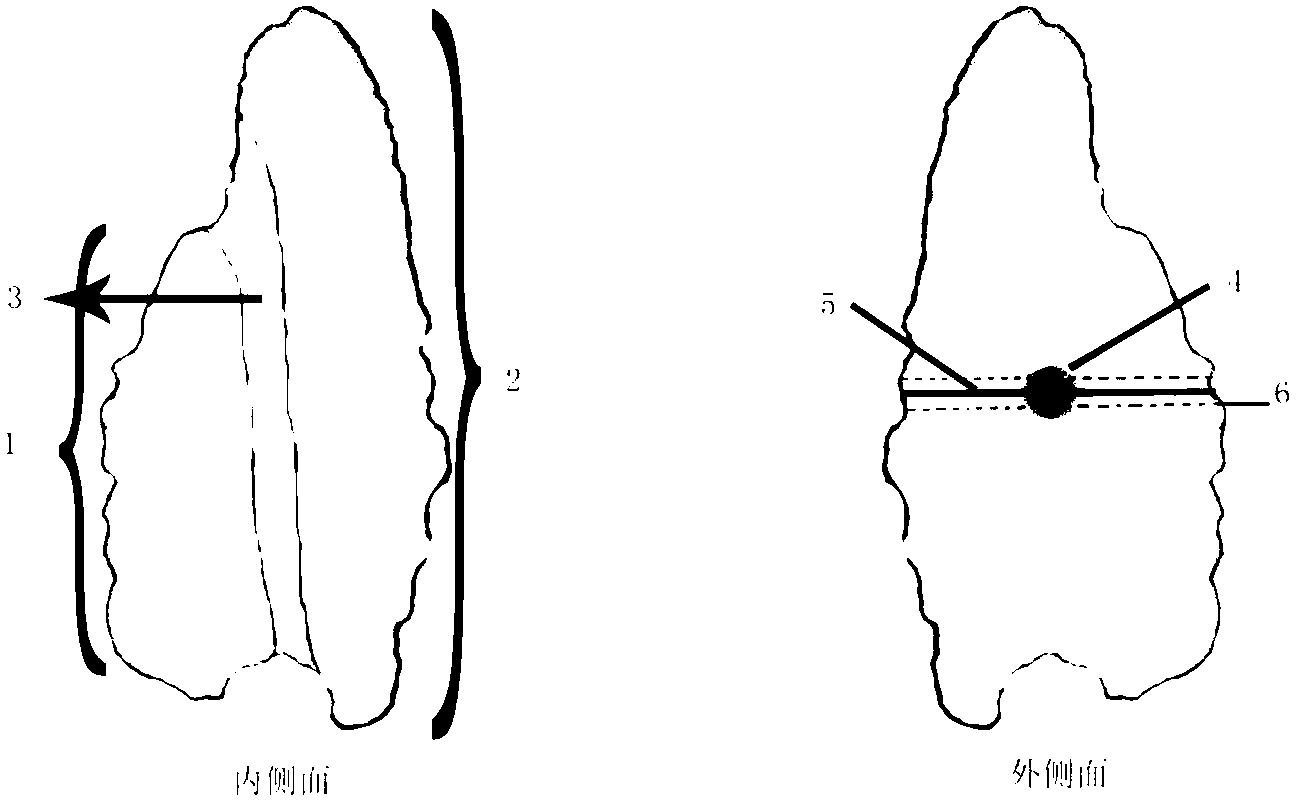
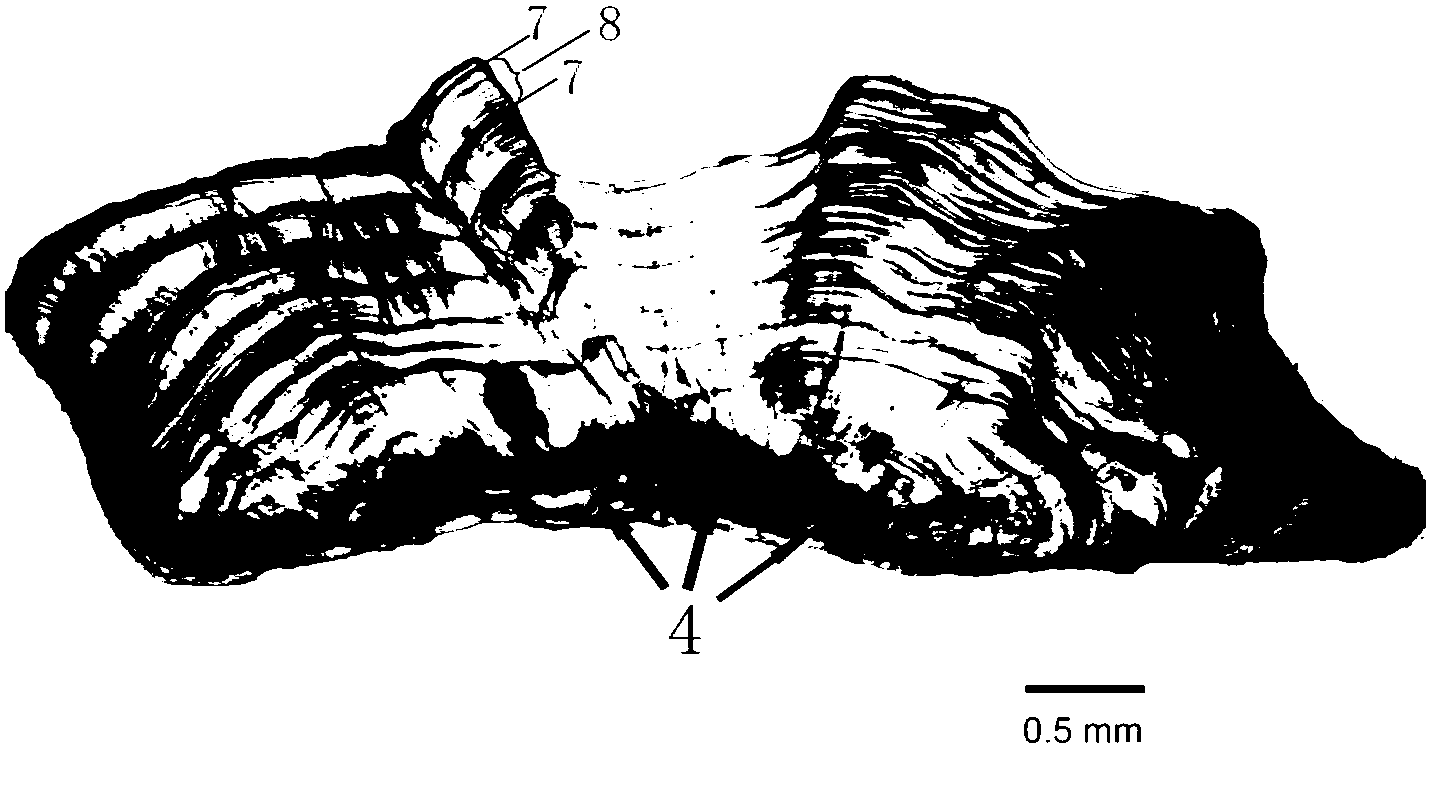
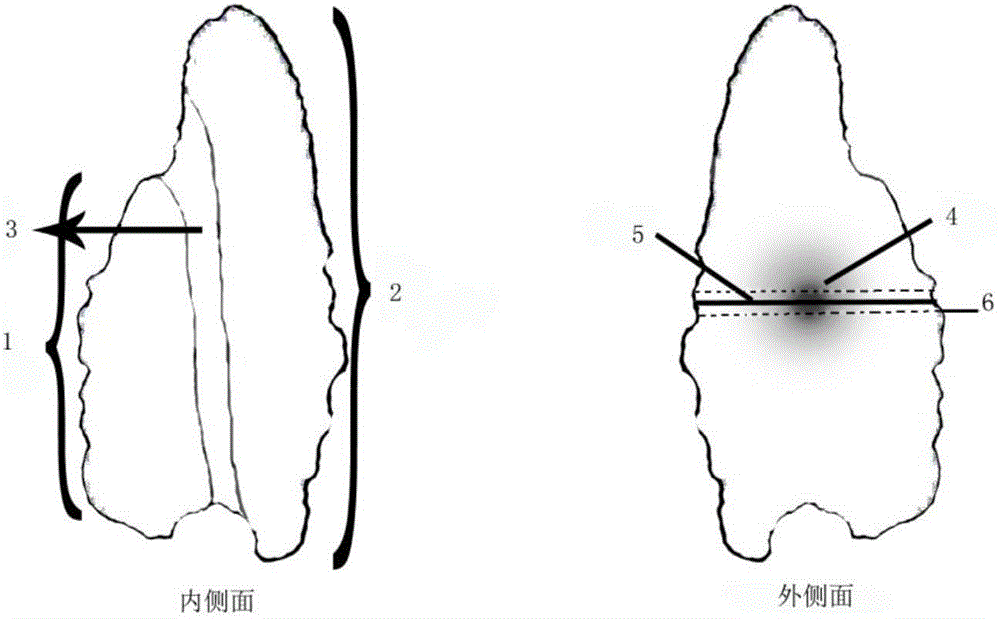
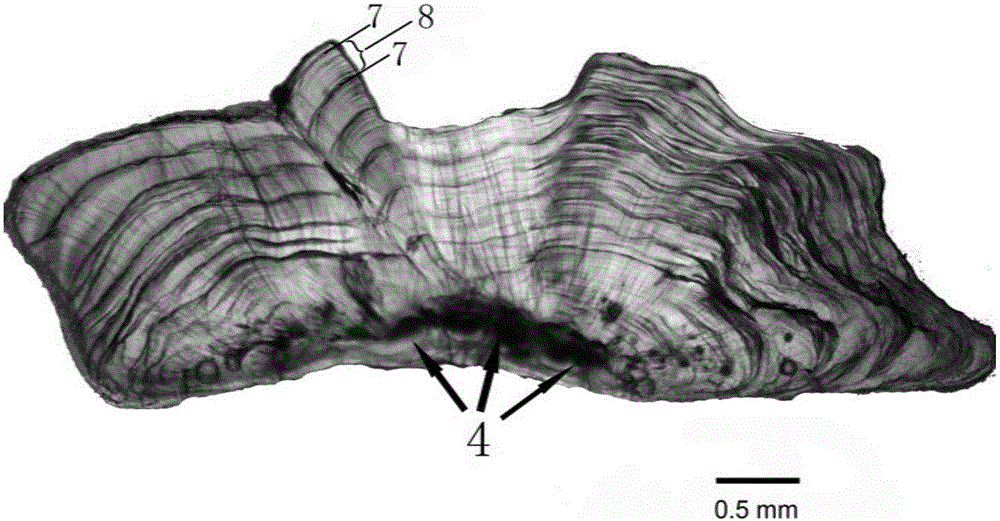
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and applications of an otolith cross section grinding sheet of a mandarin fish and belongs to the field of fish ecology. According to the manufacturing method, a sagitta serves as a research material, a cross section of the sagitta is subjected to sheet grinding, the manufactured otolith grinding sheet is placed under a microscope, the age can be identified and widths between rings can be measured through charge coupled device (CCD) software under the irradiation of incident light, ring distribution features of the otolith grinding sheet are observed, and then the age of the mandarin fish is identified. Compared with traditional identification methods, the method has the advantages that rings of the otolith of the mandarin fish are clear and visible, and an otolith nucleus is inclined towards one side of the otolith grinding sheet to form a linear nucleus area; a band area in which bright bands and dark bands are staggered is formed on the other side of the otolith starting from the otolith nucleus, bright bands are wide and are formed from spring to autumn, and dark bands are narrow and are formed in winter, so that annual rings are formed. By the aid of rings with alternating bright bands and dark bands, the age is distinguished and judged easily, so that the accuracy of identification of the age of the mandarin fish is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Sugar-free type Chaihuang granules and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN102641333ADoes not cause obesityGuaranteed tasteAntipyreticAnalgesicsSucroseMedical prescription
The invention relates to sugar-free type Chaihuang granules and a preparing method thereof. The sugar-free type Chaihuang granules are characterized in that 2500g of radix bupleuri, 180g of baikal skullcap root extract, a flavoring agent and a right amount of auxiliary materials and the like are prepared into the sugar-free type Chaihuang granules; and each bag of sugar-free type Chaihuang granules contains 0.30 to 0.40g of baikal skullcap root extract calculated according to baicalin (C21H18O11). The sugar-free type Chaihuang granules disclosed by the invention have the following advantages that: the sugar-free type Chaihuang granules do not contain cane sugar, and the condition of obesity can not be caused after long-time taking; the sugar-free type Chaihuang granules contain the flavoring agent, the mouth feel of an original recipe is kept, and the sugar-free type Chaihuang granules are especially suitable for children to take; the procedure of a preparing process is definite, the operation is easy, the quality is controllable, and the industrialized production is easy; and the sugar-free type Chaihuang granules have extensive application range and can also be used by patients avoiding eating sugar, such as diabetics and the like.
Owner:HENAN LINGYOU PHARMA
Porous dandelion-shaped Pd nanometer dendrite preparation method, material obtained with same, and application
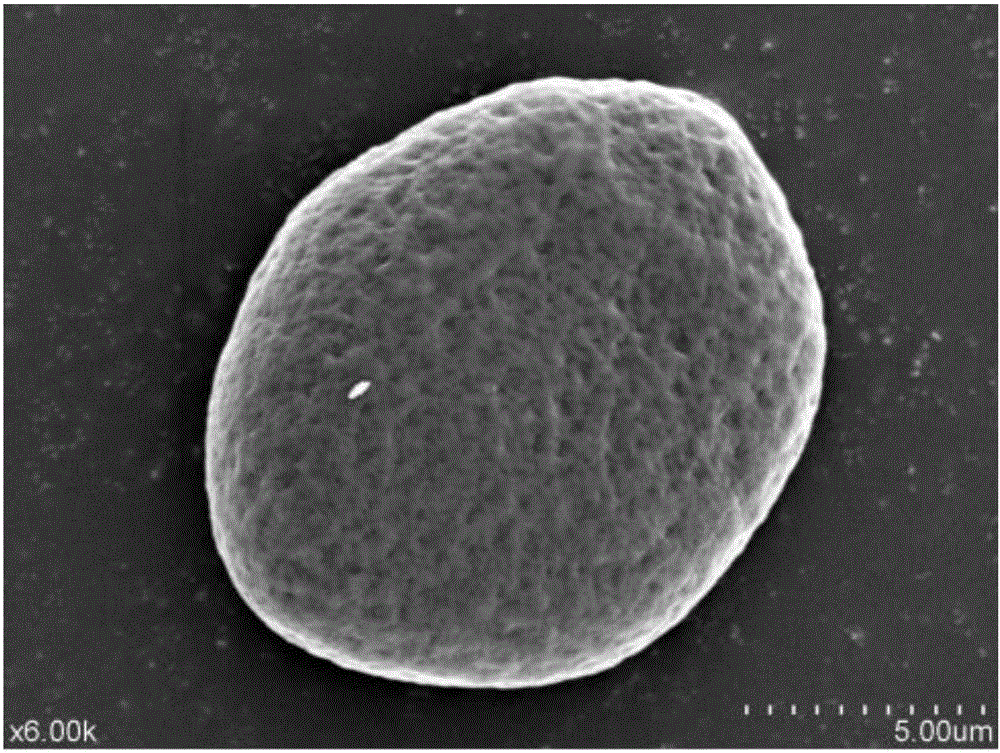
ActiveCN108543944AThe mechanism of the preparation process is clearEasy to prepareTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusMethylene bisacrylamideCathode catalyst
The invention discloses a porous dandelion-shaped Pd nanometer dendrite preparation method, a material obtained with the porous dandelion-shaped Pd nanometer dendrite preparation method, and the application using the material as an oxygen reduction cathode catalyst. According to the porous dandelion-shaped Pd nanometer dendrite preparation method, N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide (MBAA) is used as a complexing agent, a structure-directing agent and a reducing agent, and metal precursors are quickly reduced into porous dandelion-shaped Pd nanometer dendrites by adopting a standing reduction methodin one step. The porous dandelion-shaped Pd nanometer dendrites obtained with the method have the advantages of being regular in morphology, ultrafine in grain size, high in electrocatalytic activityand the like, and show high catalytic activity and stability when serving as the oxygen reduction cathode catalyst. The porous dandelion-shaped Pd nanometer dendrite preparation method is simple, efficient and universal.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sugar-free hypericum japonicum granule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103961399AIncrease sweetnessImprove securityDigestive systemAntiviralsBiotechnologySucrose
The invention relates to a sugar-free hypericum japonicum granule and a preparation method thereof. The sugar-free hypericum japonicum granule is characterized by consisting of 10-25 percent of hypericum japonicum extract, semen cassiae, 5-10 percent of kudzuvine root extract and a proper amount of auxiliary materials and flavoring agent, and each bag of sugar-free hypericum japonicum granule which contains not less than 0.55mg of hypericum japonicum based on quercetin (C15H10O7) is prepared. The sugar-free hypericum japonicum granule does not contain crane sugar and does not cause obesity due to long-term administration; the granule contains a flavoring agent, the taste of the original prescription is preserved, and the granule is conveniently taken by a patient; the preparation process is clear in process, the quality is controllable, and industrial production can be formed; and the sugar-free hypericum japonicum granule is wide in application range and can be used by diabetic patients and other sugar-free patients.
Owner:BENGBU HUOHE PHARMA
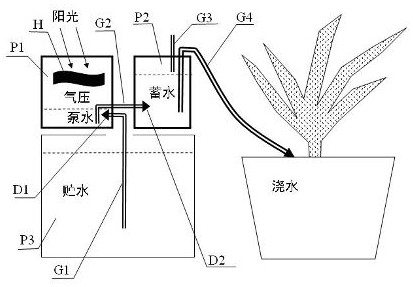
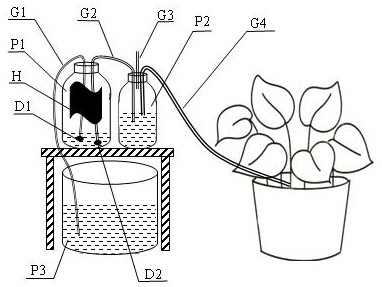
Solar pneumatic pump automatic watering device
PendingCN114027159AWatering on demandAutomatically adjust watering cycleSelf-acting watering devicesPressure pumpsWater storageWater flow
The invention discloses a solar pneumatic pump automatic watering device which comprises a pneumatic pump water container, a check valve, a water storage container and a water retaining container. The check valve is used for controlling the water flow direction to form a water inlet pipeline and a water outlet pipeline; air in the pneumatic pump water container expands with heat and contracts with cold to generate air pressure difference to achieve water pumping, water flows in from the water storage container through the water inlet pipeline when the interior of the pneumatic pump water container is in negative pressure, the water flows out to the water retaining container through the water outlet pipeline when the interior of the pneumatic pump water container is in positive pressure, and the pneumatic water pumping process is formed; and the water level in the water retaining container rises to trigger a siphon drainage process, and the water level descends to finish the siphon drainage process. Along with the alternation of day and night, the temperature in the pneumatic pump water container circularly changes in a reciprocating mode, water flow is continuously pushed to flow from the water storage container to the water retaining container, and automatic water pumping, water storage and periodic watering are achieved. The device is simple, practical, free of power consumption, energy-saving, environment-friendly and stable and reliable in operation, and existing resources and wastes can be fully utilized.
Owner:陈鑫宇
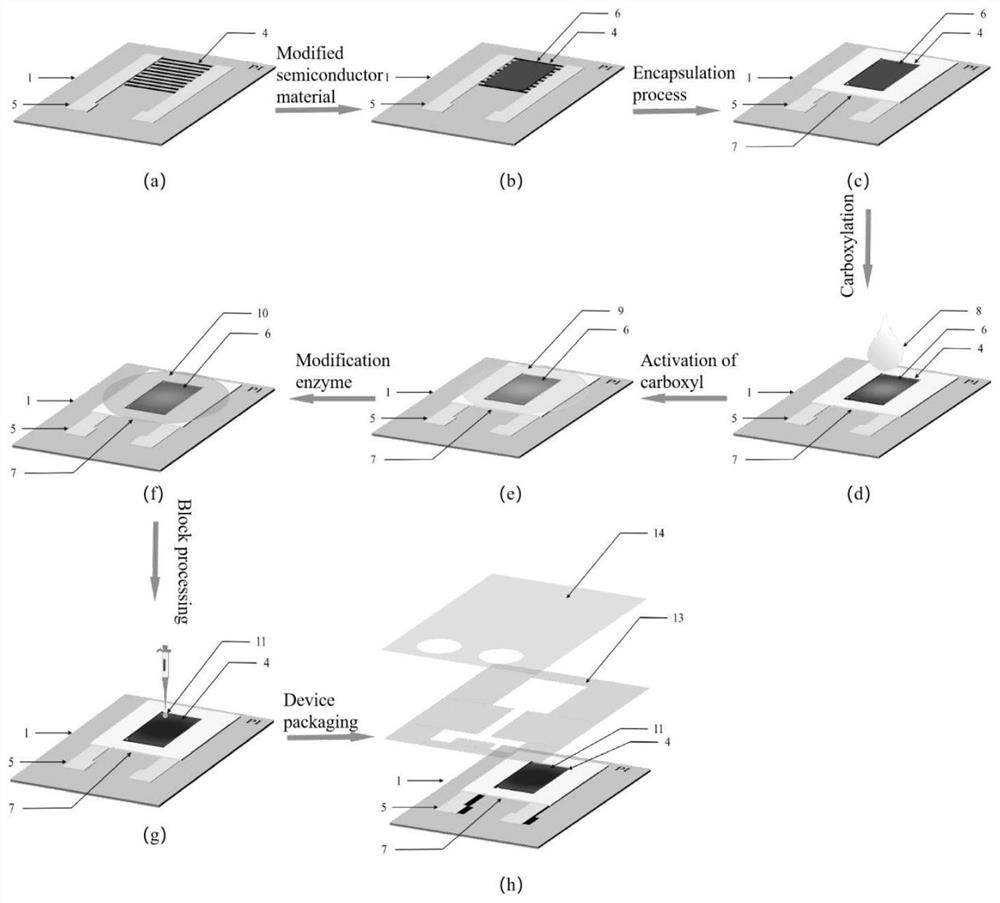
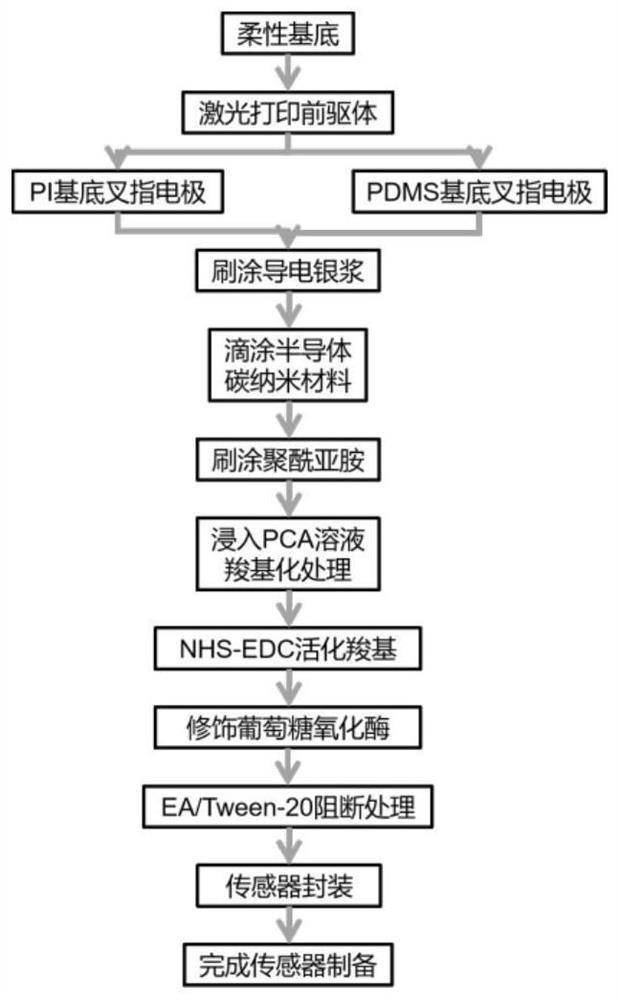
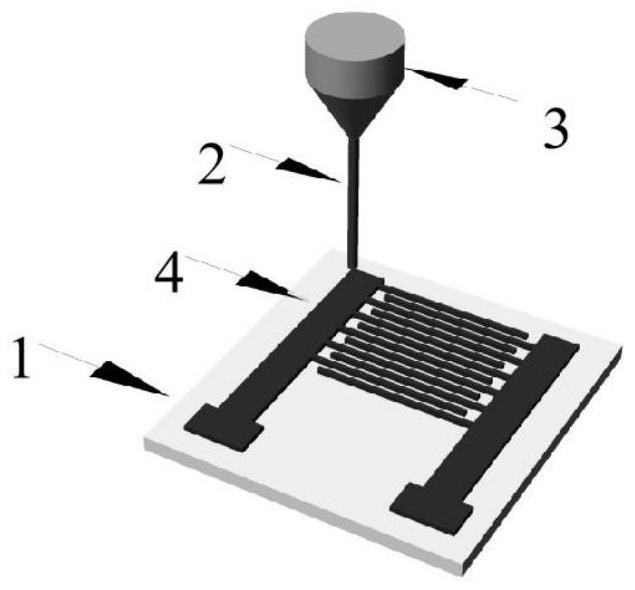
Flexible glucose biosensor and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113960134AExtended service lifeImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial electrochemical variablesCarboxyl radicalEnzyme membrane
The invention discloses a flexible glucose biosensor and a preparation method thereof. The sensor comprises a flexible substrate, a graphene interdigital electrode prepared on the flexible substrate through a laser engraving method, solid electrode wires arranged on the two sides of the interdigital electrode, a semiconductor carbon nanomaterial layer covering the surface of the interdigital electrode, a sensing enzyme membrane layer fixed on the semiconductor carbon nanomaterial layer through chemical crosslinking, and a blocking packaging layer covering the sensing enzyme membrane layer. The chemical cross-linking immobilization comprises the steps of carrying out surface carboxylation treatment on the semiconductor carbon nanomaterial layer, activating surface carboxyl, and immersing the semiconductor carbon nanomaterial layer into a solution containing glucose oxidase for chemical cross-linking immobilization. The flexible biosensor provided by the invention is high in specificity, high in sensitivity, large in detection range, low in detection limit and simple to prepare, has the flexible wearable characteristic and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
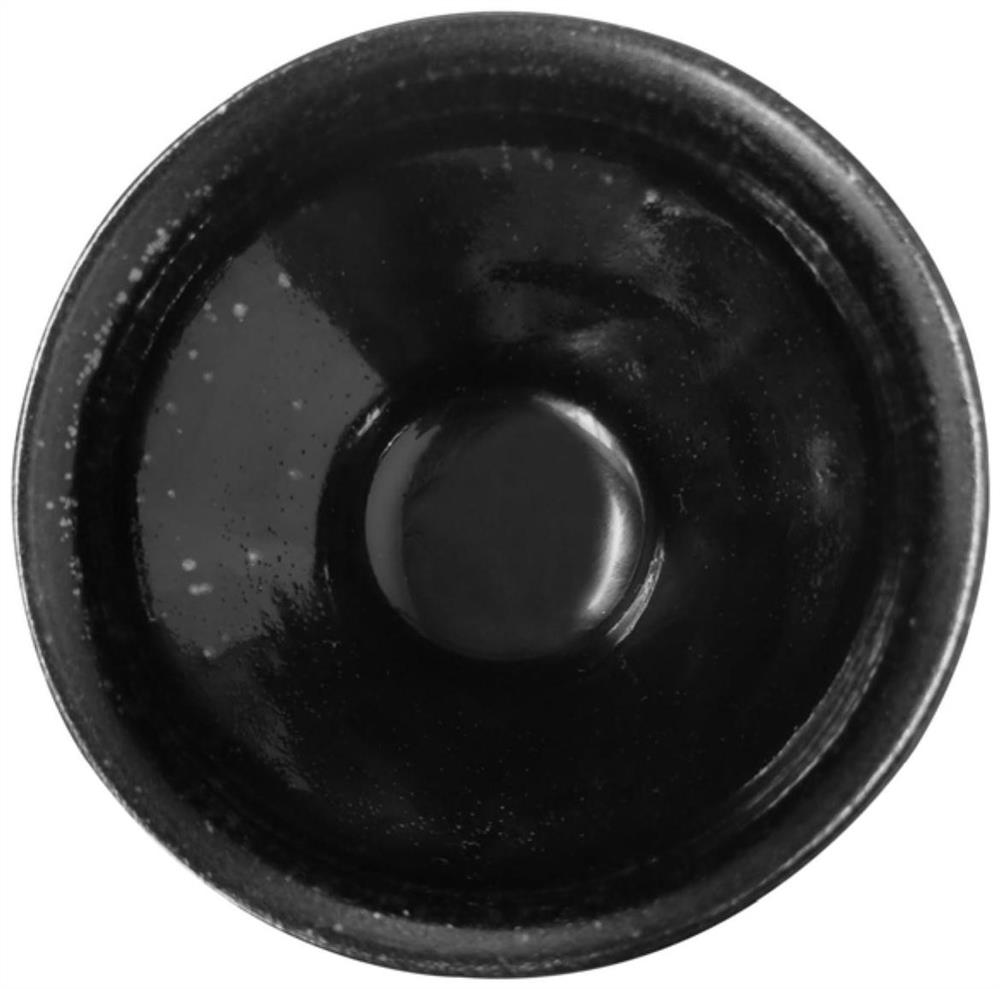
Firing method of black gold glaze built cup
The invention discloses a firing method of a black gold glaze built cup. The firing method comprises the following steps: preparing a green body and glaze slip, and glazing; and putting the glazed andair-dried green body into an electric kiln for roasting, powering off and stopping the kiln after roasting, naturally cooling, cooling and discharging. The raw ore is matched with other natural materials to prepare the green body and the glaze, the components are simple and pure, an innovative firing mode is adopted, the black gold glaze built cup is obtained, and the black gold glaze built cup is green black at the edge of the glaze built cup, and the other parts are black like paint, fine, mild, clean and bright as a mirror. And a small amount of oil drop crystals are hidden under the glaze(forming under-glaze drops), so that the product has unique artistic aesthetic feeling.
Owner:裴春元
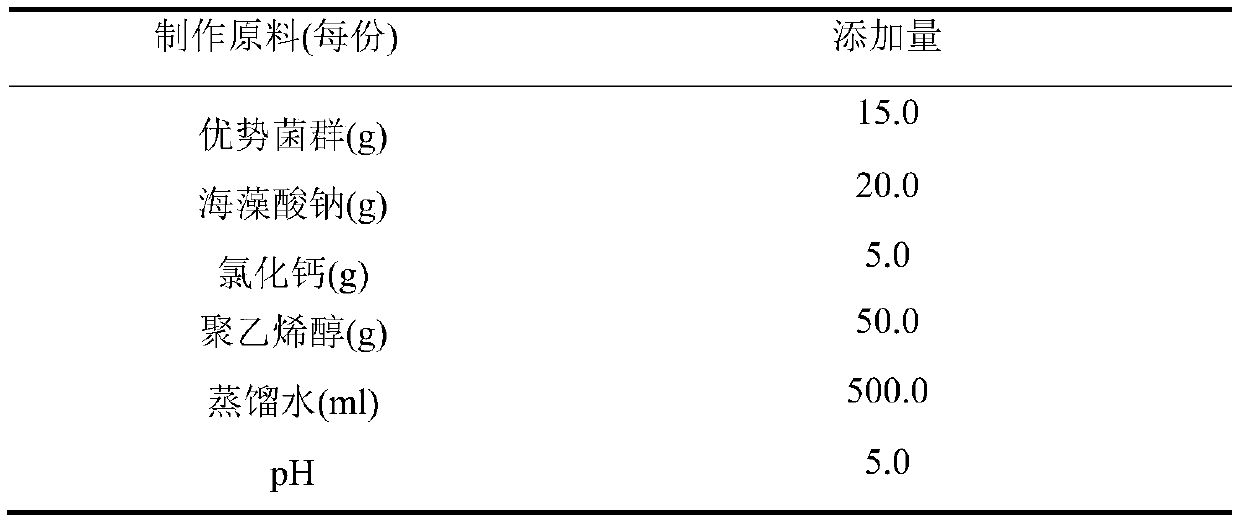
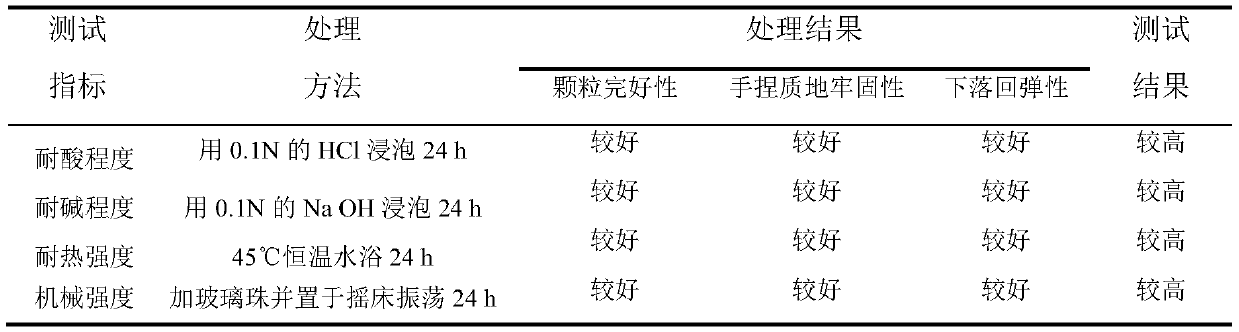
Preparation and use method of immobilized adsorbent for metal copper microorganisms in excrement
PendingCN111530430AHarm reductionThe preparation process is clearOther chemical processesWater contaminantsFecesTrichoderma sp.
The invention discloses a preparation and use method of an immobilized adsorbent for metal copper microorganisms in excrement, and belongs to the field of animal husbandry. The immobilized adsorbent is prepared by immobilizing and efficiently adsorbing microorganisms through sodium alginate gel, dominant strains are aspergillus oryzae, aspergillus niger and trichoderma, the safety of the strains is high, and the immobilized adsorbent has the advantages of accelerating excrement decomposition, killing pathogens and the like. The adsorbent is easy to prepare, low in price, high in gel strength and better in dryness resistance and acid and alkali resistance, the immobilized thallus cells can be desorbed after adsorbing copper and can be regenerated and recycled, the economic value of the adsorbent in use can be greatly improved, more binding sites on the surfaces of the cells are utilized after the thallus cells are immobilized, and the adsorption capacity is enhanced. The preparation anduse principles of the adsorbent are clear, the adsorption effect of the adsorbent is remarkable, and excessive copper in animal waste can be well reduced so that the harm to the environment is reduced, the average adsorption rate can reach 80%-90%, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV +1
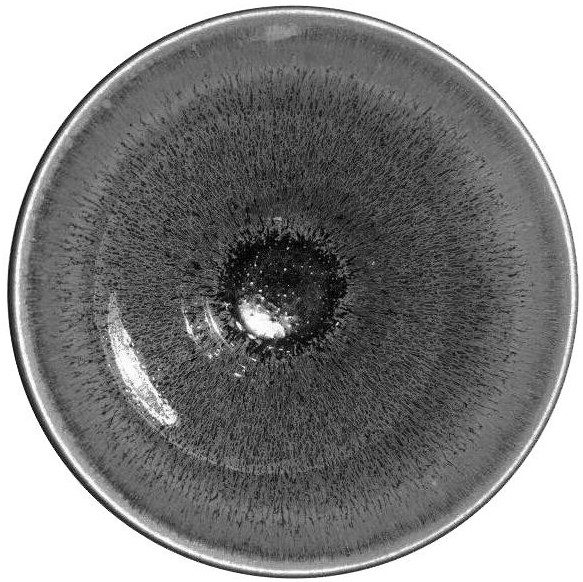
Rainbow gold hare's fur Jianzhan and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN112279621AStrong three-dimensional senseCrystallization is completeCeramic materials productionClaywaresWood ashKaolin clay
The invention discloses a rainbow gold hare's fur Jianzhan and a preparation process thereof. The rainbow gold hare's fur Jianzhan comprises a green body and glaze; wherein the green body is preparedfrom the following components by weight: 2-3 parts of kaolin, 6-7 parts of red soil and 1 part of field soil; and the glaze is prepared from the following components by weight: 60-70 parts of glazed stone, 10-20 parts of plant ash, 5-8 parts of iron oxide red, 7-8 parts of potassium feldspar, 3-4 parts of clay and 80-90 parts of water. A reasonable formula is obtained through scientific proportioning, an innovative firing mode is adopted, finally, the high-grade rainbow gold hare's fur Jianzhan is obtained, the hare's fur of the Jianzhan is thick and colorful, crystallization is thorough, hare's fur strips are clear, the three-dimensional sense of crystals is high, and the Jianzhan has a strong and striking visual impact feeling.
Owner:余明泉
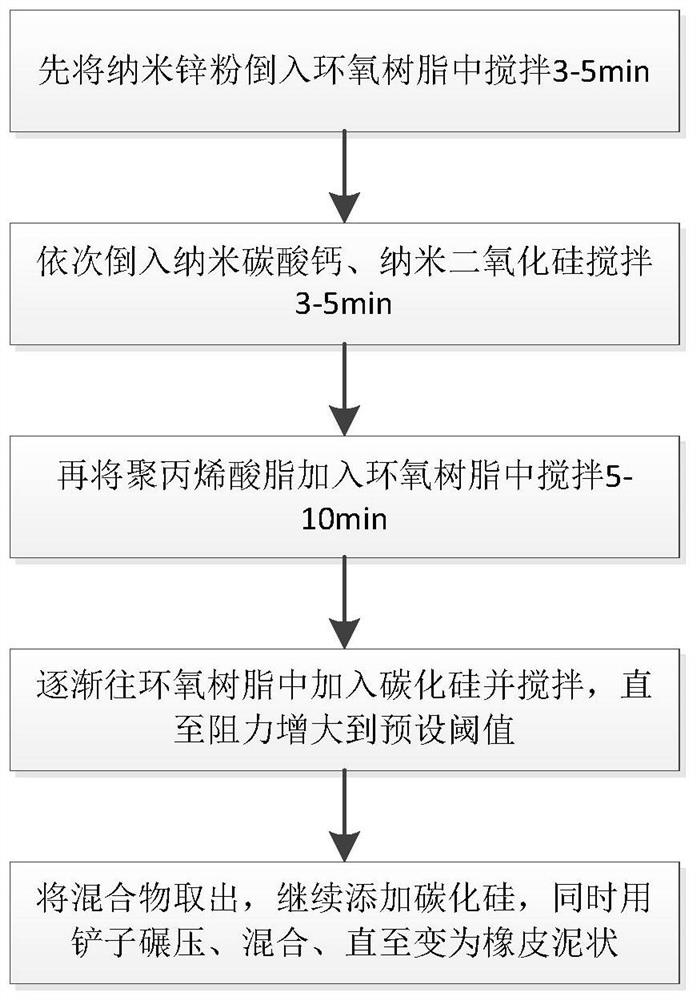
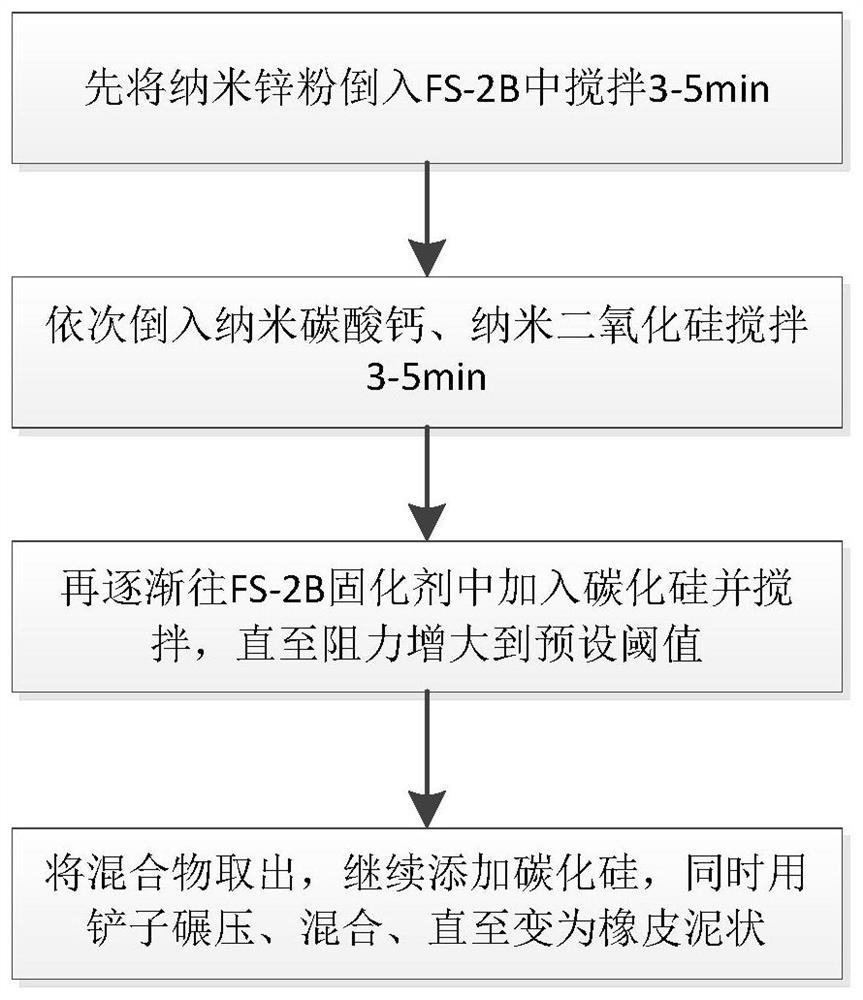
Sealing material for repairing sealing defects of oil-immersed equipment and its preparation device
ActiveCN109851994BHigh strengthReliable strengthRotary stirring mixersMixer accessoriesFirming agentSilicon dioxide
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A kind of preparation method of mandarin fish otolith cross-section grinding and application thereof
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and applications of an otolith cross section grinding sheet of a mandarin fish and belongs to the field of fish ecology. According to the manufacturing method, a sagitta serves as a research material, a cross section of the sagitta is subjected to sheet grinding, the manufactured otolith grinding sheet is placed under a microscope, the age can be identified and widths between rings can be measured through charge coupled device (CCD) software under the irradiation of incident light, ring distribution features of the otolith grinding sheet are observed, and then the age of the mandarin fish is identified. Compared with traditional identification methods, the method has the advantages that rings of the otolith of the mandarin fish are clear and visible, and an otolith nucleus is inclined towards one side of the otolith grinding sheet to form a linear nucleus area; a band area in which bright bands and dark bands are staggered is formed on the other side of the otolith starting from the otolith nucleus, bright bands are wide and are formed from spring to autumn, and dark bands are narrow and are formed in winter, so that annual rings are formed. By the aid of rings with alternating bright bands and dark bands, the age is distinguished and judged easily, so that the accuracy of identification of the age of the mandarin fish is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
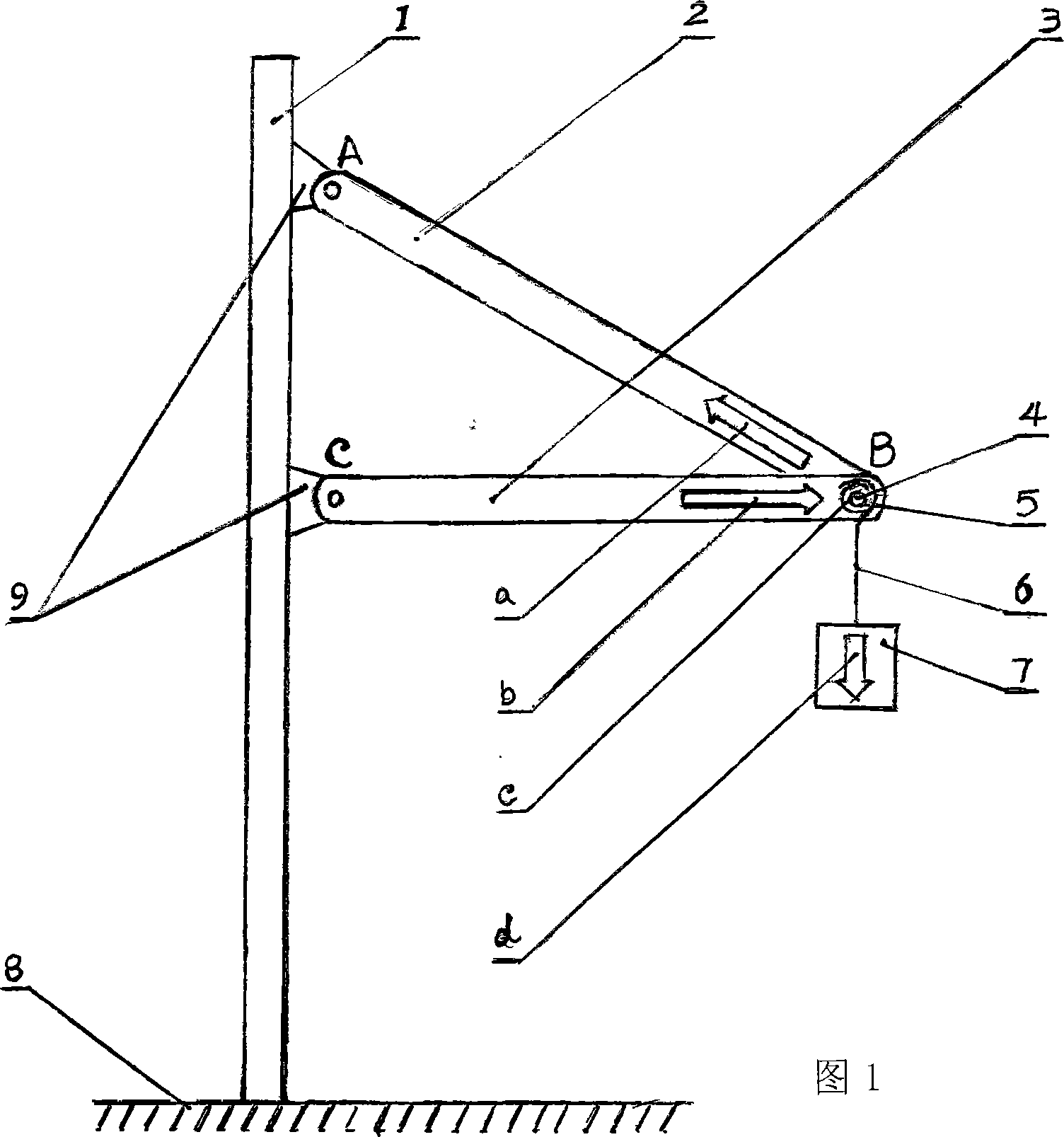
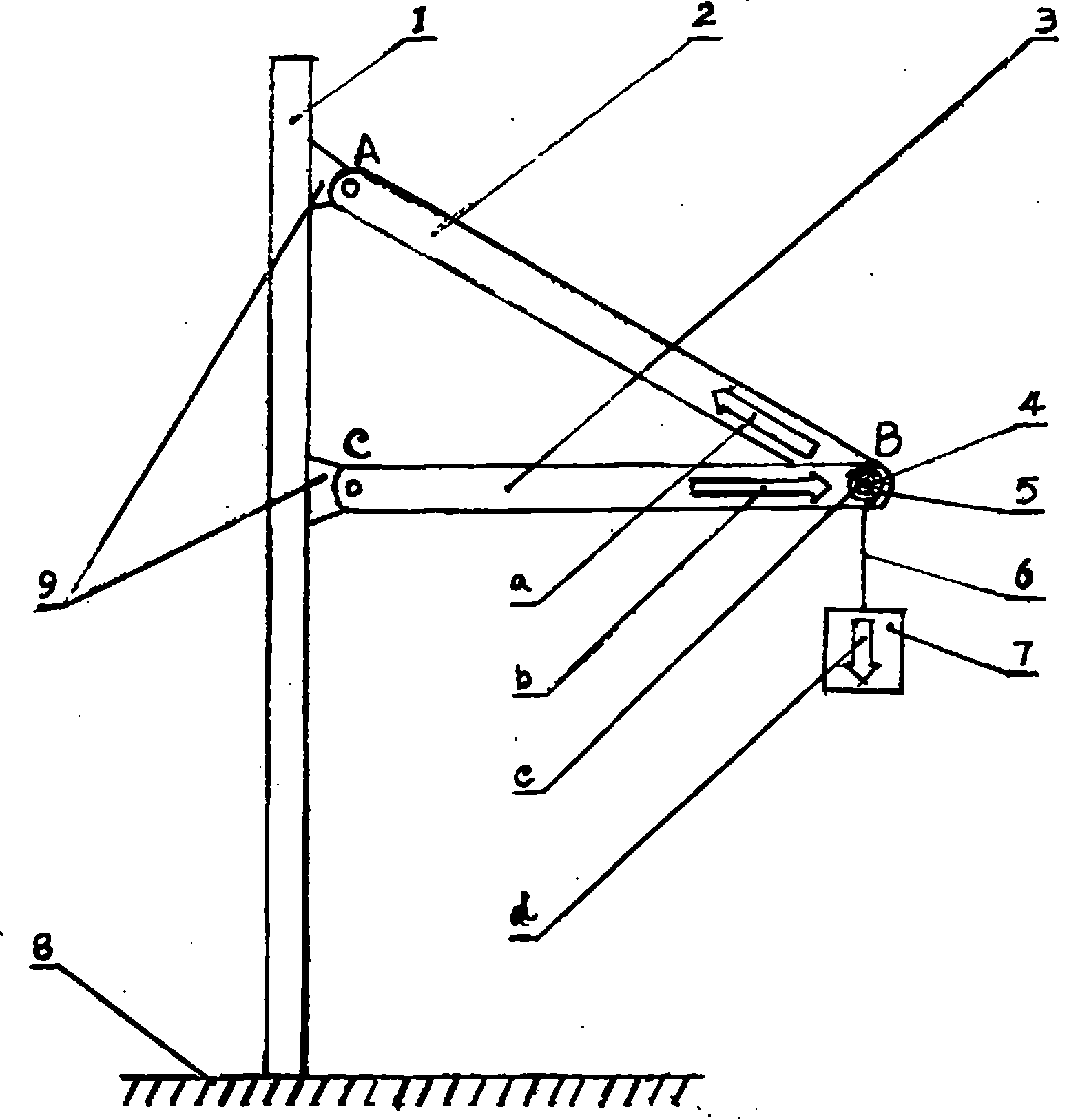
Demonstration apparatus for triangular component force bearing analysis
InactiveCN101488295BSimple structureReduce manufacturing costEducational modelsApplied mechanicsEngineering
The invention discloses a triangular member force analysis demonstration device. The device is a demonstration device in the teaching of engineering mechanics in vocational technical secondary school, in particular a force analysis demonstration device of a triangular member in statics. In the past, the teacher explains the contents about the force acting on the triangular member with temporarily-drawn figures, the students feel inexplicit about the contents during listening and watching and are difficult to understand what are acting force and reacting force and what is balance force. Especially in concurrent force system, students are confused about the forces acting on the researched object and the directions of the forces. In the invention, the action point B (the position of a pin), a pole AB, a pole CB and the object are respectively equipped with a lightening part, an arrow indicating the direction of the force and a switch. The invention shows the situation of the forces acting on the concurrent force system action points of the triangular member visually, vividly and accurately using the methods of light display and arrow expression. The device has the advantages of simple structure, easy production, low cost, convenient operation, direct-viewing demonstration, etc.
Owner:罗宇科
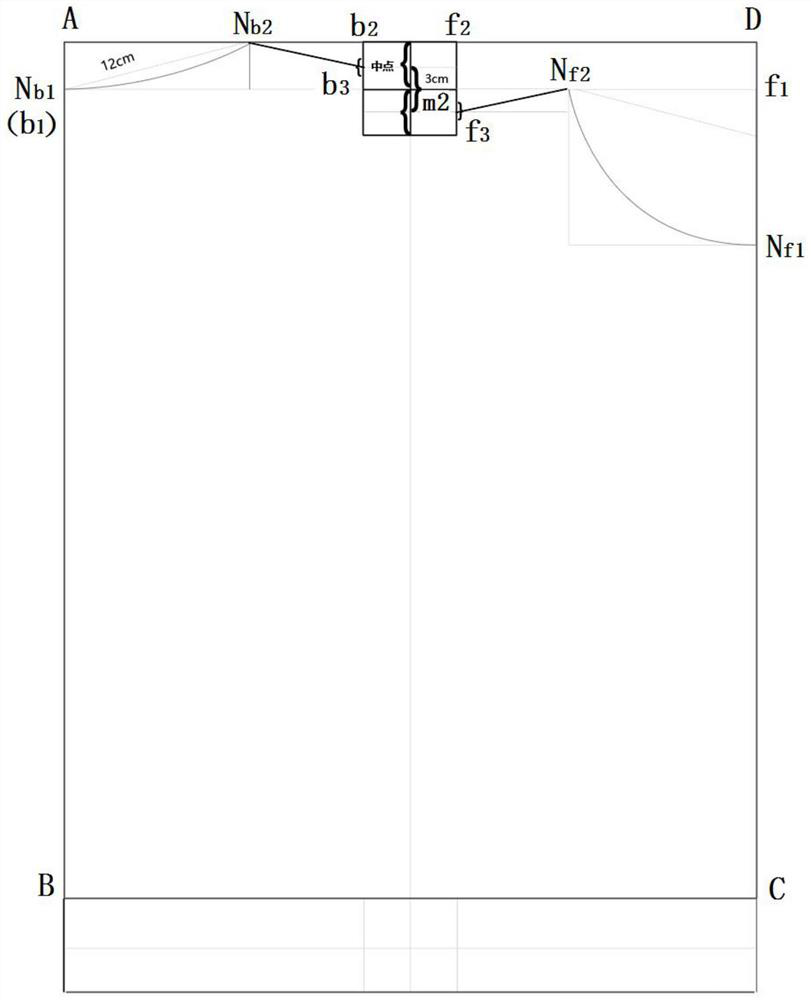
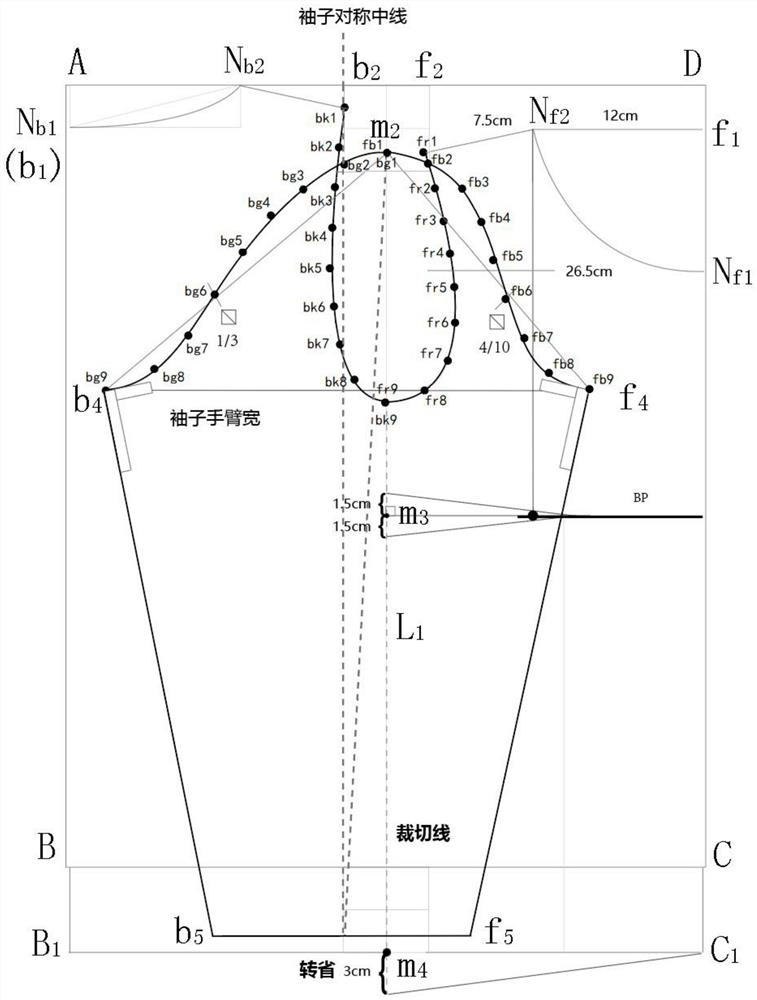
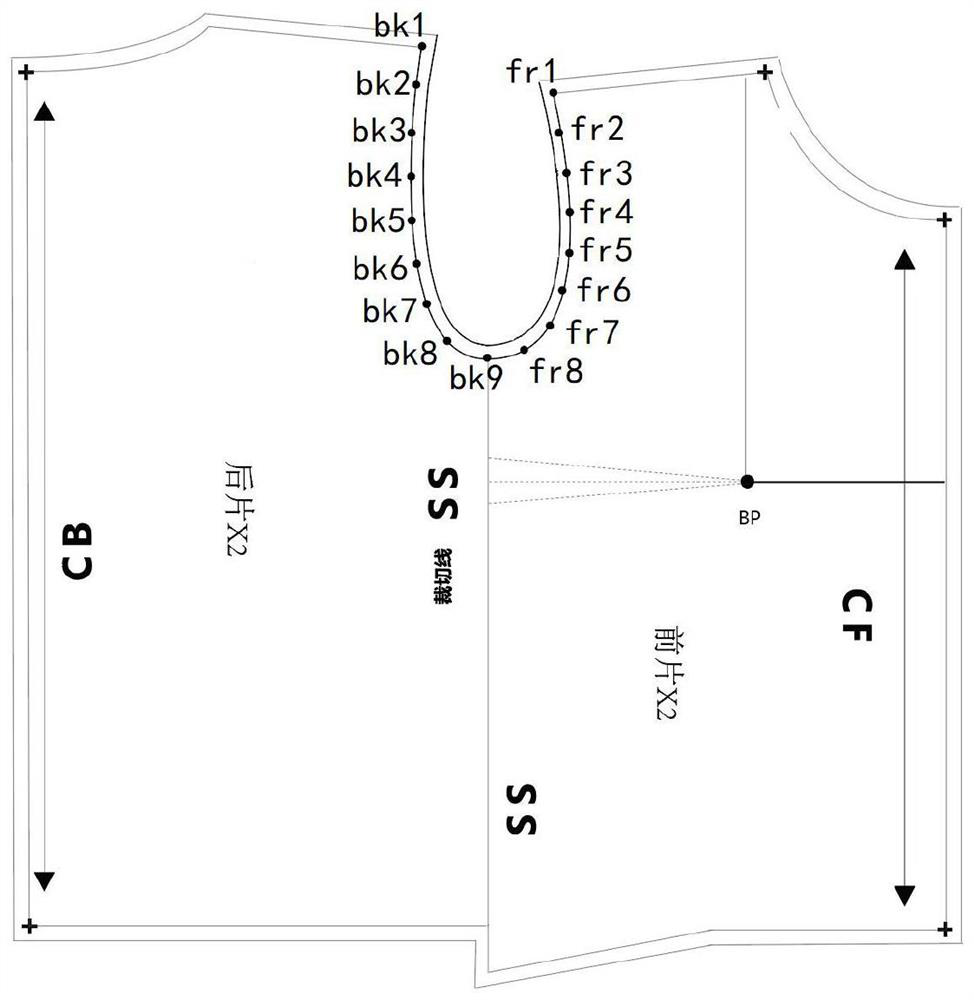
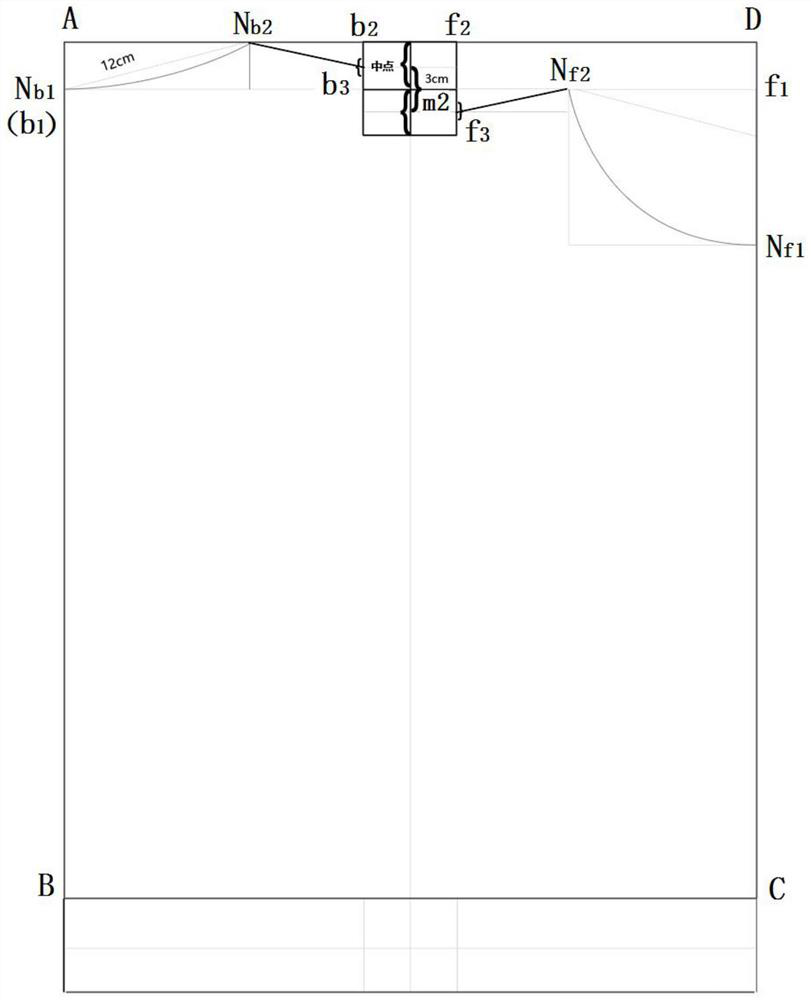
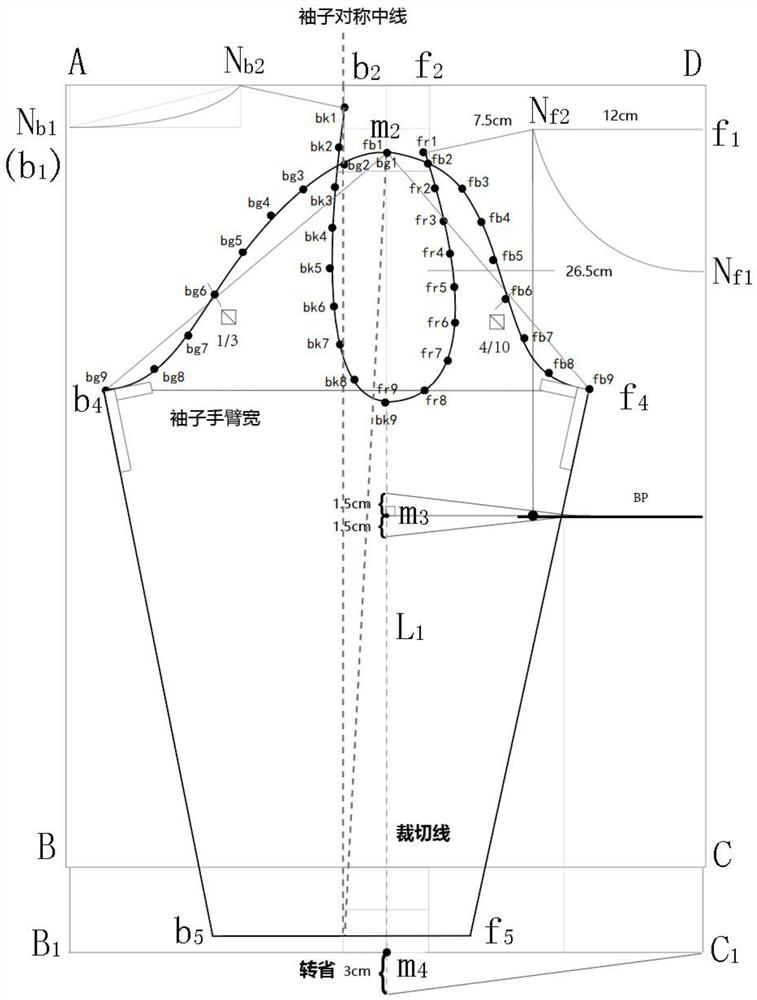
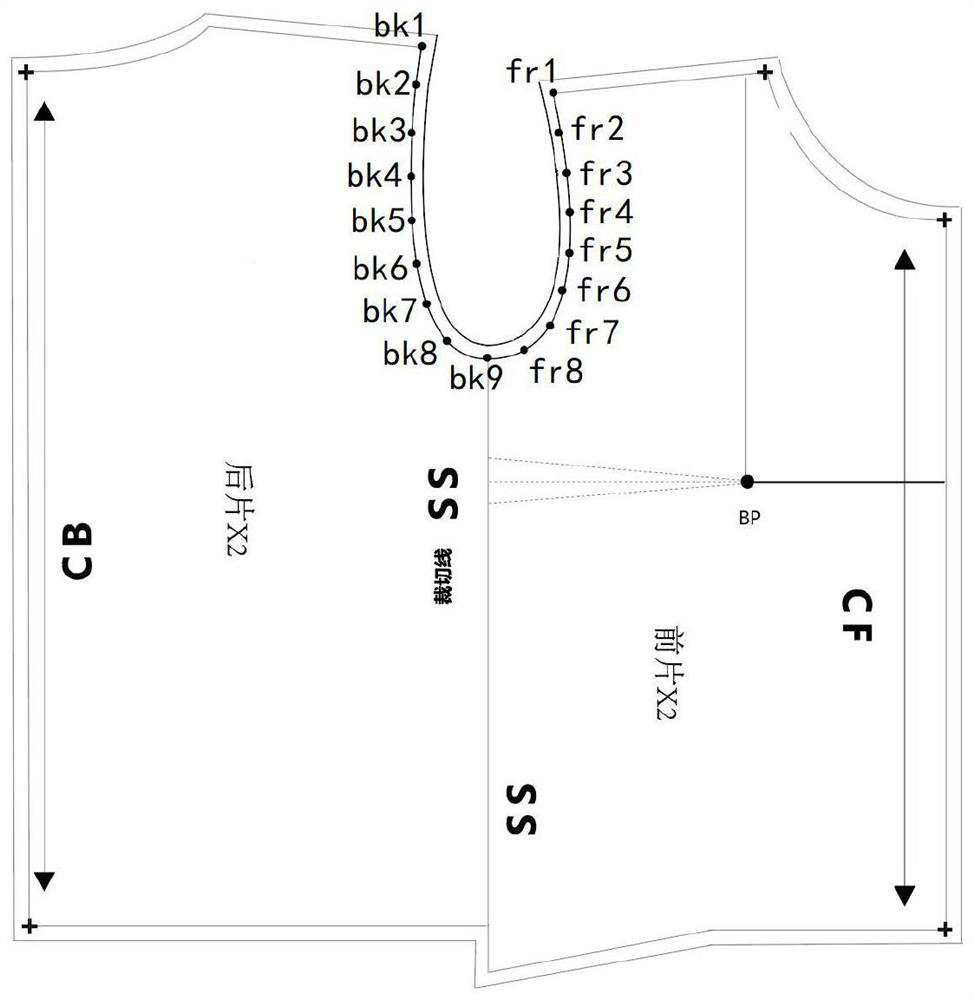
A kind of clothing plane symmetrical pattern making method
ActiveCN112137215BStandardize the pattern-making stepsEasy to analyzeClothes making applicancesStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:武汉市武昌区绿点视觉广告设计工作室
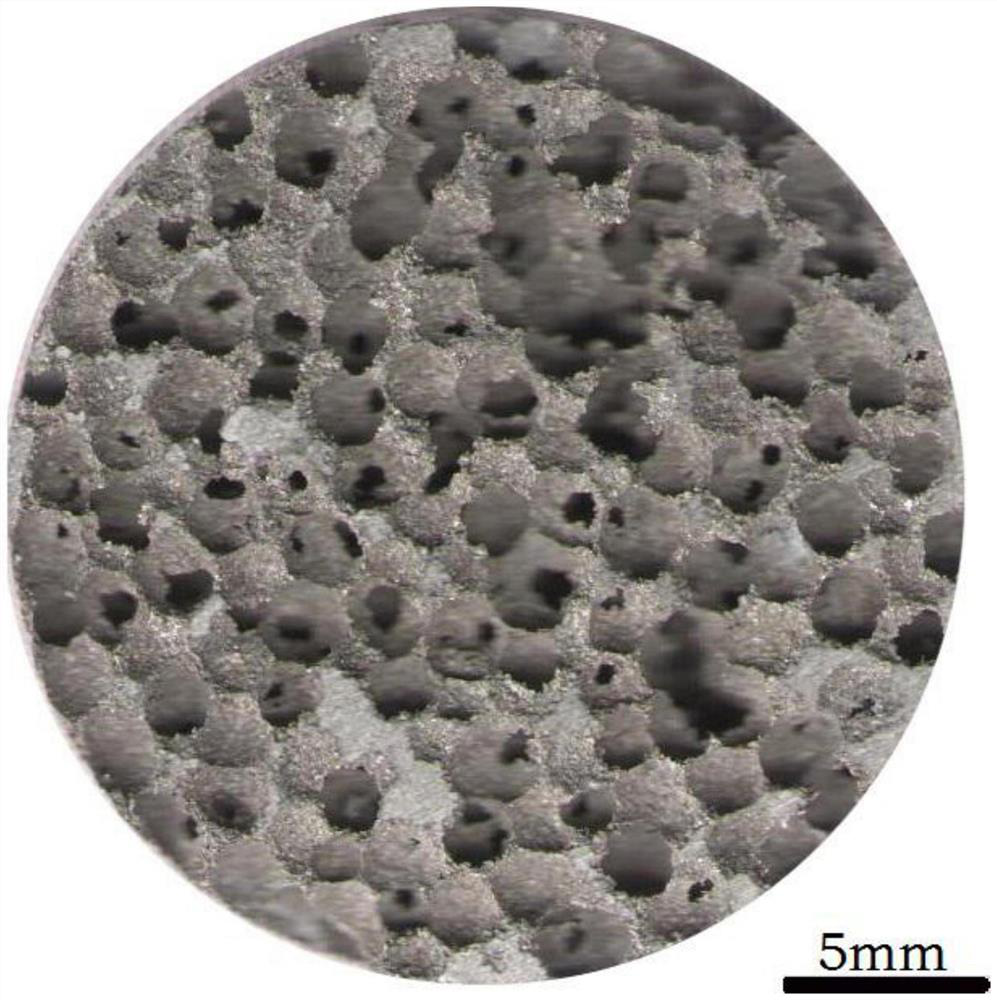
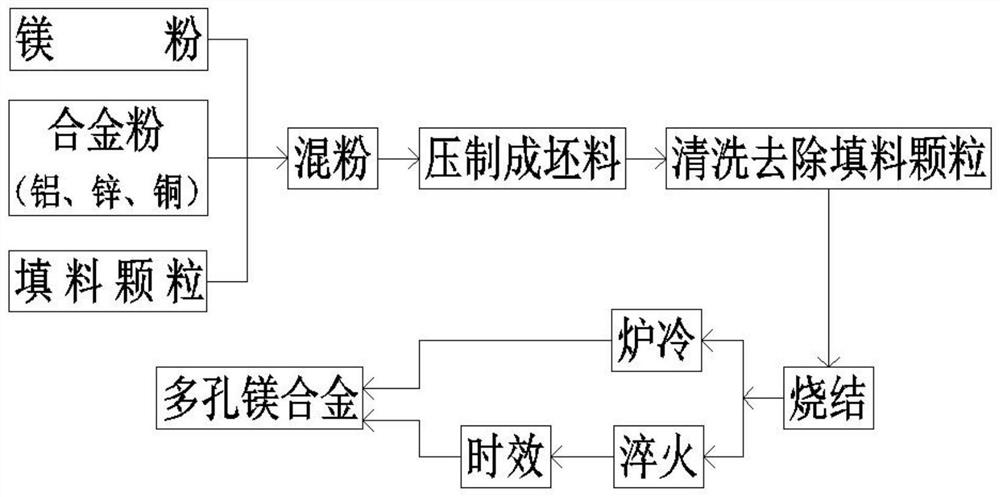
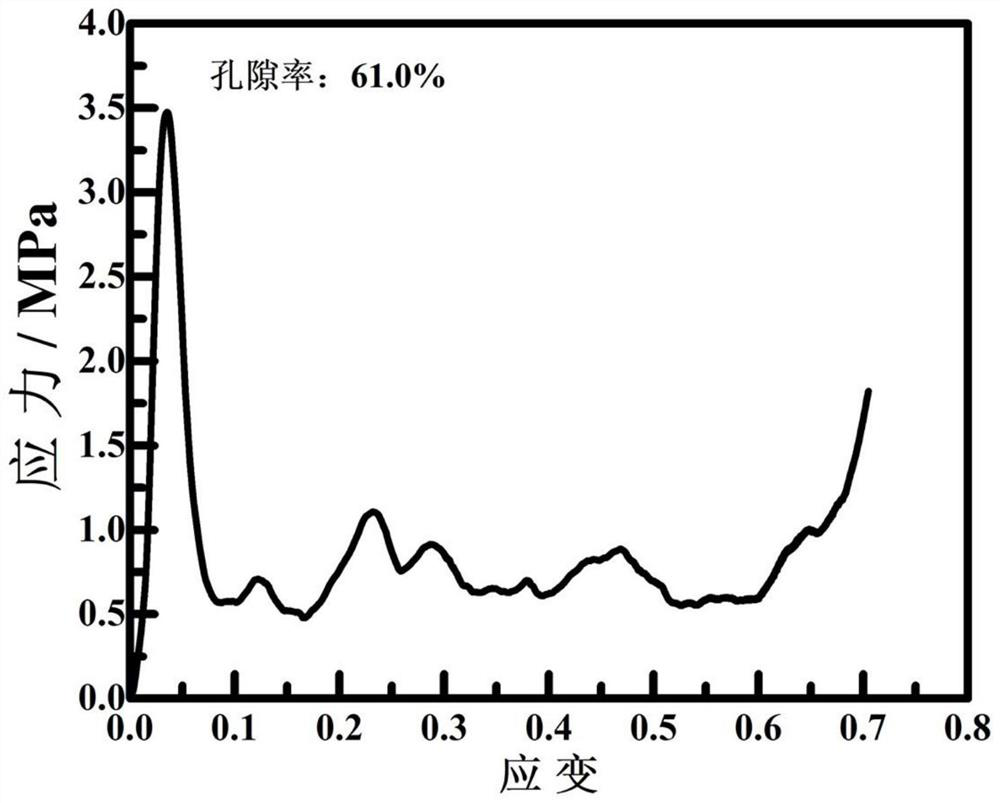
Porous magnesium alloy with through hole structure prepared by reactive sintering powder metallurgy method and preparation method of porous magnesium alloy
InactiveCN112846184APore structure can be adjustedThe preparation process is clearTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusMaterials scienceMagnesium alloy
The invention discloses a porous magnesium alloy with a through hole structure prepared by a reactive sintering powder metallurgy method and a preparation method of the porous magnesium alloy. Magnesium powder and alloy element powder are used as raw materials, urea particles or soluble salt particles are used as filler particles, and the porous magnesium alloy with the through hole structure is prepared by adopting the reactive sintering powder metallurgy method. The specific process method comprises the following steps of firstly, uniformly mixing the magnesium powder, alloy element powder and the urea particles or soluble salt particles serving as a pore-forming agent according to the expected porosity, then carrying out cold pressing on the mixture to prepare a green body, putting the green body into water or a weakly alkaline NaOH solution to remove filler particles, and then enabling the magnesium and alloy elements to react at a lower temperature to form metallurgical bonding to prepare the porous magnesium alloy with certain strength, enabling the preparation process to be safer and more energy-saving by the low sintering temperature, and meanwhile, improving the mechanical property of the porous magnesium alloy through solid solution aging treatment.
Owner:宿迁市河海大学研究院
Intelligent ball picking system based on visual identification and multi-sensor data fusion
InactiveCN103341255BStrong execution efficiencyImprove execution efficiencyBall sportsManipulatorControl systemVision based
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
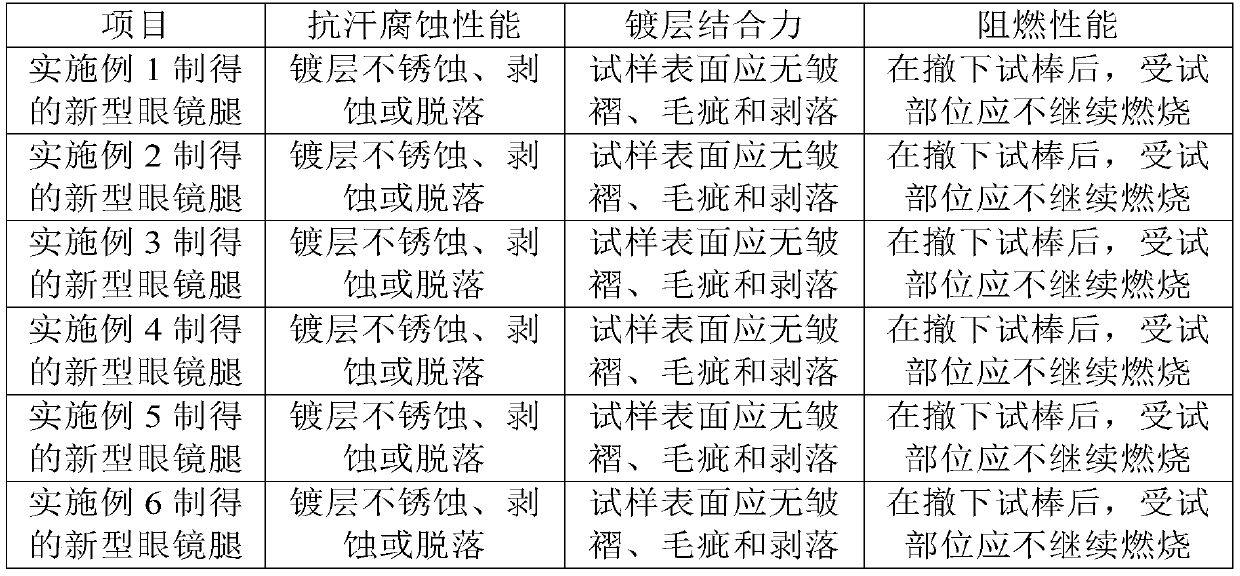
A kind of glasses leg and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a novel spectacle temple and a process for preparing the same. Ceramic materials are used as matrixes for the novel spectacle temple, and titanium and zinc alloy is electroplated on the surfaces of the matrixes. The process includes carrying out ball-milling on magnesium oxide, aluminum oxide, carbon fibers, binders and surfactants to obtain uniform slurry, injecting the uniform slurry into molds, aging and setting the uniform slurry to form platy spectacle temple blanks, transferring the platy spectacle template blanks into an atmosphere oven and firing the platy spectacle temple blanks to obtain spectacle temple ceramic substrates; electroplating the spectacle temple ceramic substrates used as templates to form uniform titanium and zinc alloy layers so as to obtain the finished novel spectacle temple. The novel spectacle temple and the process have the advantages that the problems of heavy dead weights and poor anti-dropping capacity of existing ceramic materials can be solved by the aid of the novel spectacle temple, the ranges of materials for the novel spectacle temple can be broadened, the aesthetics of the shape of the novel spectacle temple can be improved, markets for the novel spectacle temple can be opened, the novel spectacle temple can be positioned on high-end markets, and the market competitiveness can be enhanced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG IND & TRADE VACATIONAL COLLEGE
A kind of preparation method of double-walled ginger volatile oil microcapsules
ActiveCN105815784BImprove the stability of active ingredientsImprove bioavailabilityFood shapingNatural extract food ingredientsEmbedding rateDouble wall
The invention relates to a method for preparing double-wall fresh ginger volatile oil microcapsules.The method includes the steps that fresh ginger volatile oil is dispersed in an inner layer wall material and homogenized at normal temperature and high pressure, and a primary suspension is prepared; secondly, the primary suspension is dispersed in an outer layer wall material, emulsifier is added, the primary suspension is homogenized at normal temperature and high pressure, and a secondary suspension is obtained; thirdly, the secondary suspension is dried, and the double-wall fresh ginger volatile oil microcapsules are obtained.The embedding rate of the prepared fresh ginger microcapsules is 81-98%, in the preparation process, the technology that fresh ginger volatile oil is supercritically extracted and normal-temperature double-layer embedding, high-pressure homogenization and freezing or spray drying are conducted is adopted, so that the product embedding rate is high, the embedding effect is good, flowability is good, stability of effective components of the fresh ginger volatile oil can be improved, bioavailability is high, and the method is used in the food and health-care product field.
Owner:李洪清
Dissolving method for waxy substances on coccid of family Margarodidae
ActiveCN113575569AGood removal effectFully contactedDead animal preservationBiotechnologyScale insect
The invention provides a dissolving method for waxy substances on coccid of the family Margarodidae. According to the method, wax substances on female coccid of the family Margarodidae are dissolved through wax opening water, the female coccid is soaked in the wax opening water, heating is cooperatively conducted to enable the wax substances to be dissolved in an accelerated mode, and then proper vibration is conducted to allow the wax opening water to make full contact with the wax substances on the female coccid, so wax removal effect is achieved more quickly. The method is simple, convenient, time-saving and safe, easily removes wax protrusions and the wax substances on the female coccid, and lays a foundation for subsequent preparation of clear, complete and high-quality scale insect slide specimens.
Owner:广东生态工程职业学院
Planar symmetric pattern making method for clothes
ActiveCN112137215AStandardize the pattern-making stepsEasy to analyzeClothes making applicancesStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a planar symmetric pattern making method for clothes. The method specifically comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring parameters of a basic style of clothing, drawinga canvas rectangle of which the vertical length is the length of an object clothing and the horizontal length is 1 / 2 of the width of the object clothing, drawing a central axis of the canvas rectangle, and acquiring a front clothing piece rectangle and a rear clothing piece rectangle on two sides of the central axis; and step 2, drawing key points corresponding to the basic style of the clothing in the front piece rectangle and the rear piece rectangle respectively, and connecting the associated key points through straight lines or spline curves to obtain a layout drawing of the basic style ofthe clothing. According to the planar symmetric pattern making method for the clothing, the symmetric axis center line is determined in the canvas pattern, and then the position of the parameters ofthe basic style of the clothing in the canvas rectangle is calculated, so that straight lines or arcs expressed by corresponding parameters are drawn in the canvas rectangle step by step, the scientific clothing pattern making steps are standardized, and the problems that in the past, the steps of the pattern making process are prone to negligence, and cut parts are too detailed are effectively solved.
Owner:武汉市武昌区绿点视觉广告设计工作室
Accurate medicated diet food therapy product for people with damp-heat constitution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113317426AThe preparation process is clearActive ingredients are clearOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemXyloseHerb
The invention provides an accurate medicated diet food therapy product for people with damp-heat constitution and a preparation method thereof, aiming at the technical problems of an existing product for conditioning the damp-heat constitution that effective components are not clear, an acting target point and a pharmacological effect are not clear, network analysis of a component-target point-pharmacological action mechanism is lacked and a conditioning effect is not ideal enough. The product is prepared from the following substances in parts by mass: 7 to 12 parts of chicory herb, 4 to 8 parts of semen cassiae, 7 to 12 parts of herba portulacae, 4 to 8 parts of herba lophatheri, 7 to 12 parts of folium mori, 4 to 8 parts of lotus leaves and 0.3 to 2 parts of xylooligosaccharide. By adopting a conditioning principle of eliminating dampness and heat, related sub-health symptoms including acne, bitter taste and dry mouth, heavy body and sleepiness, sticky and unsmooth excrement or dryness, short and yellow urine, male scrotum dampness, female leukorrhagia and the like of the people with the damp-heat constitution are effectively conditioned. The preparation method is simple and feasible; a finished product is easy to carry and store and is convenient to use.
Owner:SHENZHEN ELDERLY MEDICAL RES INST +1
Preparation process of grey silk Jian Zhan
The invention discloses a preparation process of grey silk Jian Zhan. The preparation process comprises the following steps: preparing a green body and glaze slip; drying the laterite in the back wellin the sun, and carrying out stone hammer grinding, elutriation, sieving, filter pressing, mud refining, aging, throwing forming, fettling, biscuiting and airing to obtain the green body; elutriating, sieving, filter-pressing and calcining the green field red soil; mixing the calcined green field red soil, plant ash and water, grinding and sieving to obtain glaze slip; and glazing, putting the glazed and air-dried green body into an electric kiln for roasting, cooling and discharging. The prepared Jianzhan green body is resistant to high temperature and free of deformation during firing, theglaze surface is blue in grey, soft in color, elegant, deep, clear, thick and long in hair, just like thousands of streams converge into the sea, and the glaze surface is mild, fine and smooth and rich in charm.
Owner:蔡翔
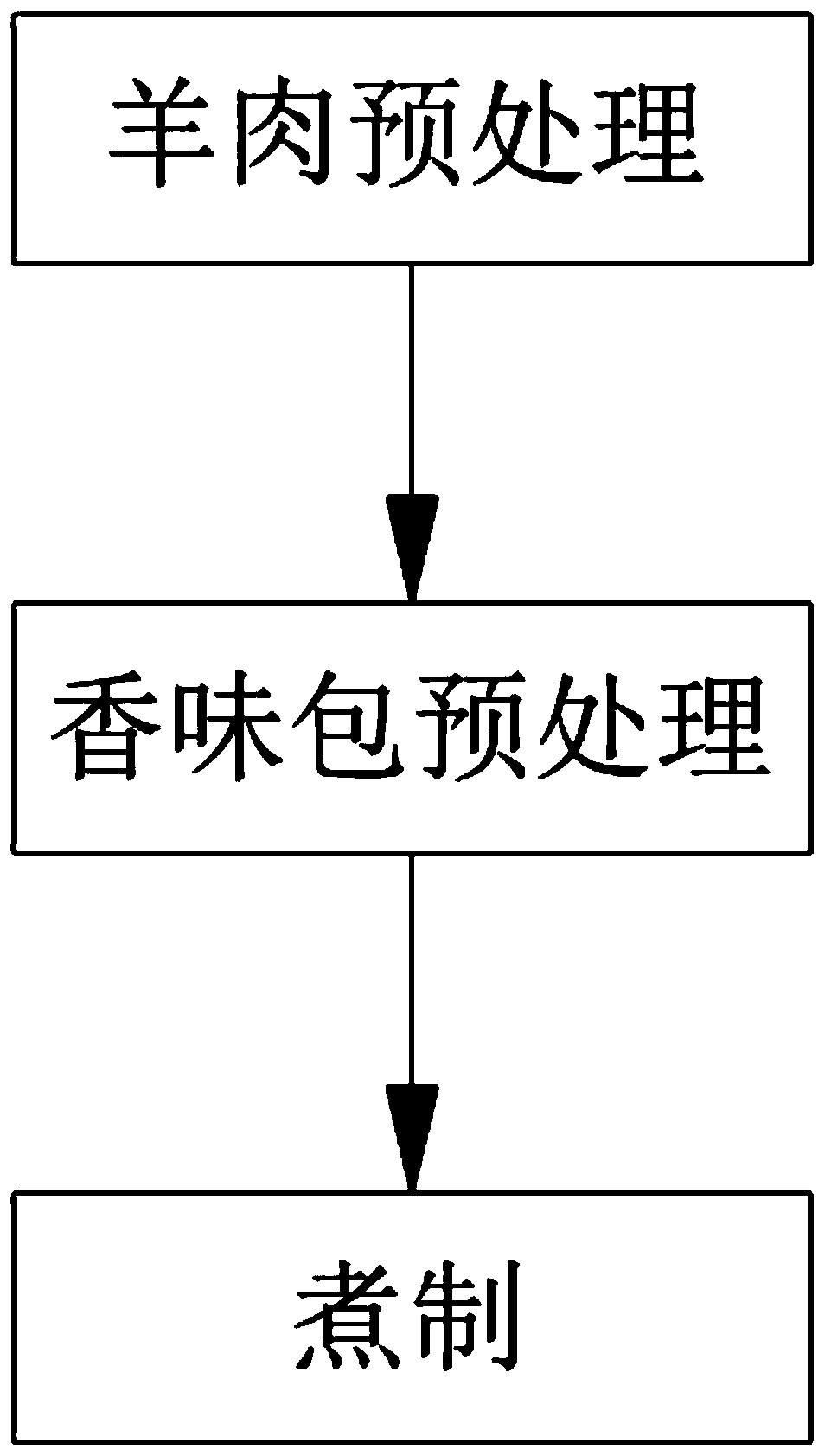
Mutton eaten with hands and preparation method thereof
The invention provides mutton eaten with hands and a preparation method thereof. The mutton eaten with hands is prepared from the following raw material, seasonings and a spice bag in parts by weight:13000-17000 parts of wether mutton; seasoning: 800 to 1200 parts of salt; spice bag: 5-9 parts of star anise, 12-16 parts of tsaoko amomum fruits, 100-140 parts of Chinese red pepper, 55-95 parts offennel, 10-50 parts of amomum cardamomum, 30-70 parts of cinnamon, 6-10 parts of galangal, 7-11 parts of dried ginger peel, 230-270 parts of fresh ginger slices, 8-12 parts of rhizoma kaempferiae, 8-12 parts of angelica sinensis and 8-12 parts of astragalus membranaceus. According to the mutton eaten with hands and the preparation method thereof provided by the invention, the taste of the mutton is effectively improved by repeatedly removing scum, the preparation is simple, the method is clear, people with different education degrees can quickly and skillfully prepare the mutton eaten with hands; and the ginger juice, rice wine and chicken juice are added, so that the mutton eaten with hands is rich in taste, non-greasy, free of strong smell and good in color and aroma; the mutton can be eaten and the soup can be drunk; and the method is reasonable, and the oral cavity, intestines and stomach are not stimulated.
Owner:溜达羊(青海)集团有限公司
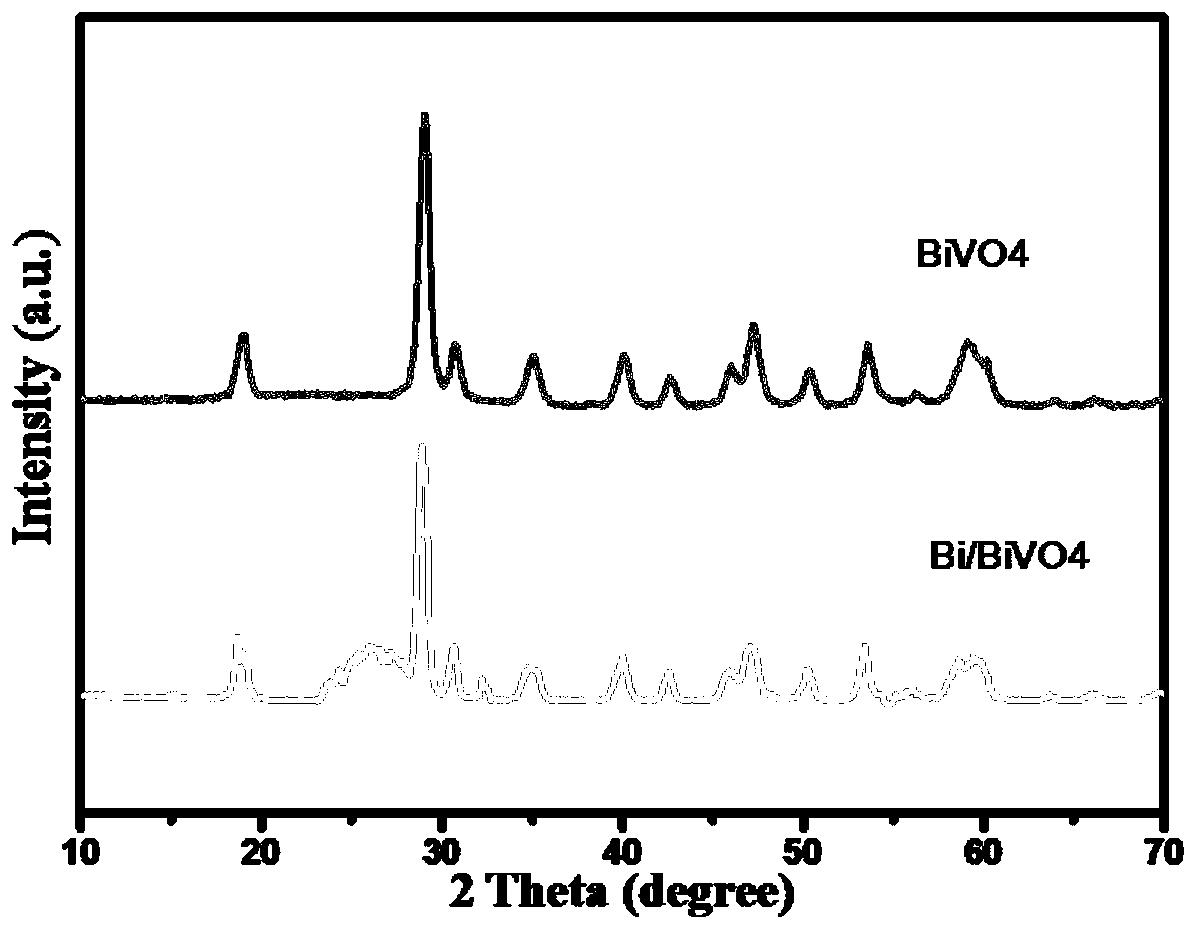
A bismuth-loaded bismuth vanadate porous nanofiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109881304BBroaden the range of visible light absorptionExpand the scope of absorptionInorganic material artificial filamentsCatalyst activation/preparationFiberN dimethylformamide
A bismuth vanadate-based porous nanofiber is characterized in that: the porous nanofiber is composed of bismuth vanadate and amorphous bismuth, and the amorphous bismuth is loaded on bismuth vanadate, and the mass percentage of the bismuth vanadate is It is about 95%-98%, and the mass percentage of the amorphous bismuth is 2%-5%. Its preparation method, it uses bismuth nitrate pentahydrate, N,N-dimethylformamide, vanadyl acetylacetonate, polyvinylpyrrolidone, citric acid, glacial acetic acid, ethanol as raw materials, through high-voltage electrostatic forming technology, muffle furnace Sintering, hydrogen plasma treatment and other steps to achieve. The raw material of the present invention is simple and easy to obtain, the whole experimental process is clear, the operation is convenient, it is easy to realize the large-scale production of the product, and the product can be 100% recovered in the use process, and the obtained amorphous bismuth vanadate porous nanofiber composite material has Excellent flexibility, the macroscopic size can reach tens of centimeters, the microstructure of the product is uniform, and it has a good effect on photocatalytic degradation of dyes. In addition, the material is also expected to have good applications in flexible batteries, flexible photoelectric hydrogen production, etc.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
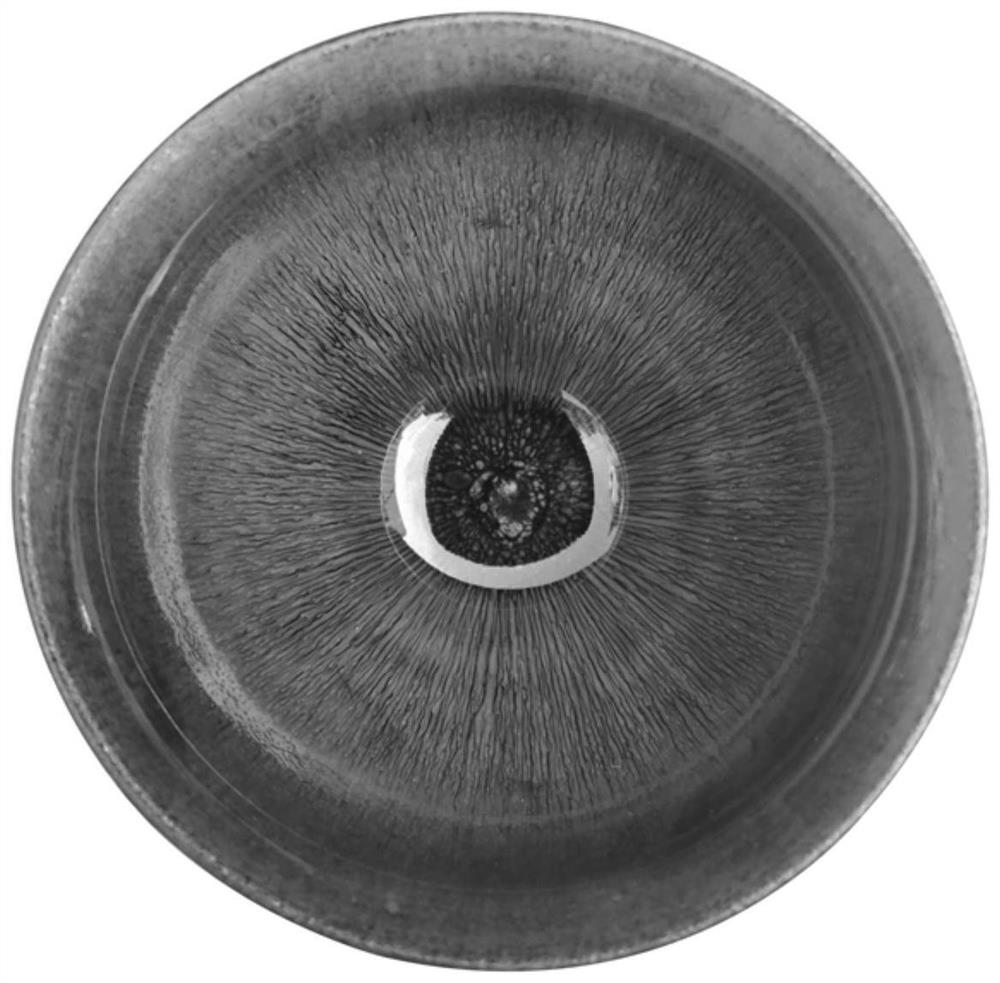
Preparation technology of relief oil drop built lamp
ActiveCN108751718BStrong three-dimensional senseCrystallization is completeClaywaresDevitrificationGlaze
The invention discloses an embossment oil drop Jian Zhan bowl and a preparing technology thereof. The embossment oil drop Jian Zhan bowl comprises a green body and glaze. The green body is prepared from, by weight, 8-8.5 parts of kaolin and 2-2.5 parts of loess; the glaze is prepared from, by weight, 70-73 parts of glaze stone, 5-5.5 parts of plant ash, 9-10 parts of iron oxide red and 68-72 partsof water. A reasonable composition is obtained through scientific proportioning, an innovative sintering mode is adopted, and finally the embossment oil drop Jian Zhan bowl with a high grade is obtained; the Jian Zhan bowl has large and dazzling oil drops, devitrification is thoroughly conducted, crystals have a high three-dimensional sense and are stacked layer by layer like an embossment, and an intense and overwhelming visual impact feeling is brought.
Owner:邱芙蓉
A kind of preparation method of porous dandelion-like PD nanodendrite and its obtained material and application
ActiveCN108543944BThe preparation process is clearThe mechanism of the preparation process is clearTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusMethylene bisacrylamideOxygen
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous dandelion-like Pd nanodendrites, the obtained material and its application as an oxygen reduction cathode catalyst. The method uses N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAA) as a complex Agents, structure-directing agents and reducing agents, the metal precursors were quickly reduced into porous dandelion-like Pd nanodendrites by one-step static reduction method. The porous dandelion-like Pd nanodendrite prepared by the method of the invention has the advantages of regular shape, ultra-fine particle size, high electrocatalytic activity, etc., and exhibits high catalytic activity and stability as an oxygen reduction cathode catalyst. The preparation method of the invention is simple, efficient and universal.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A hollow slab bridge hinge joint bearing capacity test specimen and its manufacturing method and testing method
ActiveCN105842046BEasy to makeThe preparation process is clearPreparing sample for investigationStrength propertiesConcrete beamsEngineering
The invention relates to a hollow-slab-bridge hinge joint bearing capacity test piece, a manufacturing method thereof and a test method of the test piece. The test piece includes a first concrete beam and a second concrete beam. Reinforcing steel bars are disposed in the first and second concrete beams. Forms of the reinforcing steel bars and stirrups in the first concrete beam are same as those of the reinforcing steel bars and stirrups at corresponding positions in the first concrete beam. A hinge joint is disposed between the first and second concrete beams. A whole concrete pavement layer is disposed on the first and second concrete beams. The strength grade of the first concrete beam and the strength grade of the second concrete beam are same as the strength grade of a hollow slab bridge to be tested. The test piece is simple to manufacture, strong in operationality, convenient in experiment research of hinge joint stress performance and small in volume, can conveniently perform static force and fatigue tests, and can overcome the technical difficulty, namely rapid measurement of hinge joint stress performance.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Preparation method of high-dispersity graphene
InactiveCN113897075AGood dispersionThe preparation process is clearCarbon compoundsPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsEngineeringGraphite
The invention provides a preparation method of high-dispersity graphene. According to the technical scheme, the dispersity of graphene is improved through a micromolecule covalent modification method, the high-dispersity graphene is prepared by combining organic micromolecule 4-aminopyridine with graphene in a covalent connection mode, and the graphene has the characteristics of high dispersity, difficulty in agglomeration and the like in an aqueous solution. According to the invention, the high-dispersity graphene prepared by the method has great application potential in multiple fields of catalysis, electrochemistry, biological medicine, solar cells and the like; and the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, and the preparation method is simple, economical and suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:四川烯都科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com