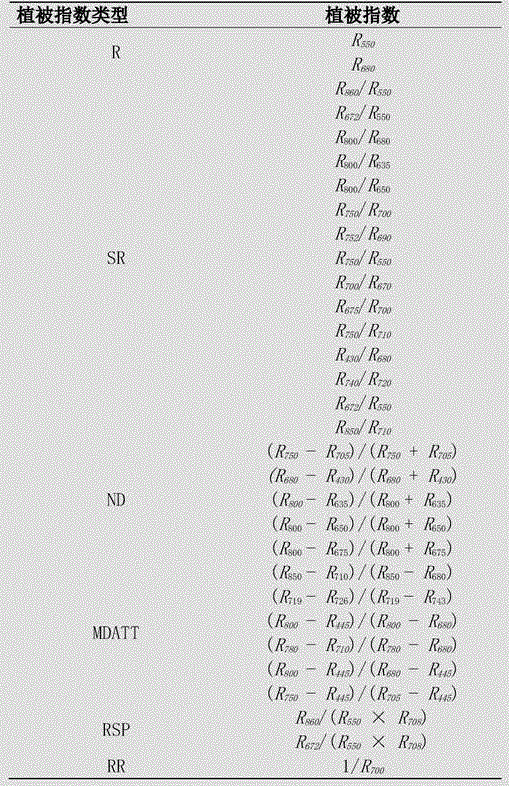Chlorophyll content detection method insensitive to leaf surface structure
A technology of chlorophyll content and detection method is applied in the detection field of chlorophyll content to achieve the effect of non-destructive testing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This embodiment discloses a method for detecting chlorophyll content that is insensitive to leaf surface structure, and is characterized in that the method includes the following steps:
[0037] 1) Obtain the hyperspectral reflectance of the plant leaf surface, and measure the chlorophyll content of the plant leaf:
[0038] 1-1) Using ASD 3 The leaf clip of the portable spectral measuring instrument (spectral analyzer, Boulder, CO, USA), collects the spectral reflection information of the front and back of the leaf within the wavelength range of 400-1000nm. During the collection process, try to select the same part for all leaves to avoid measuring the veins. Each leaf is measured three times, and a whiteboard calibration is performed every 5 minutes;
[0039] In 1-2), a hole puncher with a diameter of 6 mm was used to take out the leaf area where the reflectance of the leaf was measured, and five holes were punched for each leaf. Put the punched leaves into a mortar,...
Embodiment 2
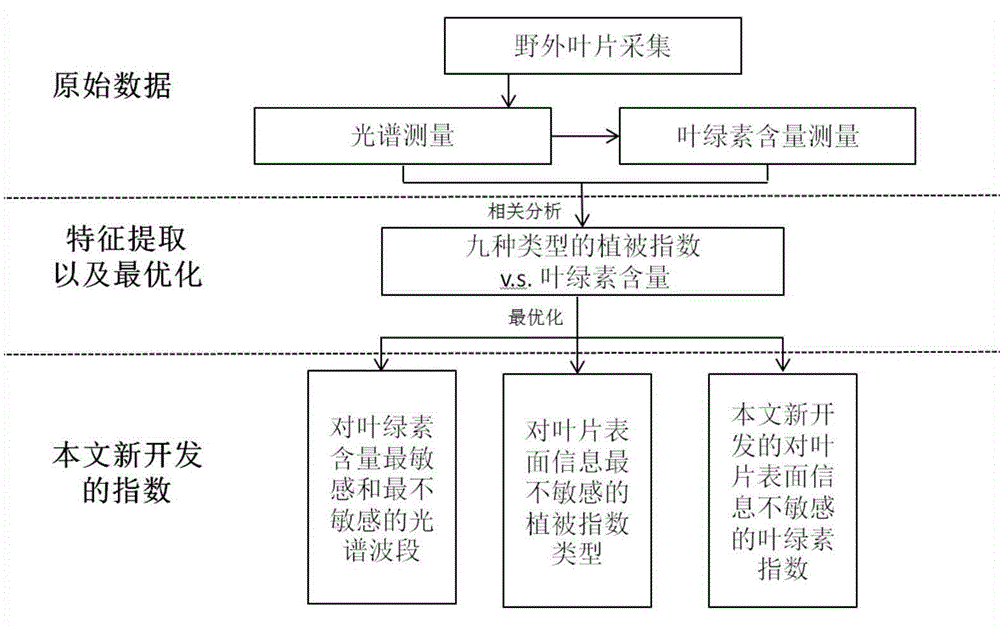
[0060] In this example, fifty-five leaves of A. chinensis, tung flower tree and Sangria apetalum were collected in the mangrove forest, and their spectral reflectance and chlorophyll content were measured to develop a new chlorophyll index that is not affected by leaf surface information.
[0061] Overall, such as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment discloses a method for detecting chlorophyll content insensitive to leaf surface structure, said method comprising the steps of:
[0062] 1) Obtain the hyperspectral reflectance of the plant leaf surface, and measure the chlorophyll content of the plant leaf;
[0063] 2) Analyze the correlation between all the band combination results of the nine types of vegetation indices and the chlorophyll content;
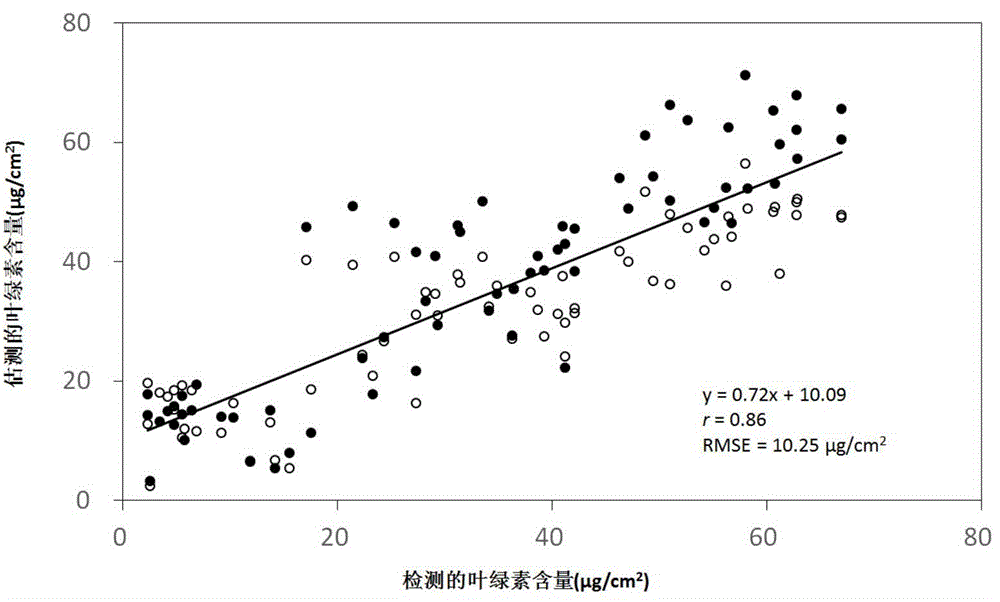
[0064] 3) Determine the most effective vegetation index for predicting chlorophyll content according to the correlation coefficient (r) and root mean square error (RMSE);
[0065] 4) Establish a regression equation between ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com