Structure for eliminating excess light, and fiber laser
A structure and optical fiber technology, applied in the field of remaining light removal structure, can solve the problems of reliability damage, achieve high reliability, improve reliability, and reduce heat generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
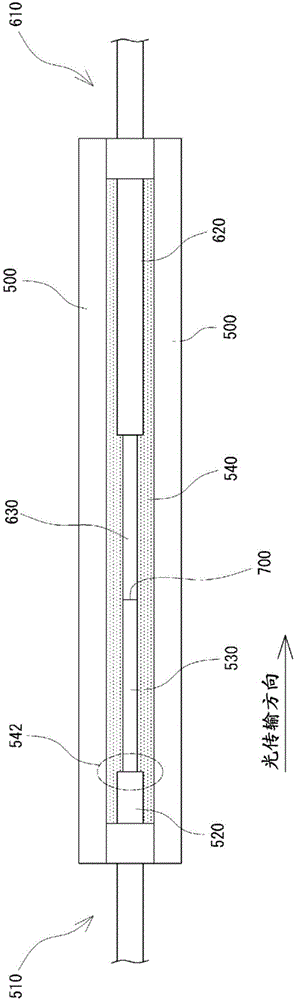
[0050] First, as a comparative example, a figure 1 Shown is the existing residual light removal configuration. As the double-clad optical fiber 510, 610, a double-clad optical fiber having a diameter of 10 μm in the core and a diameter of 400 μm in the cladding 530, 630 was used. The ends of the respective cladding members 520, 620 of the double-clad optical fibers 510, 610 were removed in the axial direction by 20 mm at a time, thereby exposing the claddings 530, 630. Ultrasonic cleaning using ethanol was performed to clean the exposed surfaces of the cladding layers 530 and 630 .
[0051]The claddings 530 , 630 of the above-mentioned double-clad optical fibers 510 , 610 are butt-fused in the reinforcement member 500 made of a ceramic member whose linear expansion coefficient matches that of silica glass. The remaining excitation light propagating in the claddings 530 and 630 is calculated based on the length of the double-clad fiber (clad pumping fiber) 510 and the claddin...
Embodiment 2
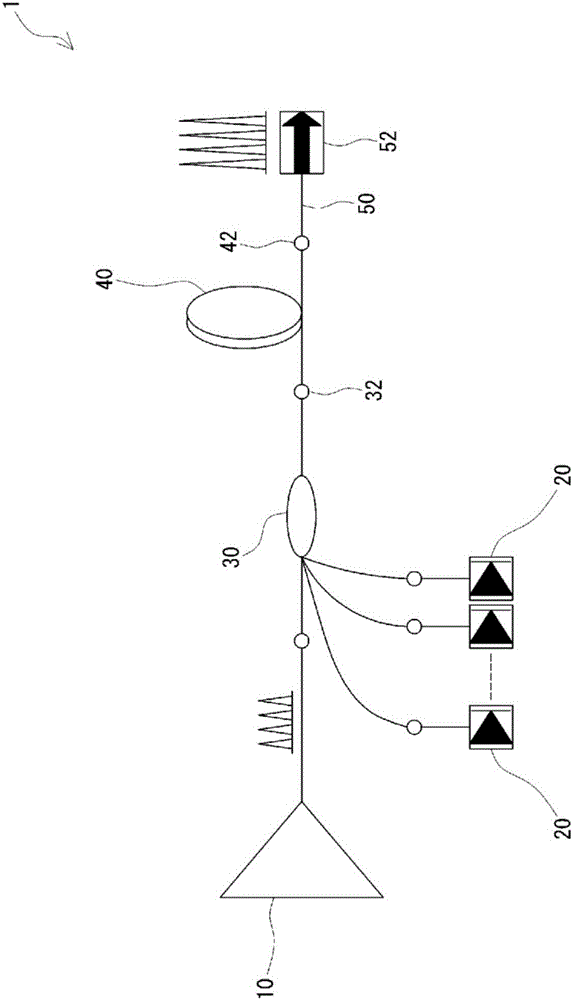
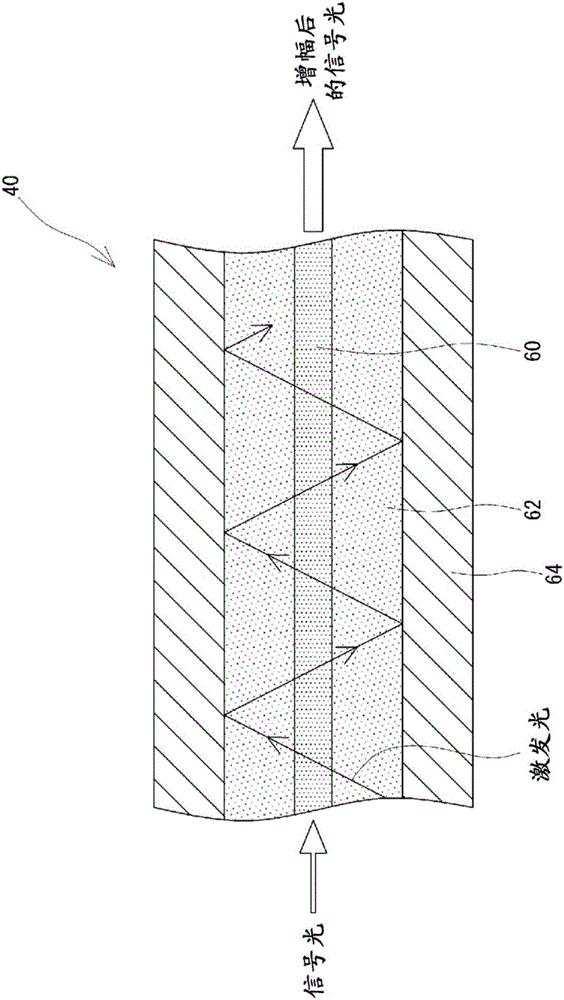
[0058] As Example 2, a Figure 4 The residual light removal configuration 70 is shown. As the cladding pumping fiber 40 , a cladding pumping fiber having a diameter of the core 60 of 10 μm and a diameter of the cladding 62 of 400 μm was used. use Figure 8 The apparatus 80 shown cuts the cladding 64 near the exit end of the clad pump fiber 40 . That is, the blade 84 was brought into contact with the surface of the clad pump fiber 40 and moved 30 mm in the longitudinal direction of the clad pump fiber 40 to expose the clad 62 from the clad 64 . Then, the angle of the clad pump fiber 40 was rotated around the axis by 20°, and cutting was performed a total of three times, so that it was exposed at an angle of 60° in total.
[0059] A ceramic member having a linear expansion coefficient equal to that of silica glass is used as the optical fiber housing portion 72 , and a hard UV curable resin is used as the resin 77 arranged at both ends of the optical fiber housing portion 72 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com