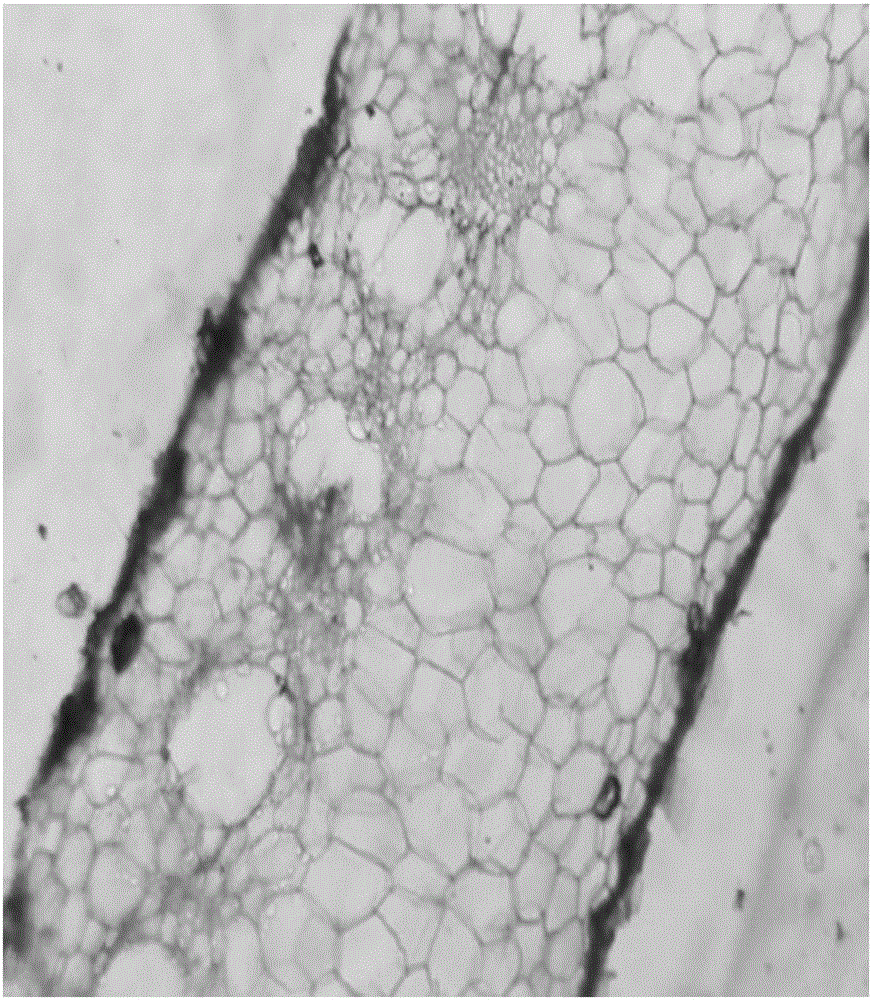
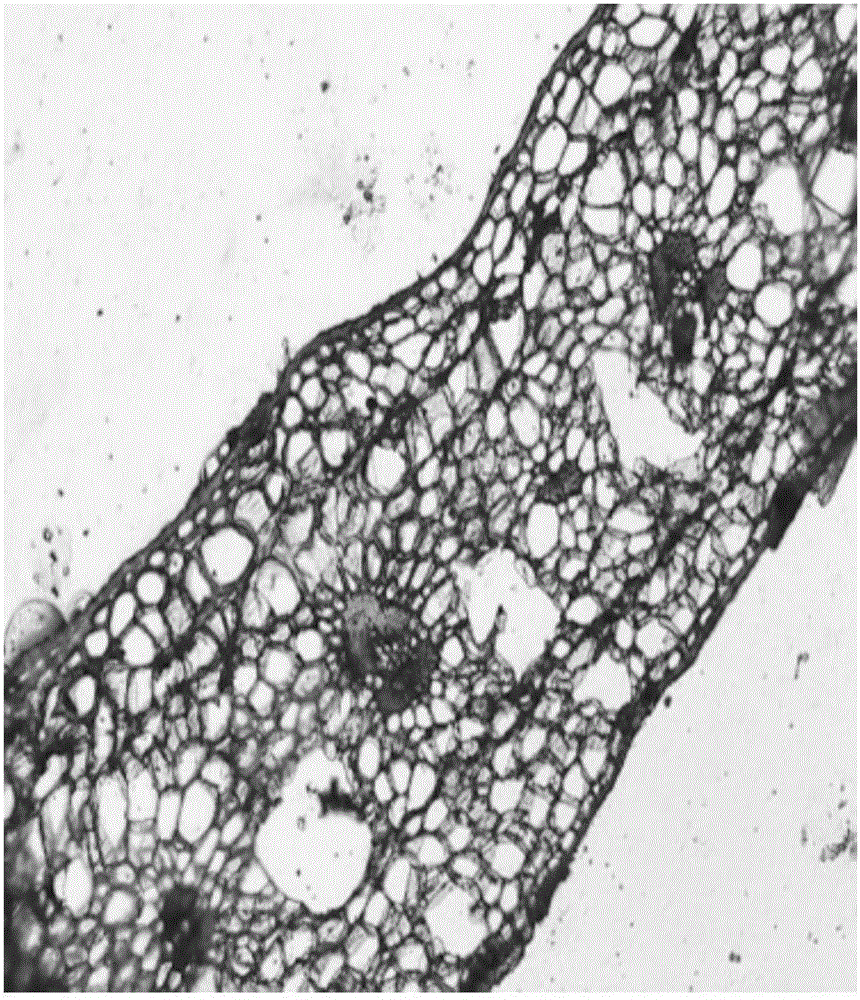
Specimen making method for observing anatomic structure of lamina of tillandsia
An anatomical structure and specimen making technology, applied in the field of leaf specimen making, can solve problems such as difficulty in application, and achieve the effects of improving the softening process, the operation method is simple, and the embedding operation procedure is simplified
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Blade selection
[0031] Select a single plant with no pests and diseases and good growth conditions, and select healthy leaves in the middle of the plant. Choose the breed as Overlord.
[0032] 2. Material fixation:
[0033] Different varieties of leaves have different sizes, depending on the size of the leaves, select a specification, cut the leaves into small rectangular pieces of 3mm×5mm, 4mm×6mm, 5mm×7mm or 6mm×8mm, wash the cut materials with clean water and put them into FAA fixative For medium fixation, the volume of fixative was 20 times that of the fixed tissue. FAA fixative configuration: 70% or 50% ethanol 90mL: glacial acetic acid: formaldehyde = 18:1:1, fixed for 30 hours.
[0034] 3. Material softening:
[0035] 1) Put the sample into a 1:1 solution of 50% glycerin + 50% ethanol (95%) and soak for 25 days.
[0036] 2) Put the material into a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and propionic acid (1:1), take out the sample with tweezers every 30 minutes t...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The selected species is Tillandsia twigs.
[0061] During the material fixing in step 2, the fixing time is 24 hours;
[0062] Step 3: During material softening, put the sample into a 1:1 solution of 50% glycerin+50% ethanol (95%), and soak for 20 days; the volume of hydrogen peroxide and propionic acid in the mixed solution is 2:1;
[0063] Step 6: Infiltrate the material into wax, and place it in an electric thermostat incubator at 37°C for 24 hours after wax sealing;
[0064] In Step 9, put the slide glass in an electric thermostat incubator at 37°C for 2 days.
Embodiment 3
[0066] The selected variety is tricolor Tillandsia.
[0067] During the material fixing in step 2, the fixing time is 36 hours;
[0068] Step 3: During material softening, put the sample into a 1:1 solution of 50% glycerin+50% ethanol (95%), and soak for 30 days; the volume of hydrogen peroxide and propionic acid in the mixed solution is 1:1;
[0069] Step 6: Infiltrate the material into the wax, and place it in an electric thermostat incubator at 37°C for 48 hours after the wax sealing is completed;
[0070] In Step 9, the material is attached to the slide, and the slide is placed in a 37°C electric constant temperature incubator for 5 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com