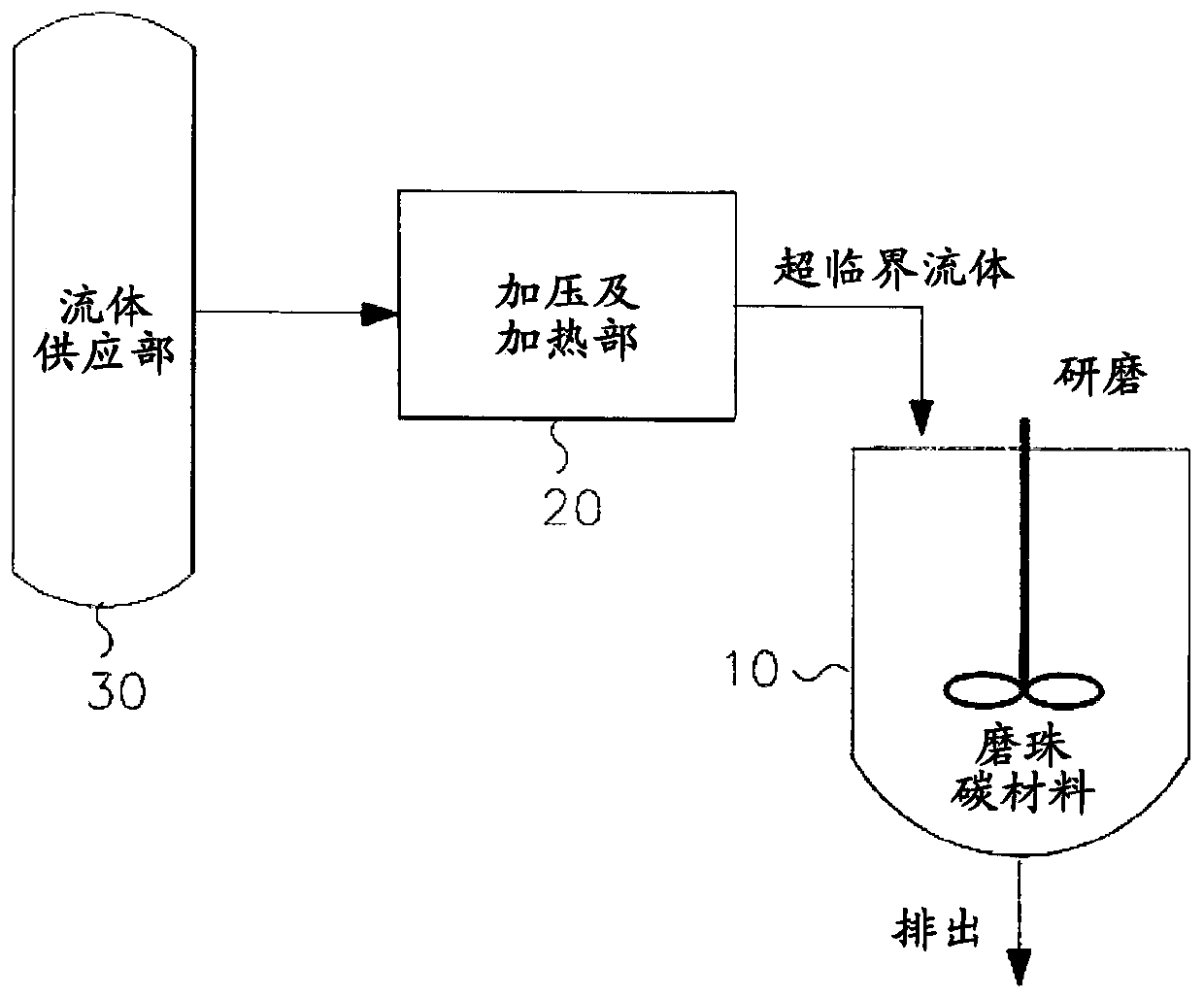
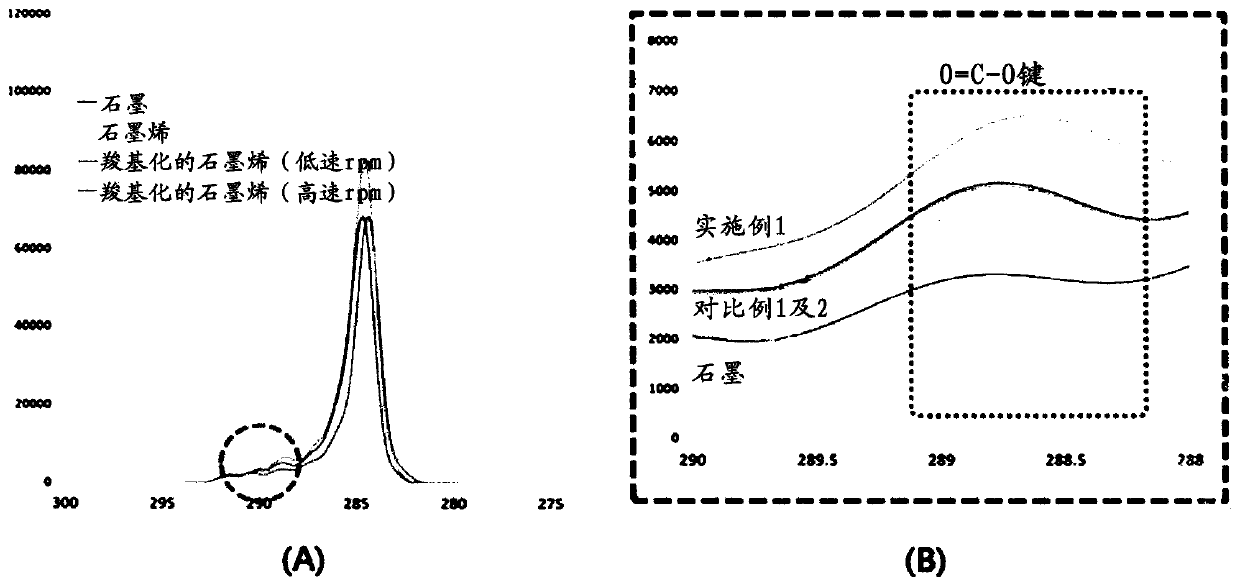
Method for producing carbon material using subcritical or supercritical fluid
A technology of supercritical fluid and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of technological process, mixing method, chemical instrument and method under supercritical conditions, which can solve the problems of long ball milling time and explosion, and achieve the effect of high-efficiency peeling or dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] [Example 1] Dispersion of carbon material using supercritical fluid and production of graphene
[0037] Add 15 parts by weight of graphite (Timcal Co., Switzerland) to 500 parts by weight of methanol, and after supplying it to the reactor, add 1.5 parts by weight of ethylene glycol (Acetylene glycol) as a dispersant in order to improve the wettability of methanol and graphite Parts were mixed for 30 minutes to produce a graphite solution (step 1). Next, after adding grinding beads (beads) in the volume ratio of 2 / 3 in the solution produced, the rpm was adjusted so that the speed of the solution could be maintained at 18m / sec flow rate, and dispersed for 80 minutes to produce a dispersion solution (step 2) , to supply CO to high-pressure vessels for supercritical manufacturing at 35°C and 100bar 2 After the gas is produced into a supercritical fluid, the fluid is transferred to the reactor containing the dispersion solution (step 3). Finally, adjust the rpm so that the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com