Pixel circuit and display device
A pixel circuit and capacitor technology, applied in the field of display devices, can solve the problems of not being suitable for displays, long set-up time, affecting aperture ratio and yield, etc., and achieve the effect of solving different threshold voltages and reducing correlation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
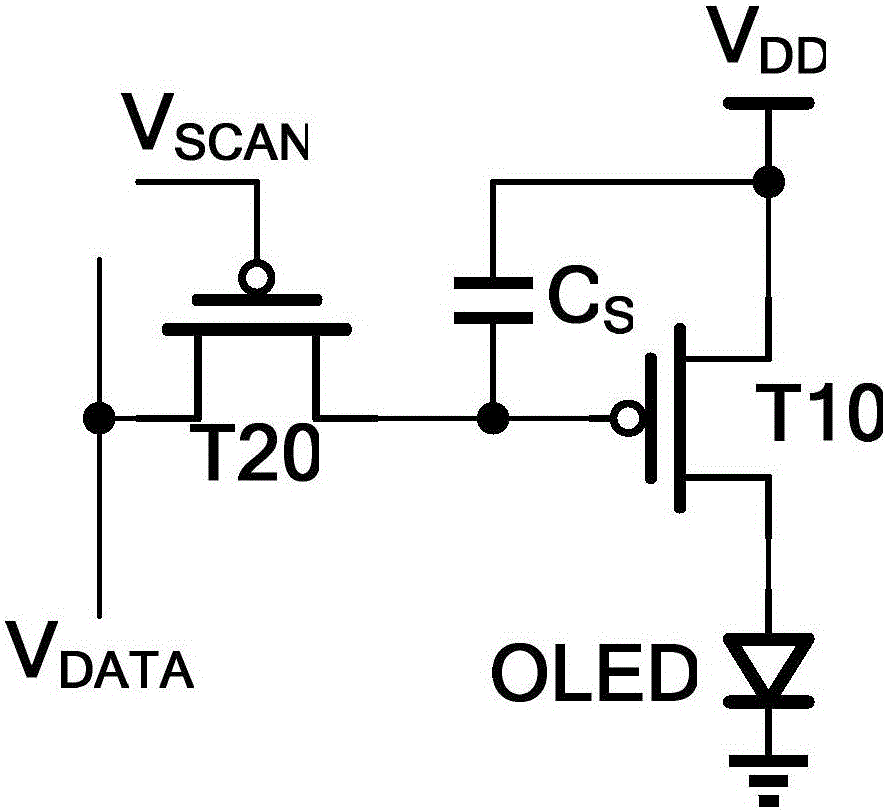
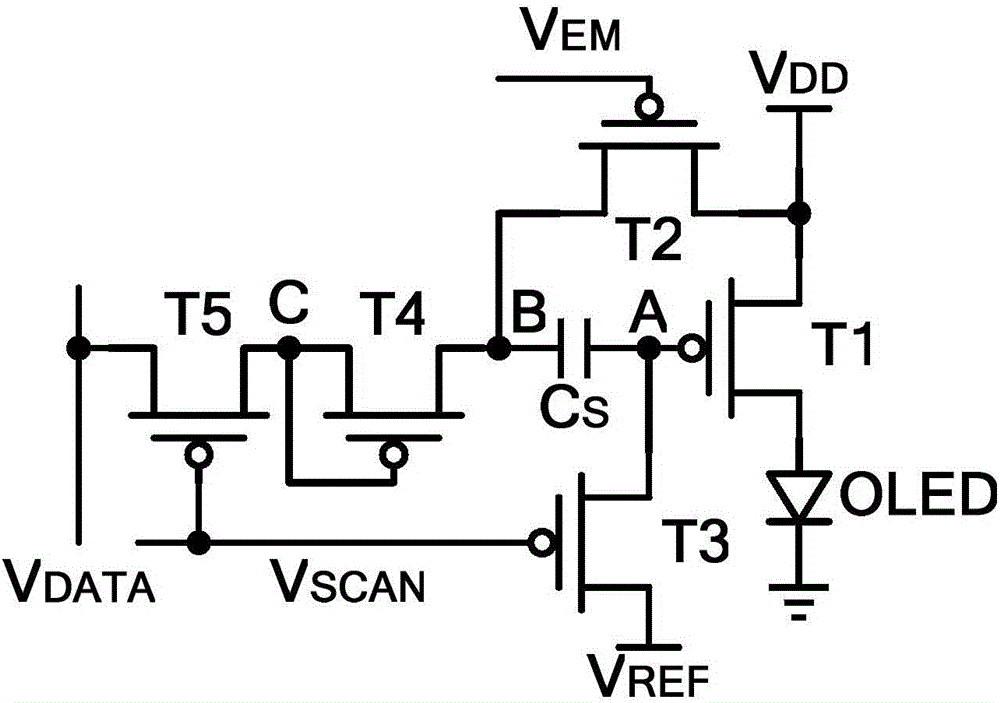
[0040] Please refer to figure 2 , the pixel circuit in this embodiment includes a first transistor T1, a second transistor T2, a third transistor T3, a fourth transistor T4, a fifth transistor T5, a first capacitor C S and the light emitting device OLED; in this embodiment, the first transistor T1 and the fourth transistor T4 are both P-type transistors, and the second transistor T2, the third transistor T3, and the fifth transistor T5 are also P-type transistors.
[0041] The first transistor T1 and the light emitting device OLED are serially connected between the power supply voltage and the ground, and the first transistor T1 is used as a driving transistor to provide a driving current for the light emitting device OLED; the gate of the first transistor T1 is connected to the second capacitor of the first capacitor CS One electrode, the first electrode of the first transistor T1 is connected to the supply voltage line V DD , the second electrode of the first transistor T1...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the main difference from the first embodiment is that the second transistor T2 is an N-type transistor, and the third transistor and the fifth transistor are P-type transistors. In this way, the light emission control signal and the scan control signal that the second transistor T2 responds to are the same control signal, and the control electrode of the second transistor T2 can be directly connected to the scan control signal line VSCAN, which can reduce a set of scan control signal generation circuits and simplify The peripheral circuit makes the control signal of the pixel circuit only need one scan line, and is directly compatible with the gate drive circuit of the display device. Devices whose connection relationship does not change in the circuit will not be described here.
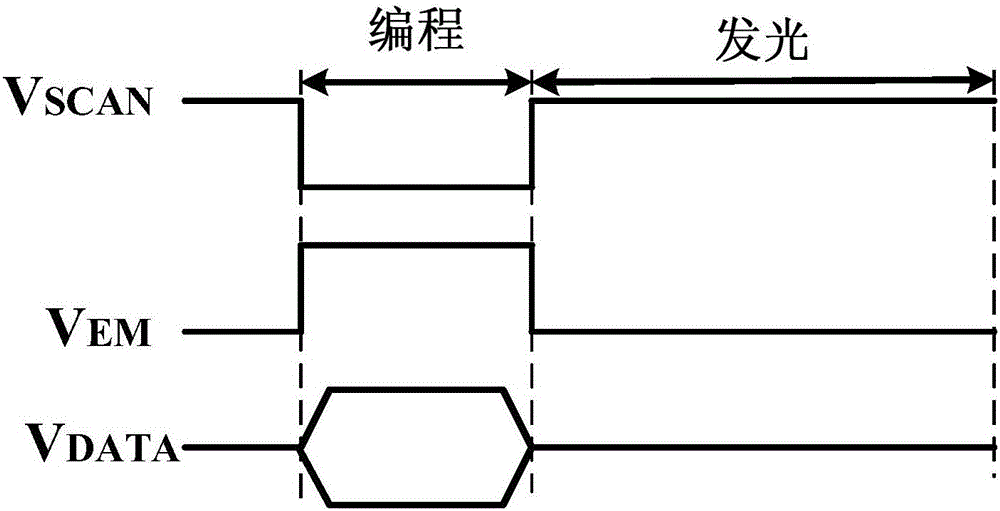
[0061] Please refer to Figure 6 , the driving process is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and also includes a programming phase and a light emitting phase. In...
Embodiment 3
[0064] In the above embodiment, in the branch formed by the third transistor T3, the first capacitor Cs and the fifth transistor T5, the fourth transistor T4 is connected between the second electrode of the fifth transistor T5 and the second terminal of the first capacitor Cs Between, this embodiment is different from the foregoing embodiments in that the fourth transistor is connected between the first electrode of the third transistor and the first terminal of the first capacitor.
[0065] Please refer to Figure 8 , the pixel circuit in this embodiment includes a first transistor T1, a second transistor T2, a third transistor T3, a fourth transistor T4, a fifth transistor T5, a first capacitor C S and the light emitting device OLED; in this embodiment, the first transistor T1 and the fourth transistor T4 are both P-type transistors, and the second transistor T2, the third transistor T3, and the fifth transistor T5 are also P-type transistors.
[0066] The first transistor T1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com