Magnetic sensitivity temperature compensation circuit and programmable linear Hall sensor chip
A temperature compensation circuit and sensitivity technology, applied in the direction of converting sensor output, using electromagnetic/magnetic devices to transmit sensing components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as sensitivity reduction and output signal amplitude reduction, and achieve the effect of increasing sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
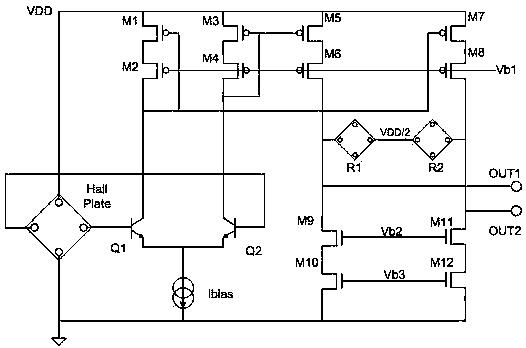
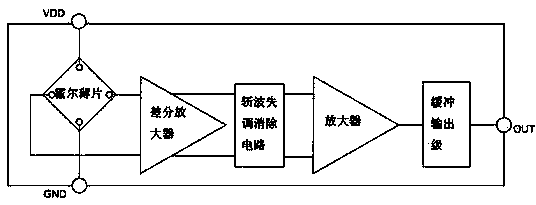
[0027] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, the present invention includes a magnetic sensitivity temperature compensation circuit, including a Hall Plate and a differential amplifier, and the Hall plate induces a magnetic field signal and converts it into a Hall voltage signal and outputs it to the input terminal of the differential amplifier. In that, the differential amplifier is a differential amplifier with adjustable gain, the tail current source Ibias on the differential amplifier is proportional to the absolute temperature, and the load resistors R1 and R2 on the differential amplifier are load resistors with the same shape and material as the Hall sheet .
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown in the middle circuit, the differential amplifier includes an op amp input NPN transistor pair Q1 and Q2, a tail current source Ibias, a current mirror used to provide the gain amplification factor of the differential amplifier, and a current mirror used to provide a series connection bet...
Embodiment 2
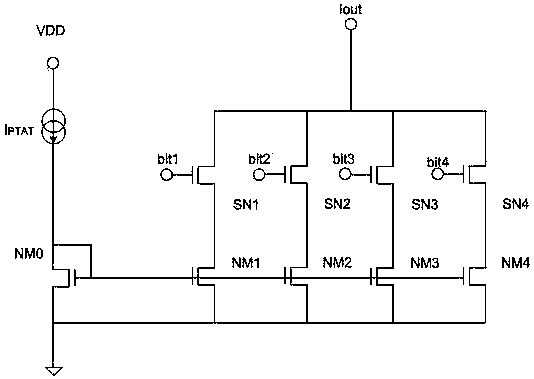
[0040] This embodiment is preferably as follows on the basis of Embodiment 1: the tail current source Ibias is a tail current source Ibias capable of programming and controlling the amplification factor of the Hall voltage.
[0041] Such as image 3As shown, it is an implementation of the tail current source Ibias. There are other different implementations of the tail current source Ibias. This example shows a programming accuracy of 4 bits, and the actual accuracy can be adjusted according to specific application needs. The tail current source Ibias includes a current source IPTAT proportional to the absolute temperature and an NMOS current mirror NM0. One end of the current source IPTAT is connected to the source of the NMOS current mirror NM0, the other end of the current source IPTAT is connected to the power supply VDD, and the drain of the NMOS current mirror is grounded. NM0 mirrors the current source IPTAT to transistors NM1 to NM4, and NMOS transistors SN1 to SN4 real...
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment is preferably as follows on the basis of the above embodiments: the voltage at the common node of the load resistors R1 and R2 is maintained at 1 / 2 of the power supply voltage through the output of a voltage follower. Only when the voltage of the common node is maintained at this value, can the output signal swing of the linear Hall sensor chip be better guaranteed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com