Light-emitting diode structure and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and manufacturing methods, applied to electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., to achieve the effects of increasing the light-emitting area, improving the efficiency of light extraction, and the best light-taking effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
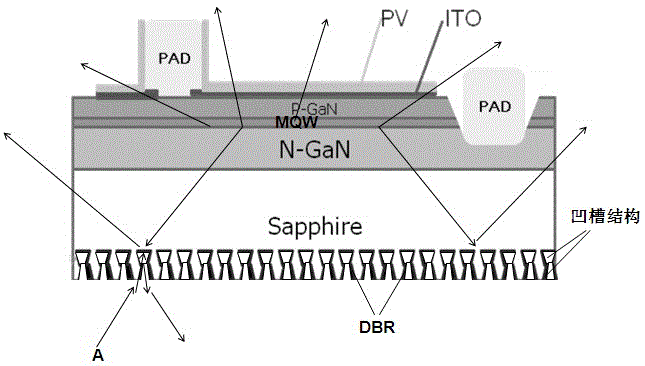
[0032] like figure 1 As shown, a positive light-emitting diode structure includes a substrate, a first semiconductor layer (N-type layer), a second semiconductor layer (P-type layer) and a quantum The light-emitting epitaxial layer composed of the well layer (MQW), the distributed Bragg reflection layer (DBR) on the back of the substrate, the current spreading layer on the P-type layer, the P electrode (PAD) on the current spreading layer and the N-type layer The N electrode (PAD) on the upper surface, and the insulating protective layer (PV), where the back of the substrate has a series of hourglass-shaped groove structures that are periodically and regularly distributed, and the distributed Bragg reflection layer (DBR) fills the groove structure inner wall.
[0033] In this embodiment, the substrate is preferably sapphire, and the above-mentioned light-emitting epitaxial layer can be bonded to the heat-dissipating substrate on the sapphire by using metal organic compound ch...
Embodiment 2
[0039] like Figure 2~6 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for preparing a light-emitting diode structure, the process steps of which include:
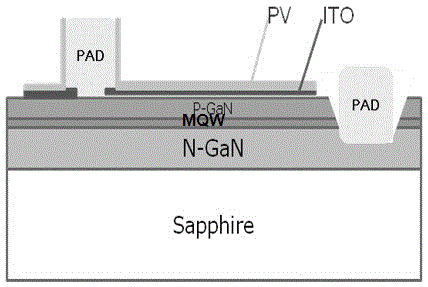
[0040] like figure 2 As shown, a substrate is provided, preferably sapphire (Sapphire), and a light-emitting epitaxial layer is formed on the sapphire (Sapphire) by metal organic compound chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). The light-emitting epitaxial layer material is a GaN-based compound, including an N-type layer (N-GaN layer), a light-emitting layer (MQW) and a P-type layer (P-GaN layer) from bottom to top. Use ICP process to etch from part of the P-GaN layer to expose part of the N-GaN layer) surface, form an ITO current spreading layer on the P-GaN layer of the light-emitting epitaxial layer, and then respectively on the ITO current spreading layer and the N-GaN layer P-type PADs and N-type PADs are fabricated to realize electrical coupling between P-type and N-type PADs and the light-emitting epitaxial layer. Final...
Embodiment 3
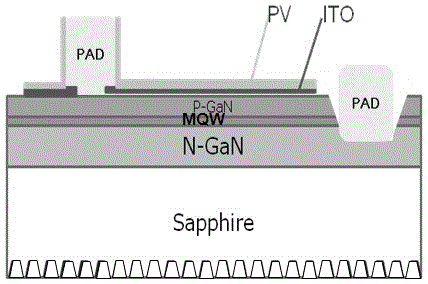
[0045] like Figure 7 As shown, the difference from Example 1 is that the DBR layer in Example 1 is filled in the hourglass-shaped groove structure but not completely, while the DBR layer in this embodiment is filled in the hourglass-shaped groove structure. Since the distributed Bragg reflection layer (DBR) has a more obvious reflection effect on light incident at a small angle, some light incident at a large angle will still pass through the DBR layer. Set the crystal-bonding silver glue (not shown in the figure) at the bottom, so that the light that penetrates the DBR layer (such as figure 1 Medium light A) will be reflected to the DBR layer in the hourglass-shaped groove structure through the crystal-bonding silver glue, and may need to be reflected several times on the inner wall of the groove structure before exiting; when this embodiment is used to make a package, it will penetrate the DBR layer light (such as Figure 7 The middle light B) will be reflected by the cry...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com