Method for rapidly and sensitively detecting hepatitis C virus (HCV) and genotype identification method
A hepatitis C virus, genotype technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem of high mutation rate of RNA genome, achieve simple procedures, low demand for primers and mechanical equipment , cost-effective and easy-to-use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
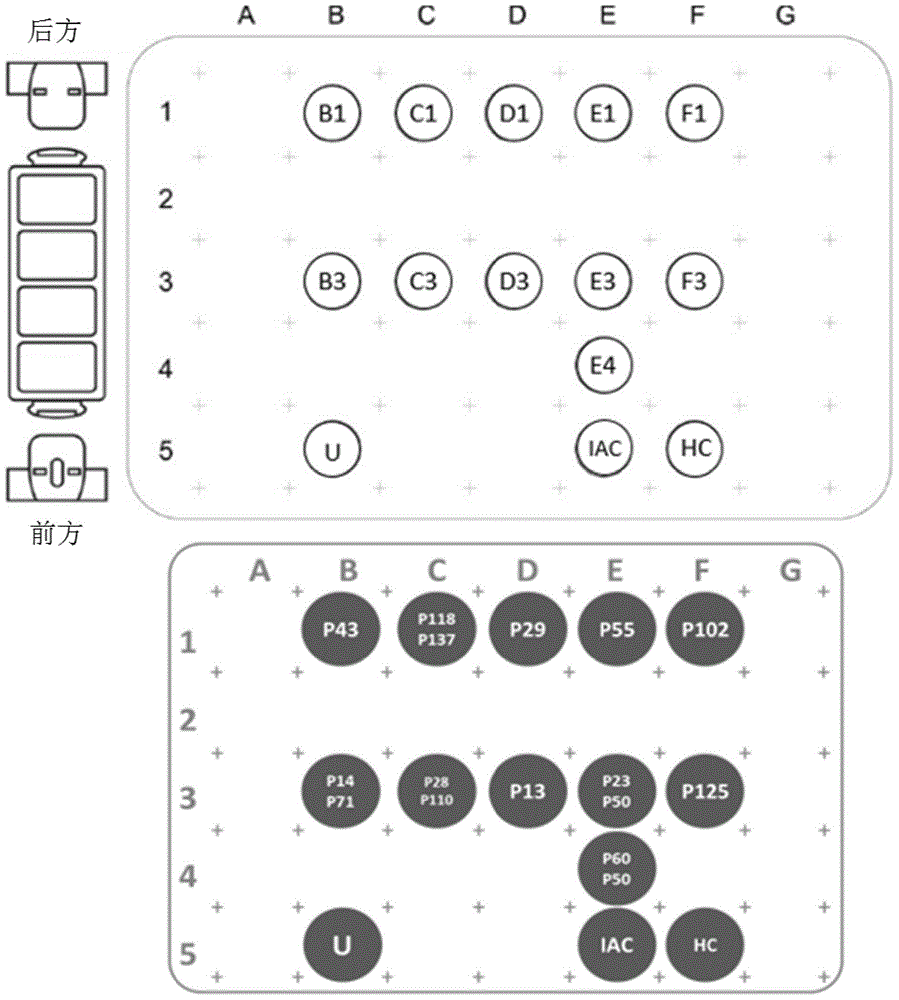
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0318] Accounting expansion
[0319]This example describes an embodiment of the invention wherein the invention is used in combination with reverse transcription and PCR amplification techniques.
[0320] RNA preparation
[0321] The RNA used in the present invention can be extracted or prepared from a sample using any commercially available or appropriate method or kit.
[0322] A sample of the invention can be any type of sample, including nucleic acid from any subject or source. In one embodiment, the sample is a biological sample, such as blood, serum, plasma, saliva, sputum, semen, lymph or other bodily fluids. In another embodiment, the sample includes nucleic acid that has been roughly purified from a biological sample.
[0323] One-step RT-PCR amplification (RT-PCR)
[0324] In one embodiment, RT-PCR can be set up using the following protocol:
[0325] reaction mixture
[0326] Element Capacity (μL) HCV PCR Master Mix 13.4 IAC 0.1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0332] rapid flow hybridization
[0333] This example describes an embodiment of the invention wherein the invention is used in conjunction with flow-through hybridization techniques.
[0334] In one embodiment, the method of detecting, identifying or distinguishing HCV comprises the steps of:
[0335] a) denaturing the solution containing the target nucleic acid and contacting it with the membrane;
[0336] b) washing the membrane with a washing solution; and
[0337] c) Color developed and measured visually or spectroscopically.
[0338] In general, the detection reagents used with the present invention can be any reagent known to be useful for the detection of nucleic acids. Detection reagents include, but are not limited to, enzymes, antibodies, proteins, fluorescent chemicals, chromophores, and visual dyes. In one embodiment, the target nucleic acid is biotin-labeled during RT-PCR amplification (e.g., using biotin-labeled target-specific primers) and cross-linked by...
Embodiment 3
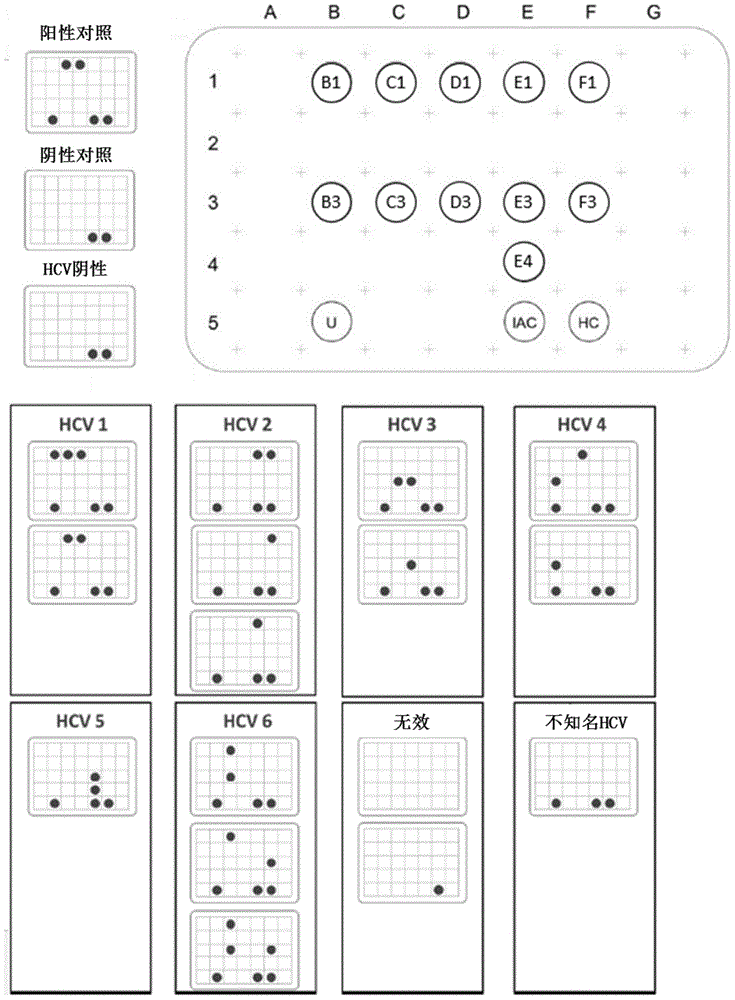
[0372] Validation using synthetic clones
[0373] This example illustrates one embodiment of the use of the invention to detect and discriminate nucleic acids from various HCV genotypes.
[0374] This example uses clones bearing the corresponding sequences of the 5'-UTR from various HCV genotypes to evaluate the specificity and sensitivity of the primers and probes described in this invention.
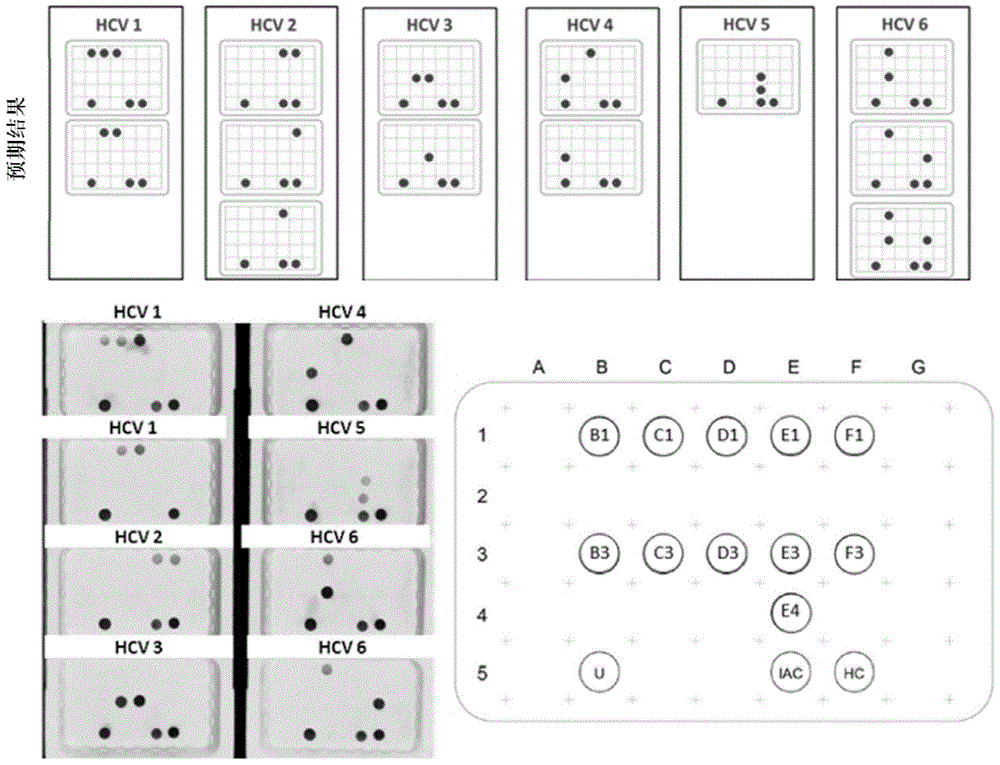
[0375] image 3 Test results of 8 synthetic clones carrying nucleic acid sequences from HCV genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 are shown. The present invention was used to amplify target nucleic acids from eight clones. The resulting amplification product is then hybridized to the probe following the procedure described above.
[0376] The test results show that the present invention can amplify and detect the target nucleic acid from all 8 clones, which is consistent with the expected result and the result of the verification control group.
[0377] Figure 4 Test results of 4 syntheti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com