Reversible physical crosslinking polymer fracturing fluid and preparation method thereof
A technology of physical cross-linking and physical cross-linking agent, which is applied in the field of reversible physical cross-linking polymer fracturing fluid and its preparation, can solve the problems of poor temperature resistance, high cost, large reservoir damage, etc. Salt has good shear resistance, stable viscosity and good shear resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Preparation of a reversible physically crosslinked polymer fracturing fluid.
[0040] Slowly add 0.4% polymer thickener (sodium acrylate, hydrophobic associating monomer, sodium p-styrene sulfonate, 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid and acrylamide five to a certain amount of deionized water). A copolymer of this kind of monomer with a molecular weight of 5 million), stir at high speed for 2 minutes, after the thickener is fully dissolved, add 0.3% clay stabilizer, stir at high speed for 1 minute, and then add 0.16% reversible physical crosslinking agent, Stir at low speed for 60 seconds, and finally add 0.05% ammonium persulfate breaker, stir evenly to obtain a reversible physical cross-linked polymer fracturing fluid.
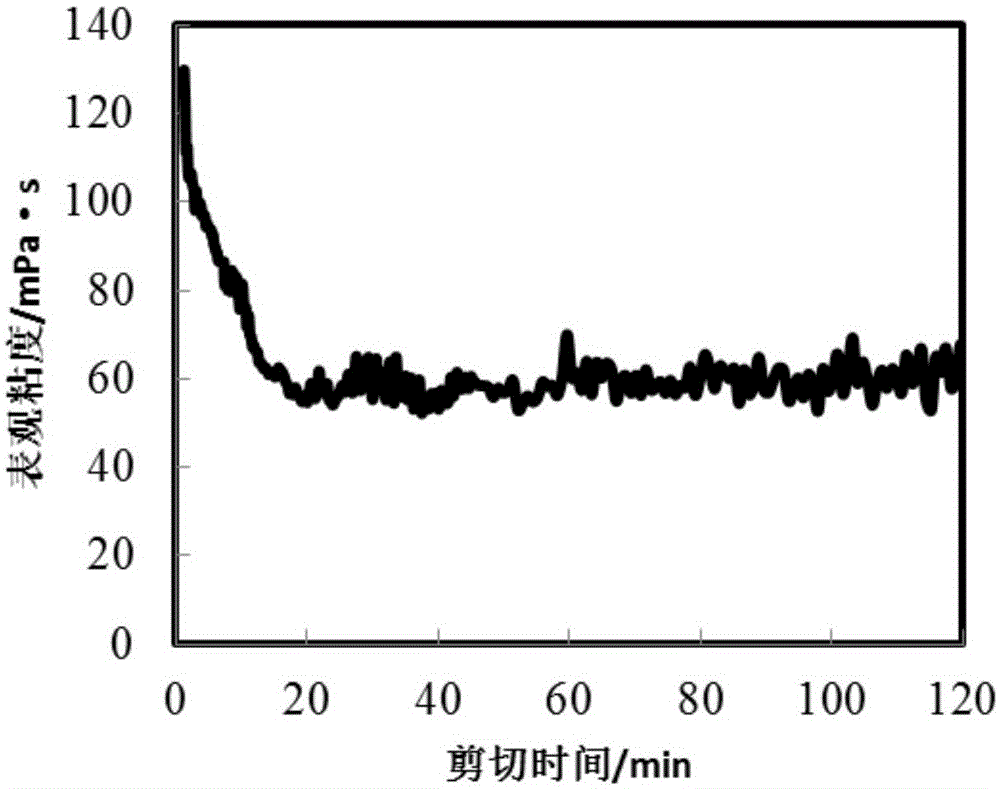
[0041] The fracturing fluid is at 90℃ and 170S -1 The rheological curve for 2 hours under shearing is as figure 1 As shown; the fracturing fluid at 60 ℃, 0.05% ammonium persulfate breaker, the surface tension data after 2 hours break Figu...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Preparation of a reversible physically crosslinked polymer fracturing fluid.
[0044] Add 0.5% polymer thickener (sodium acrylate, hydrophobically associating monomer, sodium p-styrene sulfonate, 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid and acrylamide five) slowly to a certain amount of deionized water. A copolymer of this monomer with a molecular weight of 6.8 million), stir at high speed for 2 minutes, after the thickener is fully dissolved, add 0.3% clay stabilizer, stir at high speed for 1 minute, and then add 0.2% reversible physical crosslinking agent. Stir at low speed for 120s, and finally add 0.02% ammonium persulfate breaker, stir evenly to obtain a reversible physical cross-linked polymer fracturing fluid.
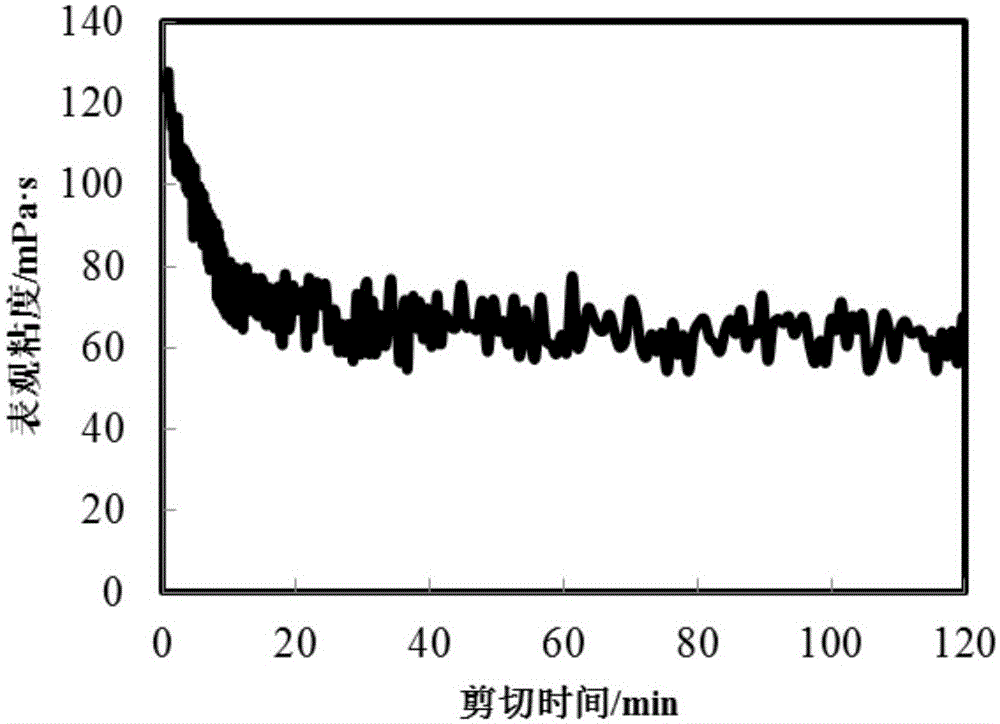
[0045] The fracturing fluid is at 120℃, 170S -1 , The rheological curve of shearing for 2 hours is as figure 2 As shown; the fracturing fluid at 70 ℃, 0.02% ammonium persulfate breaker, the surface tension data after 2 hours break Image 6 Shown. ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Preparation of reversible physically crosslinked polymer fracturing fluid.
[0048] Slowly add 0.55% polymer thickener (sodium acrylate, hydrophobically associating monomer, sodium p-styrene sulfonate, 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid and acrylamide five to a certain amount of deionized water). A copolymer of this monomer with a molecular weight of 8.5 million), stir at high speed for 2 minutes, after the thickener is fully dissolved, add 0.3% clay stabilizer, stir at high speed for 1 minute, and then add 0.25% reversible physical crosslinking agent. Stir at low speed for 150s, and finally add 0.008% ammonium persulfate breaker, stir evenly to obtain a reversible physically crosslinked polymer fracturing fluid.
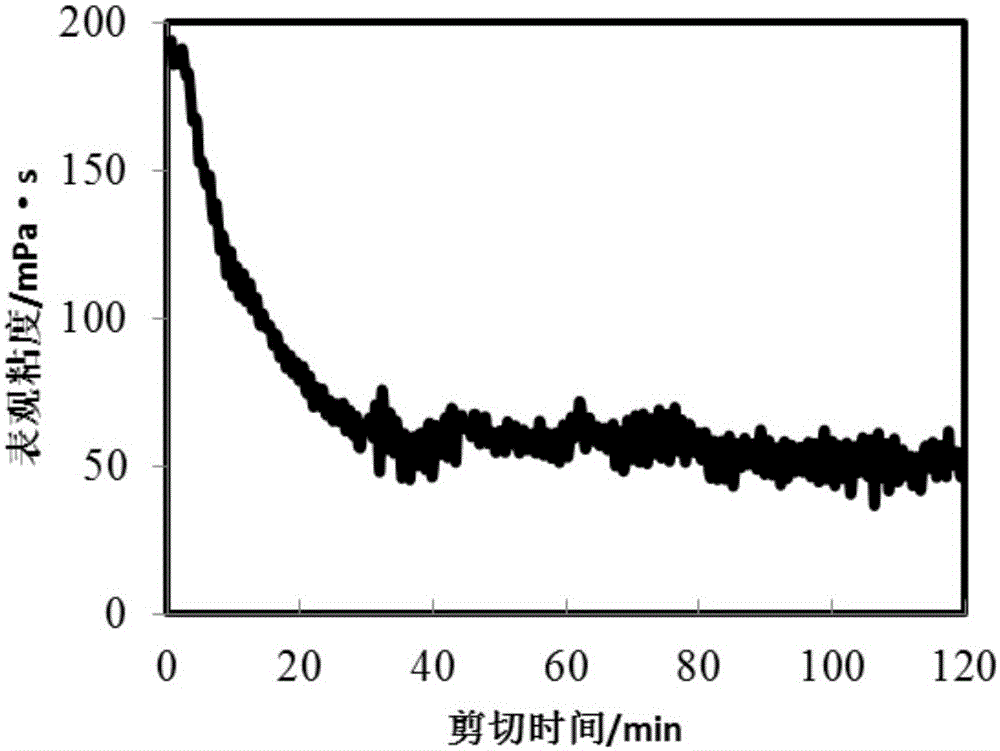
[0049] The fracturing fluid is at 140℃ and 170S -1 The rheological curve for 2 hours under shearing is as image 3 As shown; the fracturing fluid at 80 ℃, 0.008% ammonium persulfate breaker, the surface tension data after 2 hours broken Figure 7...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Breaker viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com