A Temporal Spectral Encoding Method for Measuring Long Pulse Fine Structure
A fine-structure, long-pulse technology, applied in optical radiometry, spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromator, measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as low pulse time resolution and small measurement window of optical streak cameras , to achieve the effects of high time measurement accuracy, large measurement window range, and simple method
Inactive Publication Date: 2014-10-22
SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
View PDF0 Cites 1 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
The pulse time resolution measured by the former method is low, and its time resolution is up to about 10 ps
The measurement window of the optical streak camera is relatively small, generally around several hundred picoseconds
At present, there is no pulse fine structure measurement method that can achieve high time accuracy (about 1ps) and large time window (>1ns) at the same time
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
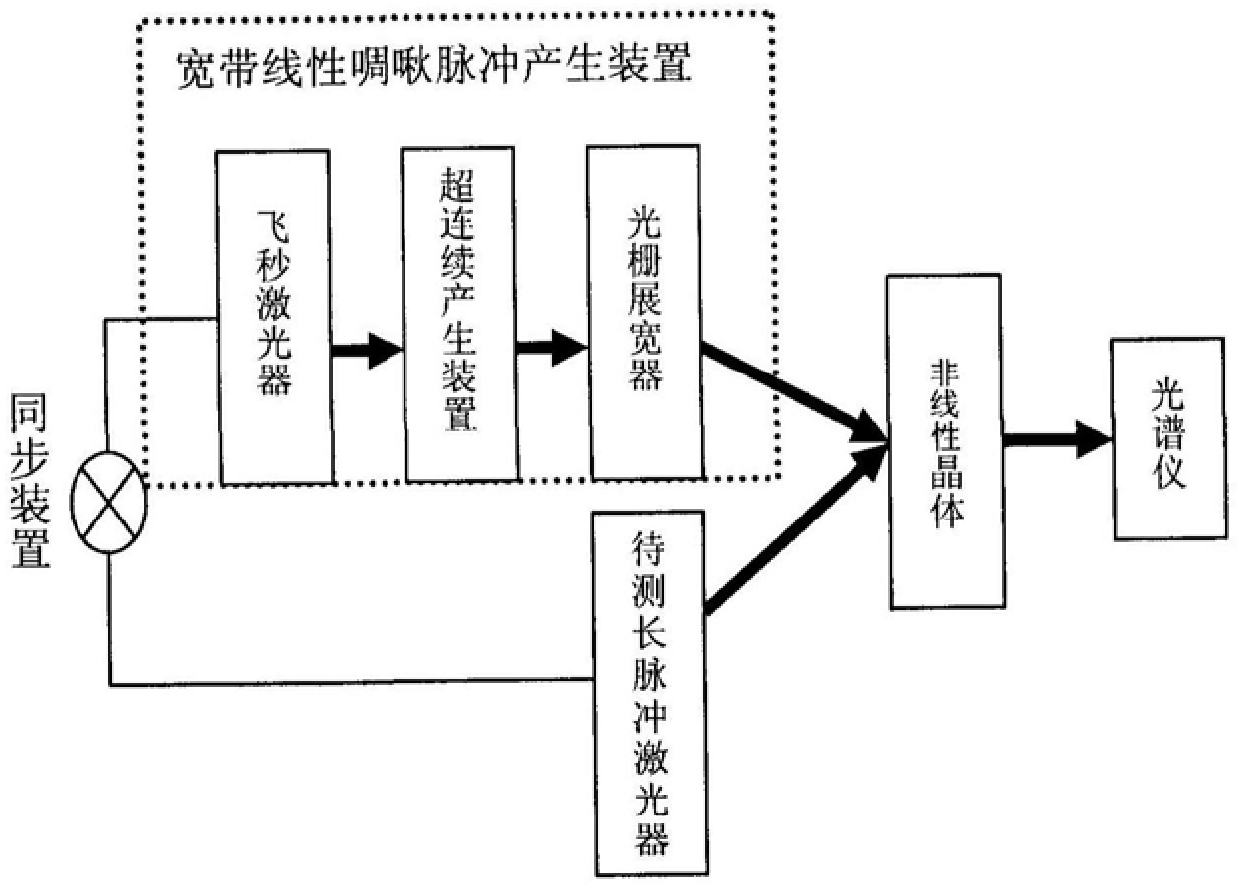
A method for measuring long-pulse fine structure with time-spectral coding, which is implemented by the following steps: Step 1: Synchronize the long-pulse laser to be measured with the femtosecond laser in the ICF driver, and make the long-pulse laser to be measured and the femtosecond laser emit Time synchronization of pulses; Step 2: The femtosecond laser generates femtosecond pulses, and transmits the femtosecond pulses to the supercontinuum generation device to generate supercontinuum white light with a spectral width of several hundred nanometers, and transmits the generated supercontinuum white light Emitted to the grating stretcher; step 3: the grating stretcher produces a broadband linear chirped pulse with a pulse width equivalent to the long pulse to be measured produced by the long pulse laser to be measured; step 4: the broadband linear chirped pulse and the pulse to be measured The length measurement pulse is incident into the nonlinear crystal at a certain non-collinear angle, and the sum frequency is performed in the nonlinear crystal, and the generated sum frequency pulse is sent to the spectrometer to measure the sum frequency pulse spectrum; Step 5: Calculate the length to be measured The time domain structure of the pulse.
Description
A Time Spectral Coding Method for Measuring Long Pulse Fine Structure technical field The invention relates to a method for measuring long pulse fine structure, in particular to a method for measuring long pulse fine structure with time spectrum coding. Background technique In inertial confinement fusion (ICF) laser drivers, amplitude-frequency effects can cause intensity modulations of long pulses, and these intensity modulations may cause damage to optical components after amplification. In order for optical components to work safely, it is necessary to control the time-domain intensity characteristics of laser pulses. The first task is to accurately measure the time-domain intensity characteristics of long pulses. In other long-pulse lasers, it is also necessary to measure the temporal structure of the long pulse in order to understand the actual shape and properties of the pulse. The current methods for measuring the time-domain structure of long pulses include high-s...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Patents(China)
IPC IPC(8): G01J3/00G01J11/00
Inventor 谢国强刘绩刚钱列加袁鹏
Owner SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com