Method for sorting broken plastics in waste household appliances through near infrared absorption spectroscopy analysis device
A near-infrared spectroscopy and sorting technology, applied in the field of resource utilization and waste plastic treatment, can solve the problems of operator health threat, low accuracy of separating plastics, environmental pollution, etc., to eliminate pollution and harm, avoid low accuracy, The effect of high efficiency and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
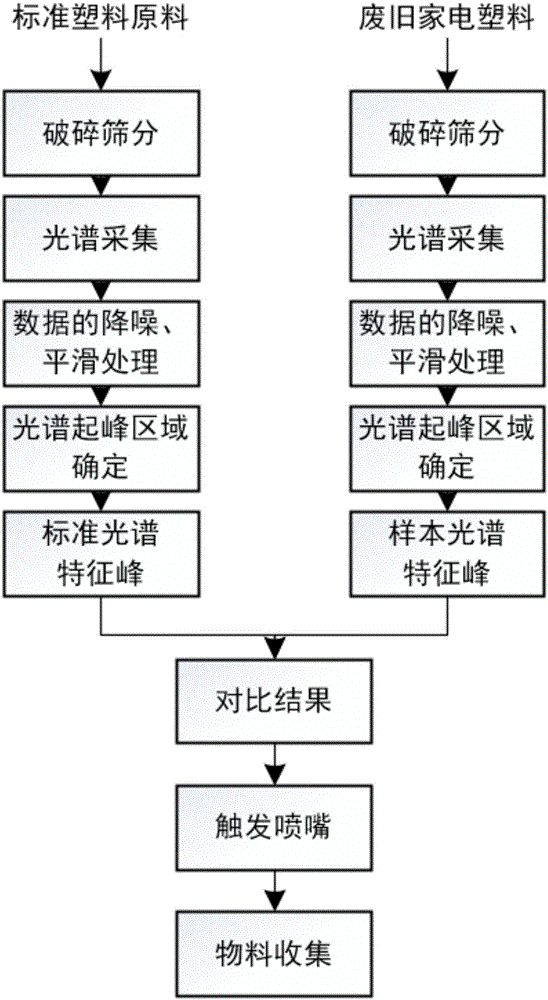
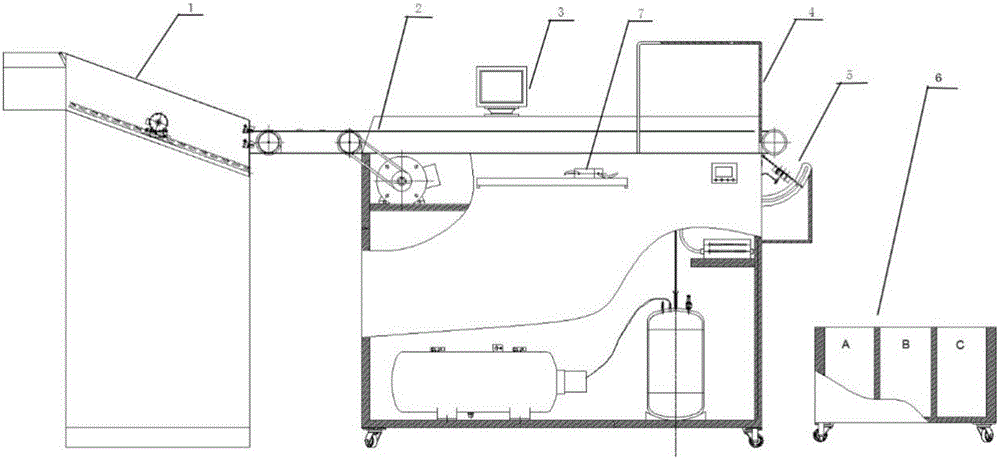
[0031] Select a plastic mixture composed of two plastics, PS and PP, and add it to the photoelectric separator (such as figure 2 Shown) in the near-infrared spectrum identification process. specific:
[0032] Step 1. Add standard PS plastic sheets to the photoelectric sorter (such as figure 2 As shown), the plastic flakes pass through the vibrating dispersing sieve 1 in turn, and the crushed plastics are vibrated and dispersed through the feeding dispersing sieve 1. When they enter the flake conveyor belt 2, they will be accelerated suddenly, so that the flakes do not overlap and are evenly distributed on the conveyor belt. distributed.
[0033] Step 2: When the flakes pass through the data collection area 4 irradiated by the full-spectrum light source evenly and without overlapping, the optical fiber receives the light reflected by the flakes and transmits it to the near-infrared spectrometer 7 .
[0034] Step 3: In the industrial control host 3, the spectral data is seq...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Select a plastic mixture composed of three plastics, PS, PP, and ABS, which are recycled in the refrigerator, and add it to a photoelectric separator (such as figure 2 Shown) in the near-infrared spectrum identification process. specific:
[0040] Step 1. Add standard PS plastic sheets to the photoelectric sorter (such as figure 2 As shown), the plastic flakes pass through the vibrating dispersing sieve 1 in turn, and the crushed plastics are vibrated and dispersed through the feeding dispersing sieve 1. When they enter the flake conveyor belt 2, they will be accelerated suddenly, so that the flakes do not overlap and are evenly distributed on the conveyor belt. distributed.
[0041] Step 2: When the flakes pass through the data collection area 4 irradiated by the full-spectrum light source evenly and without overlapping, the optical fiber receives the light reflected by the flakes and transmits it to the near-infrared spectrometer 7 .
[0042] Step 3: In the indus...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com