Automatic elevating apparatus and method of aeration tube of floating aerator
An automatic lift and aerator technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water aeration, aerobic process treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor effect and short oxygenation time, and achieve small water flow resistance, small cross-section, prolonged The effect of time of contact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
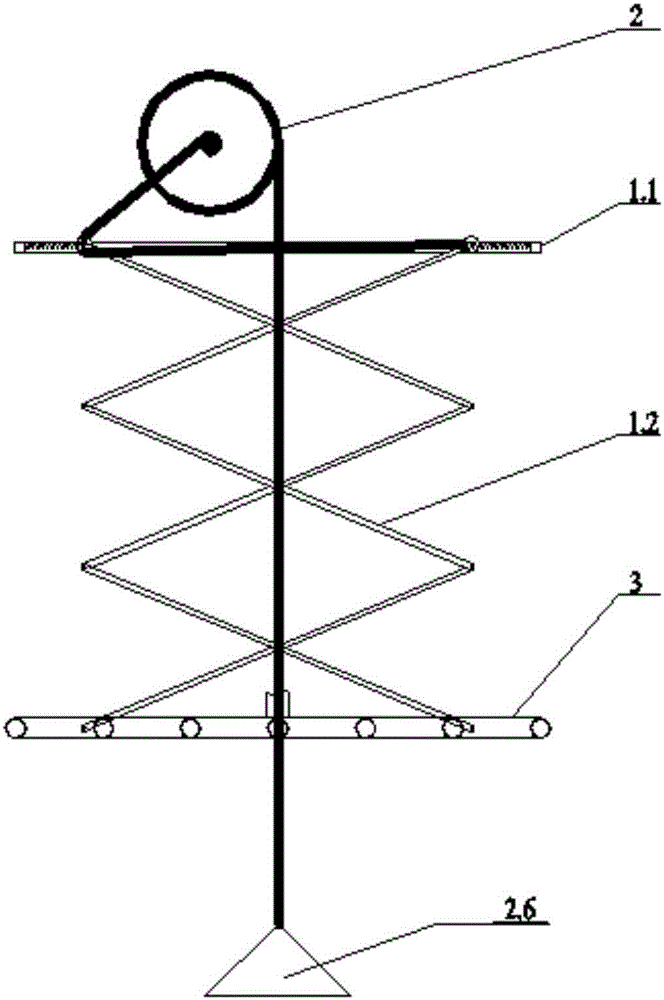
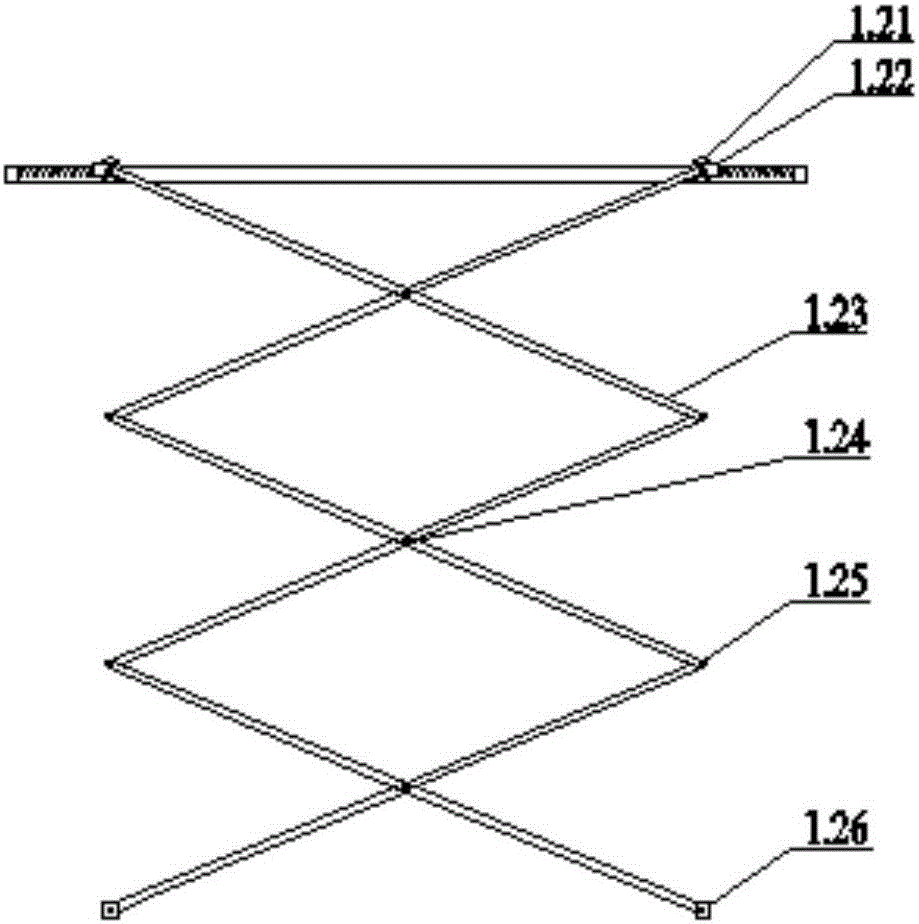
[0062] When it is placed in the river for the first time, the robotic arm 1.2 automatically adapts and stretches out.
[0063] When moving the aerator or the river water level drops to cause the distance between the riverbed and the liquid surface to become smaller, the fixed slide rail 1.1 on the solar aerator moves down relative to the weight 2.6, and the pulley on the mechanical arm 1.2 pulls the spring 1.12 on one side The pulling force is greater than the pulling force provided by the steel cable III, and the pulley 1.21 moves outward until the force on both sides of the pulley 1.21 reaches a balance. The arm 1.2 shrinks upwards, and the shortened distance is similar to the shortened length between the weight 2.6 and the slide rail 1.1. The mechanical arm 1.2 drives the aeration branch pipe 3.3 to move upwards, and the rotating wheel 3.1 rotates to roll up the excess air delivery hose 3.2 to complete the upward movement process of the aeration branch pipe 3.3.
[0064] W...
Embodiment 2
[0066] When the river is rising:
[0067]The fixed slide rail 1.1 on the solar aerator moves upwards relative to the weight 2.6. Since the weight 2.6 is close to being fixed on the river bed, the pulling force on one side of the pulley traction spring 1.12 on the mechanical arm 1.2 is less than the pulling force provided by the steel cable III, and the pulley 1.21 moves inward until the forces on both sides of the pulley 1.21 are balanced, and the pulley 1.21 drives the mechanical arm 1.2 to move, making the upward angle between the mechanical arms 1.2 smaller and extending the mechanical arm 1.2 downward. 2.6 is similar to the length of growth between slide rail 1.1. The mechanical arm 1.2 drives the aeration branch pipe 3.3 to move down, and the rotating wheel 3.1 rotates to release the rolled up air delivery hose 3.2 to complete the downward movement process of the aeration branch pipe 3.3.
Embodiment 3
[0069] Move the aerator to a shallower area:
[0070] The fixed slide rail 1.1 on the solar aerator moves downward relative to the weight 2.6, the pulling force on one side of the pulley traction spring 1.12 on the mechanical arm 1.2 is greater than the pulling force provided by the steel cable III 2.43, and the pulley 1.21 moves outward until the pulley 1.21 When the force on both sides is balanced, the pulley 1.21 on the mechanical arm 1.2 drives the mechanical arm 1.2 to move, so that the upward angle between the mechanical arms 1.2 becomes larger, and the mechanical arm 1.2 shrinks upwards, shrinking the distance, and the weight 2.6 and sliding The shortened lengths between rails 1.1 are similar. The mechanical arm 1.2 drives the aeration branch pipe 3.3 to move upwards, and the rotating wheel 3.1 rotates to roll up the excess air delivery hose 3.2 to complete the upward movement process of the aeration branch pipe 3.3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com