High heat monomers and methods of use thereof
A stand-alone, compound technology for use in products and materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 11
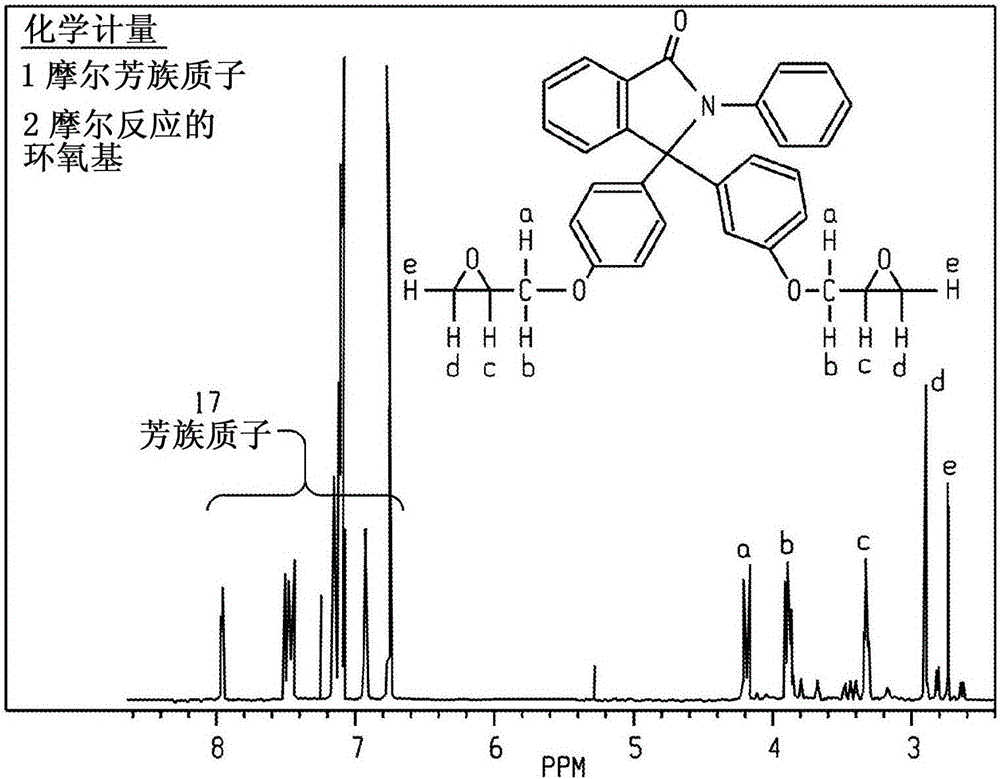
[0243] Embodiment 1.1, the synthesis of 1-bis(4-epoxyphenyl)-N-phenylbenzopyrrolone
[0244]
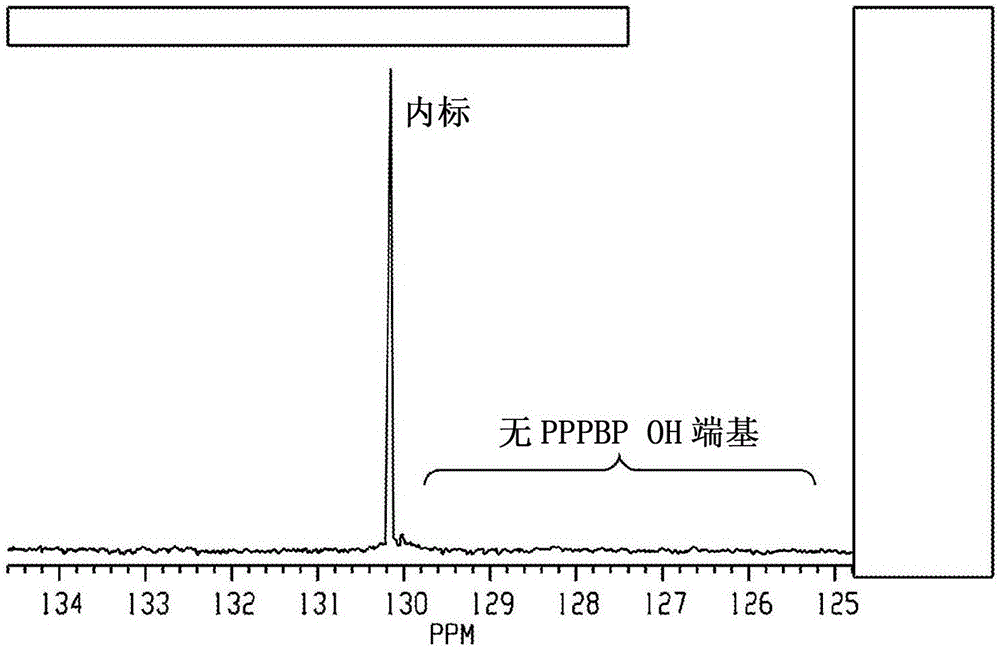
[0245] To a mixture of PPPBP (100 g, 254 mmol) in 225 ml epichlorohydrin (1.182 g / ml, 266 g, 2874 mmol, 11.3 eq) was slowly added potassium hydroxide (13.1 g, 40.6 mmol, 0.16 eq). The resulting mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. The reaction was gradually built up by treatment with water and ethyl acetate. The aqueous layer was repeatedly extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were washed with brine and washed with anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 dry. A total of 164 g of crude product was obtained as a clear oil (theoretical yield 128 g). The residue was purified by chromatography on silica gel. Use 9:1CH 2 Cl 2 / Et 2 O (dichloromethane / diethyl ether) eluted the product. Fractions were checked by HPLC. There are 12 fractions. Fractions 109 were combined and dried in vacuo. Yield 108 g (84% isolated). The purity by HPLC analysis was 99% (area pe...
Embodiment 21
[0254] Example 2.1, Evaluation of 1-bis(4-epoxyphenyl)-N-phenylbenzopyrrolone in curing casting
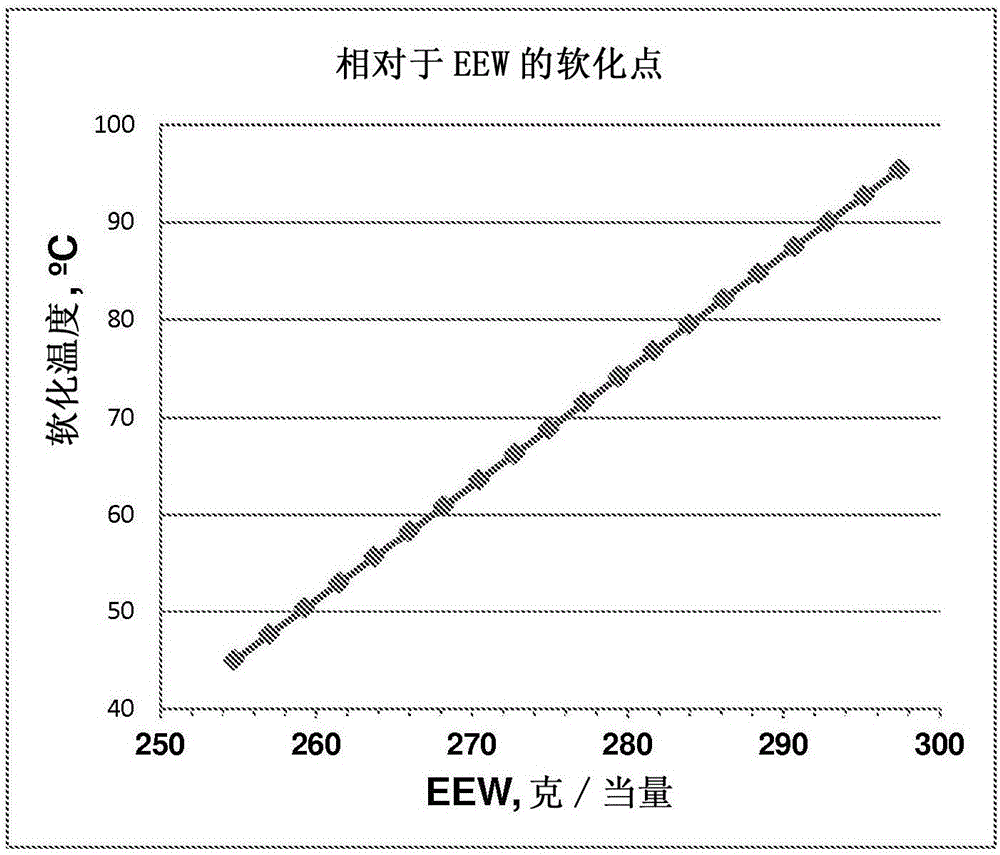
[0255] By making and evaluating cured epoxy castings, 1,1-bis(4-epoxyphenyl)-N-phenylbenzopyrrolone and BPA epoxy resin (Epon 828; diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A ) and TGDDM (N,N,N',N'-tetraglycidyl-4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane) were compared. The curing agent is dissolved in the epoxy resin with heat. The mixture was placed in an oven at 100°C. After 30 minutes, the temperature was raised to 150°C. After 30 minutes, the temperature was raised to 200°C. When 200°C was reached, the oven was turned off and allowed to cool overnight. Samples were analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry. The results are shown in Table 6. Apparently, 1,1-bis(4-cyclophenyl)-N-phenylbenzopyrrolone gave a larger Tg relative to BPA epoxy resin (Epon 828), and compared to tetrafunctional TGDDM epoxy resin A similar Tg is given.
[0256] Table 6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis of Cu...
Embodiment 3
[0258] Example 3. Improved method for the formation of bisphenol diglycidyl ethers
[0259] The reaction of bisphenols with epichlorohydrin Figure 4 The mechanism shown in . Bisphenols react with epichlorohydrin in the presence of a base to form chlorohydrins. The chlorohydrin intermediate undergoes base-catalyzed ring closure to form epoxyethers of bisphenols. However, the presence of base in the reaction mixture not only results in the conversion of chlorohydrins to the desired diglycidyl ethers, but also promotes unwanted oligomeric by-products such as Figure 5 shown.
[0260] To minimize the extent of oligomer formation, the reaction conditions were modified to increase the yield of the desired glycidyl ether. The following experiments describe the effect of temperature, reaction time, solvent and other reaction variables on the desired product purity. Table 7 provides a list of compounds used in the synthesis studies. The synthetic method employed involved the rea...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap