City building group seismic hazard matrix dynamic prediction method
A technology for dynamic forecasting and building, applied in protective buildings/shelters, forecasting, construction, etc., can solve the problems of different ages and imperfections in residential quarters, and achieve simple form, high feasibility, and few model parameters Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0030] Specific implementation mode one: a kind of residential house earthquake damage matrix dynamic prediction method of the present implementation mode, the specific process is:
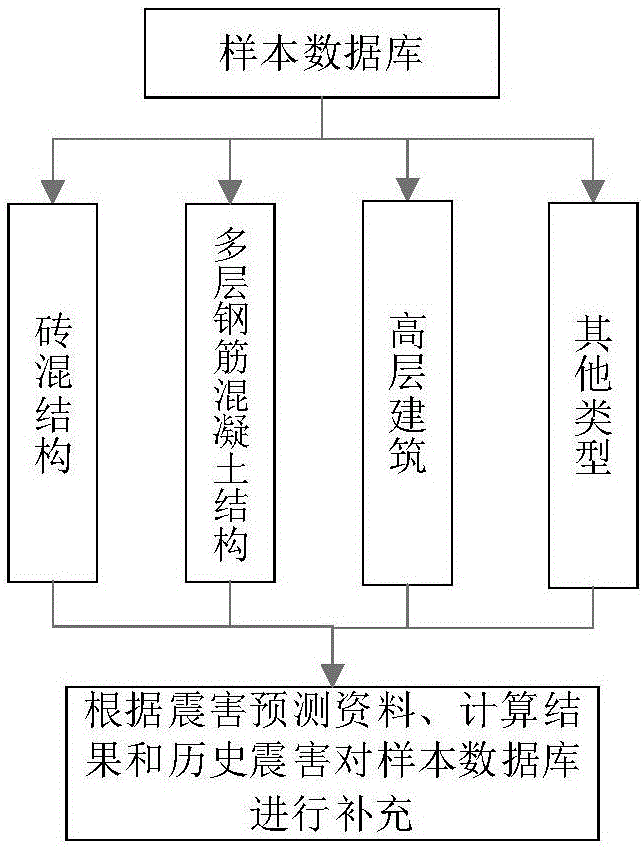
[0031] The sample data can adopt the method of coexistence of earthquake damage prediction data and actual earthquake cases to meet the diversity of data. Considering that the current urban buildings are mainly brick-concrete structures, multi-storey reinforced concrete structures, and high-rise structures, it is recommended to distinguish them mainly by structure types when constructing the urban building database. See image 3 .
[0032] The samples in the sample database must first be tested for integrity. Whether a single sample has no data for parameters or a wrong data format, the format of the data that requires calculations is generally selected as a value. Then check its logic to see if the result makes sense. The discreteness of the sample data is equally important. The amount of data ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0046] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is: in the step 3, the values of i are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7; d ij The i-th earthquake damage factor that meets the classification of item j is specifically:
[0047] For brick-concrete structures:
[0048] When the value of i is 1, the earthquake damage factor is the fortification intensity, and the number of fortification intensity categories M is 3 categories:
[0049] 1), VI degree and below, d ij 1.5; 2), VI degrees, d ij 1.1; 3), VII degree, d ij is 0.95;
[0050] When the value of i is 2, the earthquake damage factor is the site environment, and the number of site environment categories M is 3 categories:
[0051] 1), favorable location, d ij is 1.0; 2), unfavorable location, d ij is 1.8; 3), dangerous area, d ij is 2.8;
[0052] When the value of i is 3, the seismic damage factor is the site type, and the number of site types M is 4 categories:
[0053] 1), Class...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0108] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: the calculation of each type of earthquake damage factor in the step four is specifically:
[0109]
[0110] In the formula, d ij is the i-th earthquake damage factor that meets the classification of item j; m ij is a power exponent, which takes 1 when the situation of the i-th earthquake damage factor meets the j-th classification, and takes 0 for the rest.
[0111] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com