Diamond heat sink GaN-based different-side electrode LED manufacturing method
A production method and diamond technology, applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of complex process, limited thermal conductivity, affecting LED life and lighting performance, etc., to achieve simple process, avoid the impact of LED performance, The effect of heat dissipation is obvious
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] A method for manufacturing a diamond heat sink GaN-based different-side electrode LED, comprising the following steps:
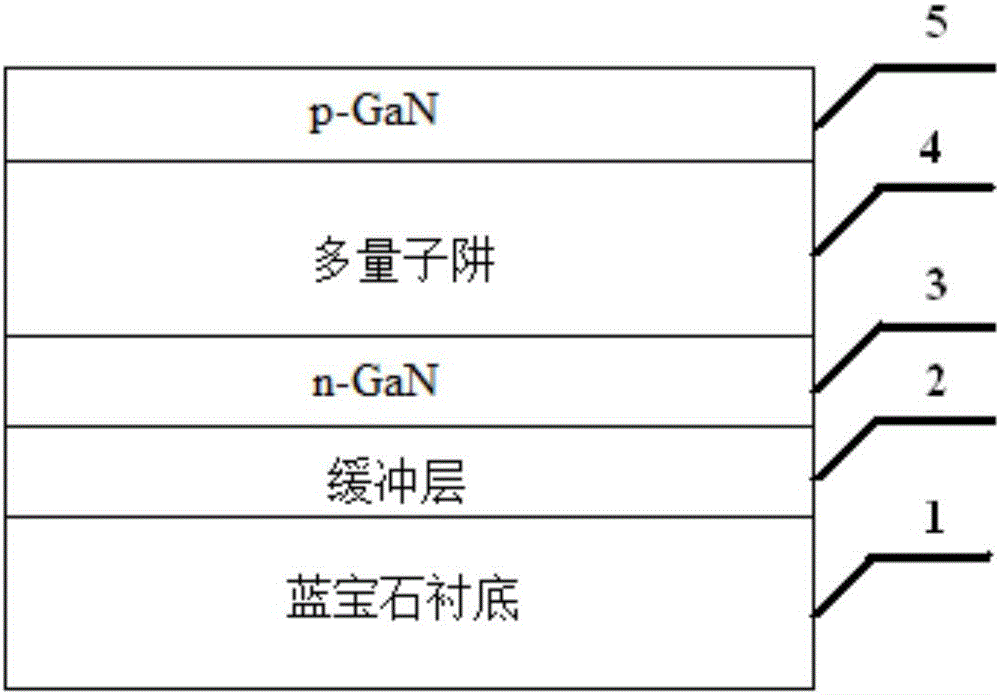
[0061] S1: MOCVD growth of GaN-based LED epitaxial material on sapphire substrate 1;
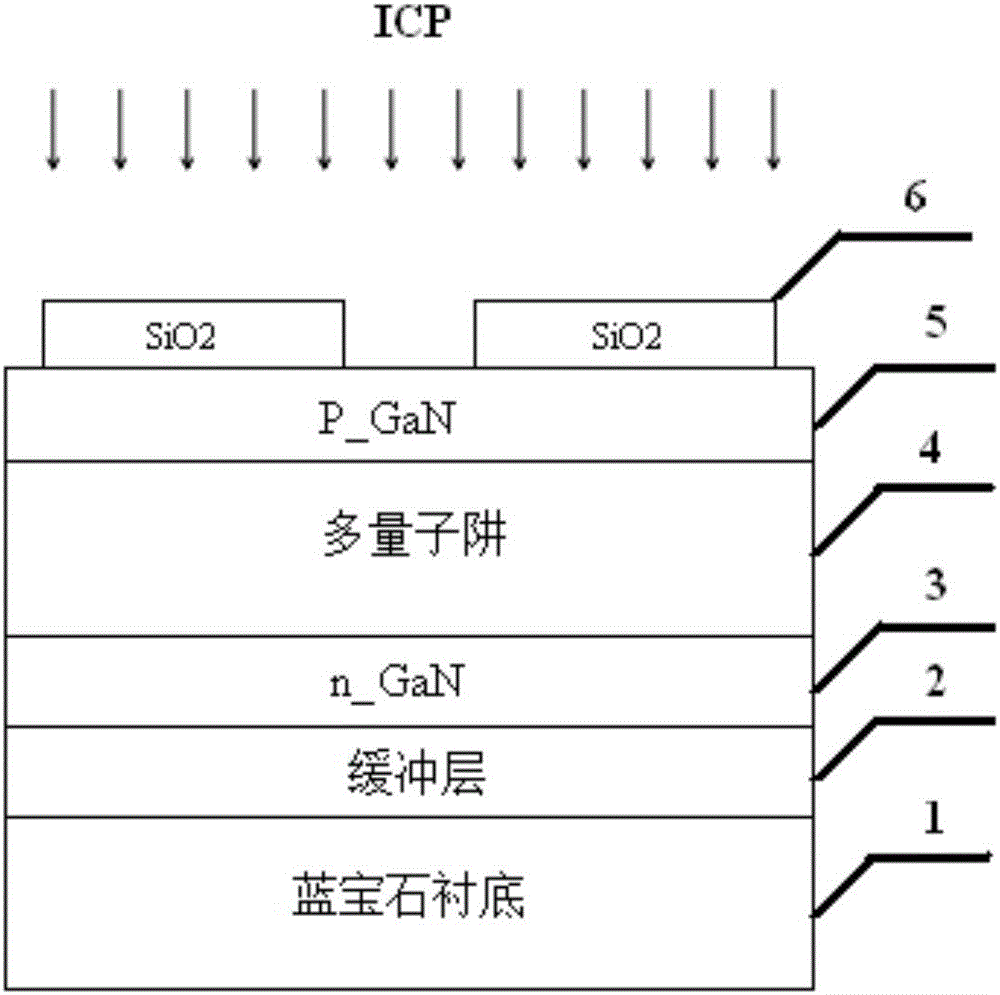
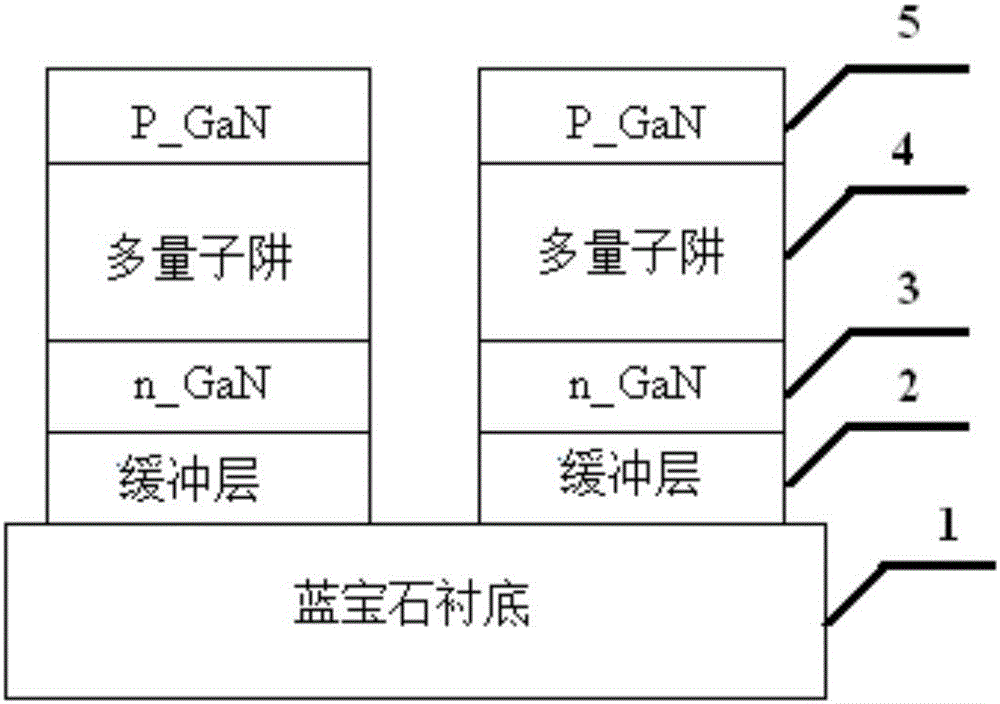
[0062] see figure 1 As shown, the sapphire substrate GaN-based LED epitaxial material is specifically, the sapphire substrate (0001) is polished on one side, the thickness is 500 μm, the thickness of the intrinsic GaN buffer layer 2 is 50 nm, and the thickness of the n-GaN layer 3 is 2 μm. The GaN / InGaN multiple quantum well 4, the p-GaN layer 5 has a thickness of 0.2 μm, and after the GaN-based LED epitaxial material is epitaxially grown on the sapphire substrate, the isolation groove is etched, including the following steps:
[0063] S11: cleaning the sapphire substrate, ultrasonication with acetone and deionized water for 2-3 minutes each.
[0064] S12: Put the sapphire substrate in H at 900-1000°C 2 Baking is carried out under the atmosphere to remove surface...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com