A kind of preparation method of open-cell organic foam material
An organic foam and open-cell technology, which is applied in the field of porous foam materials, can solve the problems of low BET specific surface area and low porosity of porous foam materials, and achieve the effect of high recycling rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] A method for preparing an open-cell organic foam material, comprising the following steps:
[0033] Add surfactant, initiator and foaming agent to the monomer respectively, stir evenly to obtain oil phase solution;
[0034] Add water dropwise to the oil phase solution under stirring condition, the amount of water added is 74-99% in volume percentage, and continue stirring for 10-60min to obtain a thick emulsion;
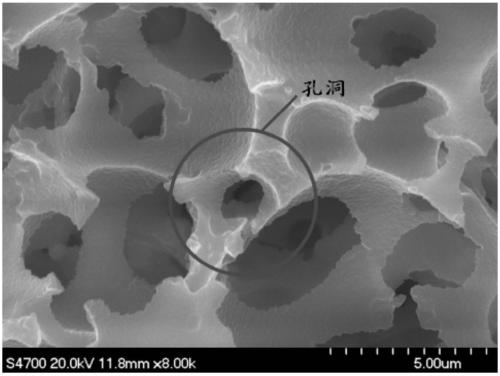
[0035] Pour the concentrated emulsion into a mold, seal it at 50-90°C for 24-48 hours to carry out the polymerization reaction, and then dry it at 60-90°C for 24-48 hours to volatilize the water phase and form holes to obtain an open-cell organic foam base. The temperature should not be too high during the polymerization and drying process. If the polymerization temperature is too high, the emulsion will be directly destroyed. If the drying temperature is too high, the material will soften and cause the pores to disappear. Therefore, the polymerization tempera...
Embodiment 1
[0049] Weigh 5.0 g of methyl methacrylate as a monomer, add 0.1 g of Tween 20, 0.005 g of azobisisoheptanonitrile and 0.005 g of sodium bicarbonate into the monomer, mix and stir until uniform, and obtain an oil phase solution;
[0050] Add 15 g of deionized water dropwise to the oil phase solution under stirring, and continue stirring for 30 minutes to obtain a thick emulsion;
[0051] Pour the concentrated emulsion into a mold, seal it at 50°C for polymerization for 24 hours, and dry it at 60°C for 24 hours. After the water phase volatilizes, holes are formed to obtain an open-cell organic foam substrate;
[0052] The open-cell organic foam substrate is used as the secondary foaming matrix, and the foaming agent and the foaming inducer are used to perform secondary foaming treatment at 93°C for 30 minutes, and cooled to room temperature to obtain open cells. Type organic foam material.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Weigh 5.0 g of methyl methacrylate as a monomer, add 0.1 g of Tween 20, 0.005 g of azobisisoheptanonitrile, 0.005 g of sodium bicarbonate and 0.005 g of toluene into the monomer, mix and stir until uniform to obtain oil phase solution;
[0055] Add 15 g of deionized water dropwise to the oil phase solution under stirring, and continue stirring for 30 minutes to obtain a thick emulsion;
[0056] Pour the concentrated emulsion into a mold, seal it at 50°C for polymerization for 24 hours, and dry it at 60°C for 24 hours. After the water phase volatilizes, holes are formed to obtain an open-cell organic foam substrate;
[0057] The open-cell organic foam substrate is used as the secondary foaming matrix, and the foaming agent and the foaming inducer are used to perform secondary foaming treatment at 93°C for 30 minutes, and cooled to room temperature to obtain open cells. Type organic foam material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com