Device for intracavity in-situ fenestration and puncture
A fenestration, in-situ technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of inability to precisely adjust the puncture depth, accidental injury to the contralateral tissue, and excessive puncture depth, etc., to reduce risks, concentrate puncture, and improve effectiveness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
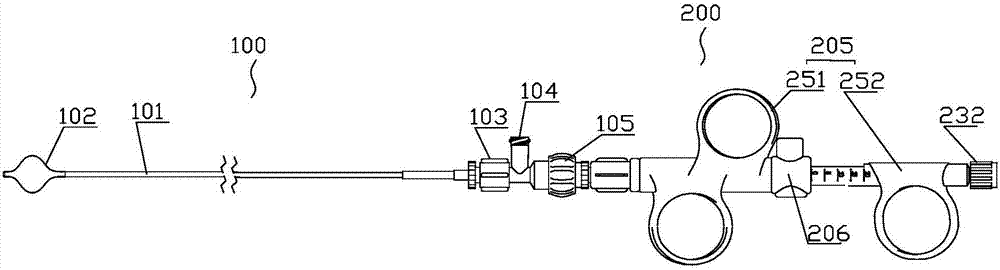
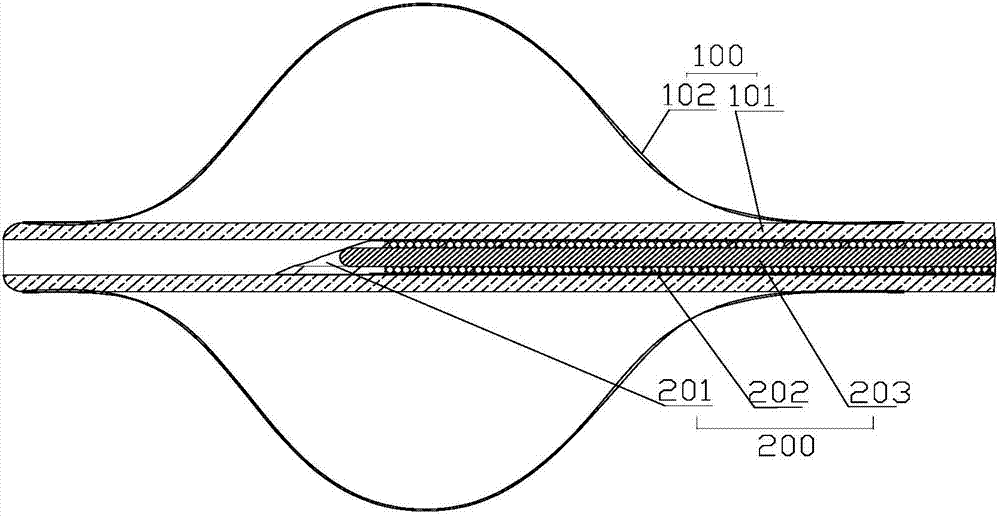
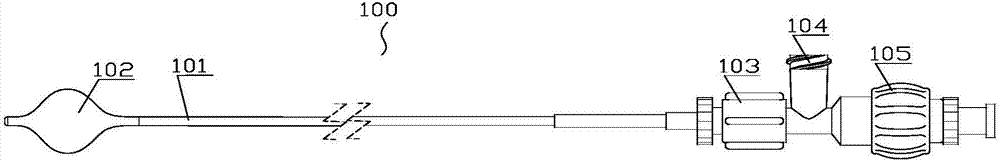
[0046] Embodiment 1, the main technical problem to be solved in this embodiment is to precisely control the puncture depth, adjust the puncture depth and lock the puncture, and solve the problem of accurate puncture, that is, ensure that the puncture position is in the center of the blood vessel. Such as Figure 1-17 As shown, a puncture device for intraluminal in situ fenestration includes a balloon catheter 100 and a puncture needle assembly 200 coaxially sleeved in the balloon catheter 100; the balloon catheter 100 includes at least two cavities The balloon pusher rod 101, the balloon body 102 arranged at the distal end of the balloon pusher rod 101, the balloon catheter seat 103 arranged at the proximal end of the balloon pusher rod 101; the puncture needle assembly 200 includes a puncture pusher rod 202, The puncture needle 201 and the puncture handle 205 arranged at the distal end of the puncture push rod 202; the puncture handle 205 includes a proximal handle 252 and a ...
Embodiment approach
[0057] Such as Figure 12 Shown is the first embodiment of the puncture control mechanism 206, which can be driven quickly to achieve puncture, and realize quantitative and precise puncture. The maximum stroke control assembly 260 includes a stroke groove 260a arranged on the proximal handle 252 or the distal handle 251, and the corresponding distal handle 251 or the proximal handle 252 is provided with a limit block 260b; The puncture push rod 202 is arranged axially, and the limit block 260b slides in the travel groove 260a and its maximum sliding distance is the maximum depth that allows the puncture needle to puncture. The maximum depth is determined according to the diameter of the blood vessel, usually not exceeding 40mm. The lateral width of the stroke groove 260a is slightly larger than that of the limiting block 260b, and the two are clearance fit or sliding fit.
[0058]The puncture locking assembly 261 is provided with a plurality of positioning locking grooves 261...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2, the main technical problem to be solved in this embodiment is: the puncturing push rod 202 is not easy to be discounted, and the puncturing is more concentrated and effective.
[0065] A puncture device for intraluminal in situ fenestration, comprising a balloon catheter 100 and a puncture needle assembly 200 coaxially sleeved in the balloon catheter 100; the balloon catheter 100 includes a balloon pusher with at least two cavities rod 101, the balloon body 102 arranged at the distal end of the balloon push rod 101, the balloon catheter seat 103 arranged at the proximal end of the balloon push rod 101; The puncture needle 201 and the puncture handle 205 at the far end of the push rod 202; Lining silk 203. The concrete structure of above-mentioned parts is the same as embodiment 1.
[0066] Wherein the structure of the balloon catheter 100 can be the same as that of Embodiment 1, including the balloon pushing rod 101 and the balloon body 102, but the ball...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com