Method for reducing non-point source pollutants of farmland
A pollutant and farmland technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, sustainable biological treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of farmland non-point source pollution, nitrogen and phosphorus loss, etc., to achieve appropriate water flow and reduce nitrogen Phosphorus loss, effect of increasing settling and adsorption absorption time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A method for reducing farmland non-point source pollutants, comprising the following steps:
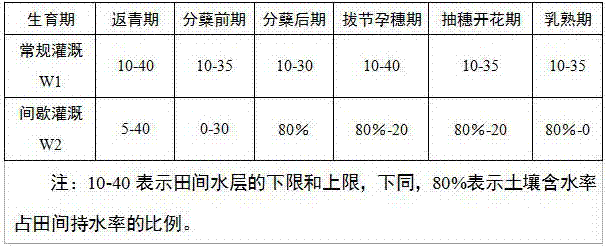
[0030] S1. Irrigation method: reduce the loss of nitrogen and phosphorus in the farmland by using intermittent irrigation; fertilization method: four times of nitrogen fertilizer application, the base fertilizer is applied to 30% of the total weight of nitrogen fertilizer, and nitrogen fertilizer is applied 10 to 12 days after transplanting 30% of the total weight is used as tillering fertilizer, 30% of the total weight of nitrogen fertilizer is applied as jointing fertilizer 35 to 40 days after transplanting, and 30% of the total weight of nitrogen fertilizer is applied as 10% ear fertilizer after 60 to 65 days of transplanting. That is, the 4th nitrogen fertilization ratio is 3:3:3:1.
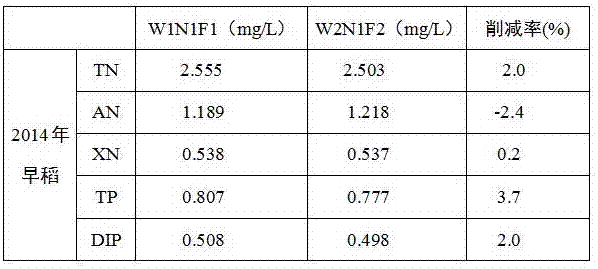
[0031] S2. The water discharged from the farmland flows into the drainage grass ditch. The vertical section of the drainage grass ditch is trapezoidal, with an upper bottom of 0.3m, a lower bo...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The steps of S1, S2, and S4 in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and only another processing is performed on the step of S3.
[0085] The pond weir wetland is divided into 4 connected parts of No. 1 pond weir, No. 2 pond weir, No. 3 pond weir and No. 4 pond weir; No. 1 pond weir and No. 3 pond weir part are water inflowed from the upper part and water out from the lower part, and floating leaf plants are planted , one or more of submerged plants, floating plants, and vegetables floating on the water surface using soilless culture; No. 2 pond weir part and No. 4 pond weir part enter water from the bottom, and water comes out from the top, planting emergent plants; floating leaves Plants include water lilies, submerged plants include black algae and foxtail algae; floating plants include water hyacinth; vegetables include water spinach, watercress, and lettuce; emergent plants include reeds and reeds.
[0086] Planting method: Water lilies, reeds, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com