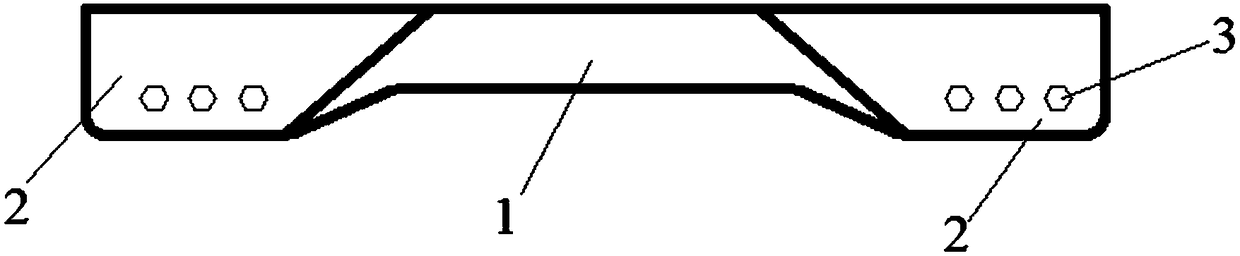
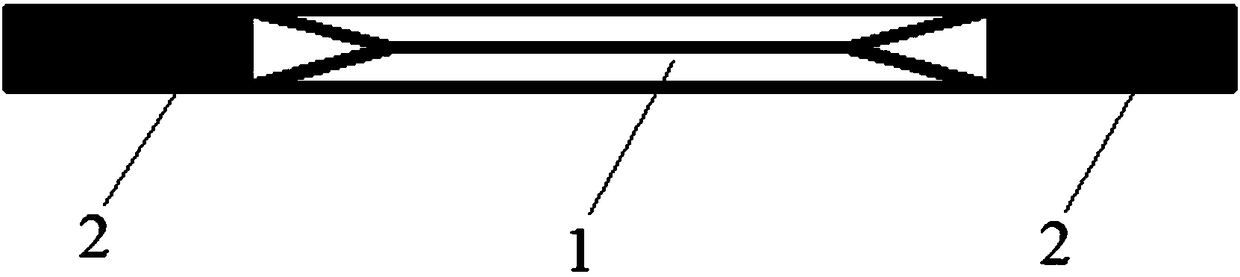
Blade preparation method and blade
A technology for blades and installation parts, which is applied to earth movers/shovels, construction, etc. It can solve problems such as difficulty, large investment in mass production, and irreversibility, and achieve stable mechanical properties, excellent comprehensive performance, and reduced installation costs. effect of number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for preparing a blade, including:
[0026] Smelting high-purity alloys as raw materials, and processing the raw materials into blade blanks;
[0027] Pre-open mounting holes for the blade blanks to obtain semi-finished blades;
[0028] Forging and rolling of semi-finished blades to obtain finished blades;
[0029] Finish machining the mounting holes on the finished blade to obtain the blade;
[0030] Among them, the high-purity alloy contains: vanadium, chromium, boron, carbon, nickel, manganese, titanium, boron, and iron. The composition design used in the high-purity alloy is (wt%): vanadium: 0.016-0.019, chromium: 0.014- 0.017, boron: 0.001-0.002, carbon: 0.22-0.25, nickel: 0.0017-0.0019, manganese: 1.11, titanium: 0.0013-0.0021, cobalt: 0, molybdenum: 0, the balance is iron and unavoidable impurities.
[0031] Specifically, the purity of the blade blank is ensured by smelting alloy in a certain propor...
Embodiment 1
[0035] High-purity alloys are smelted through a vacuum furnace. Among them, the high-purity alloys contain: vanadium, chromium, boron, carbon, nickel, manganese, titanium, boron, and iron. The composition of the high-purity alloy is designed as (wt%): Vanadium: 0.016, chromium: 0.017, boron: 0.002, carbon: 0.22, nickel: 0.0017, manganese: 1.12, titanium: 0.0021, cobalt: 0, molybdenum: 0, the balance is iron and inevitable impurities.
[0036] Smelting high-purity alloys as raw materials, and processing the raw materials into blade blanks;
[0037] Pre-open mounting holes for the blade blanks to obtain semi-finished blades;
[0038] Forging and rolling of semi-finished blades to obtain finished blades;
[0039] Finish machining the mounting holes on the finished blade to obtain the blade.
Embodiment 2
[0041] High-purity alloys are smelted through a vacuum consumable furnace. Among them, the high-purity alloys contain vanadium, chromium, boron, carbon, nickel, manganese, titanium, boron, and iron. The high-purity alloys are designed with the following composition (wt%): Vanadium: 0.019, Chromium: 0.014, Boron: 0.001, Carbon: 0.25, Nickel: 0.0019, Manganese: 1.13, Titanium: 0.0013, Cobalt: 0, Molybdenum: 0, the balance is iron and inevitable impurities.
[0042] Smelting high-purity alloys as raw materials, and processing the raw materials into blade blanks;
[0043] Pre-open mounting holes for the blade blanks to obtain semi-finished blades;
[0044] Forging and rolling of semi-finished blades to obtain finished blades;
[0045] Finish machining the mounting holes on the finished blade to obtain the blade.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com