Double-fed fan crowbar adaptive cut-out control method for preventing repeated switching of crowbar
A control method and technology of doubly-fed wind turbines, applied in the auxiliary control strategy of rotor-side converters, and in the field of doubly-fed wind turbine crowbar adaptive cut-off control, can solve the safety hazards of wind turbines, DFIG electromagnetic torque impact, and increase system reactive power Power and other issues to achieve the effect of reducing safety impact, improving transient stability, and avoiding re-investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
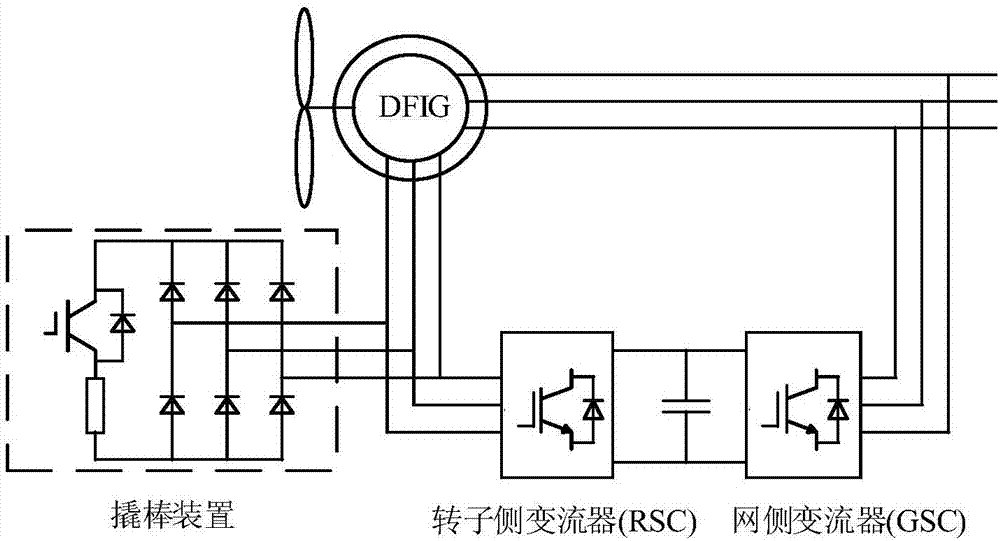
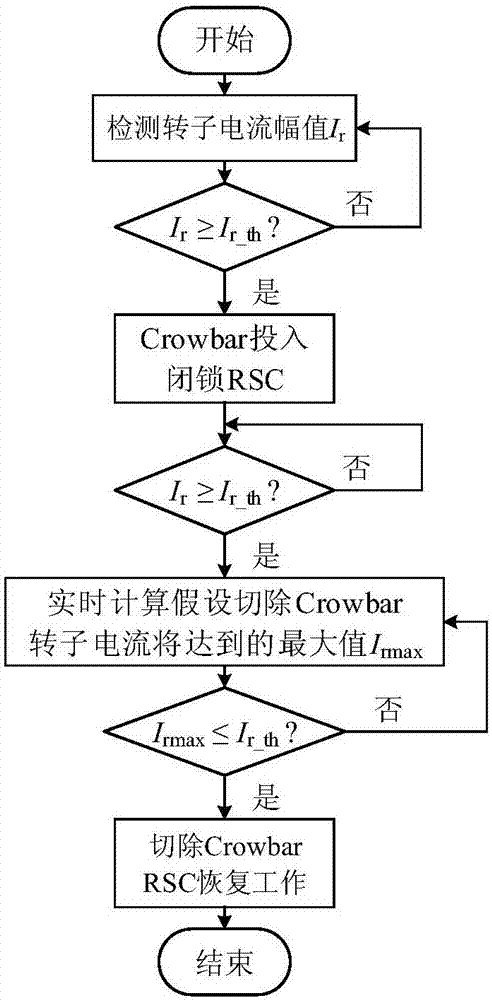
[0039] An embodiment of the present invention provides a DFIG crowbar adaptive cutting control method to prevent repeated switching of the crowbar, see figure 1 with figure 2 , the method includes the following steps:
[0040] 101: Through real-time calculation, assume the maximum value of the rotor current that will appear when the crowbar is cut off at the current moment;
[0041] 102: If the maximum value of the rotor current is less than the action threshold of the crowbar, cut off the crowbar;
[0042] In actual implementation, this step removes the crowbar as early as possible on the premise that the crowbar will not be switched repeatedly, so as to reduce the reactive power absorbed from the system when DFIG operates as an asynchronous machine, and reduce the impact on the safety of the fan and its control device.
[0043] 103: Obtain the auxiliary control strategy of the rotor-side converter that matches with the crowbar removal, and formulate the reference value of...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The scheme in embodiment 1 is further introduced below in combination with specific calculation formulas, see the following description for details:
[0047] In the embodiment of the present invention, a crowbar protection circuit is added on the rotor side of DFIG, and its switching state is controlled by IGBT. The control signals are respectively the rotor current and the maximum value that will be generated by cutting off the crowbar rotor current calculated according to formula (2) at the current moment; At the same time, corresponding auxiliary control is performed on the rotor side converter of DFIG. figure 1 Shown is the DFIG structure diagram of the protection scheme, which includes the following contents:
[0048] 201: Calculation of the possible maximum value of the rotor current after the crowbar is cut off;
[0049] Taking the time when the crowbar is cut off as zero time, the expression of the rotor current after the crowbar is cut off is:
[0050]
[...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Combine below Figure 3-Figure 5(d) The scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
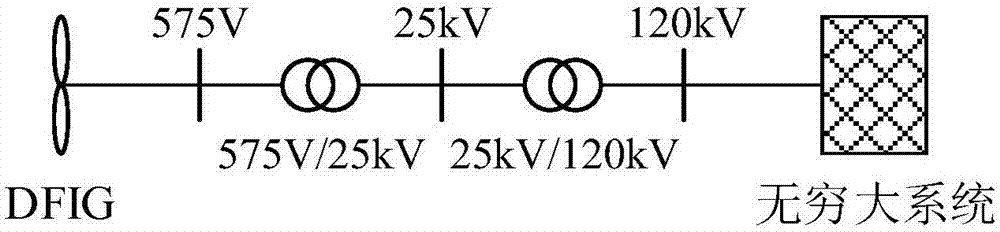
[0078] A stand-alone infinite system with DFIG wind farm such as image 3 As shown, the wind farm consists of six 1.5MW (unit) DFIGs. Assume that a three-phase short circuit occurs at the grid-connected point of the fan at 0.05s, and the voltage drop depths are 60% and 80% respectively. The fault is removed at 0.25s, and the fault lasts for 200ms. The crowbar resistance is 0.1Ω. The traditional control strategy of the crowbar circuit and the action value of the rotor current in this method are both I r_th = 2(pu). In addition, the crowbar traditional control method returns the value I r _ re =1.5(pu), the delay is cut off by 1 synchronous period.
[0079] From Figure 4(a) and Figure 4(d), it can be observed that when the voltage drop depth at the grid-connected point is 60%, when the traditional crowbar control ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com