Identification methods and uses of seed plant species
An identification method and technology for gymnosperms, applied in the field of biological detection, can solve problems such as being too large, not considering the genetic distance between species, etc., and achieve the effects of high application value, high accuracy, and low coverage requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A method for identifying a seed plant species, comprising the steps of:
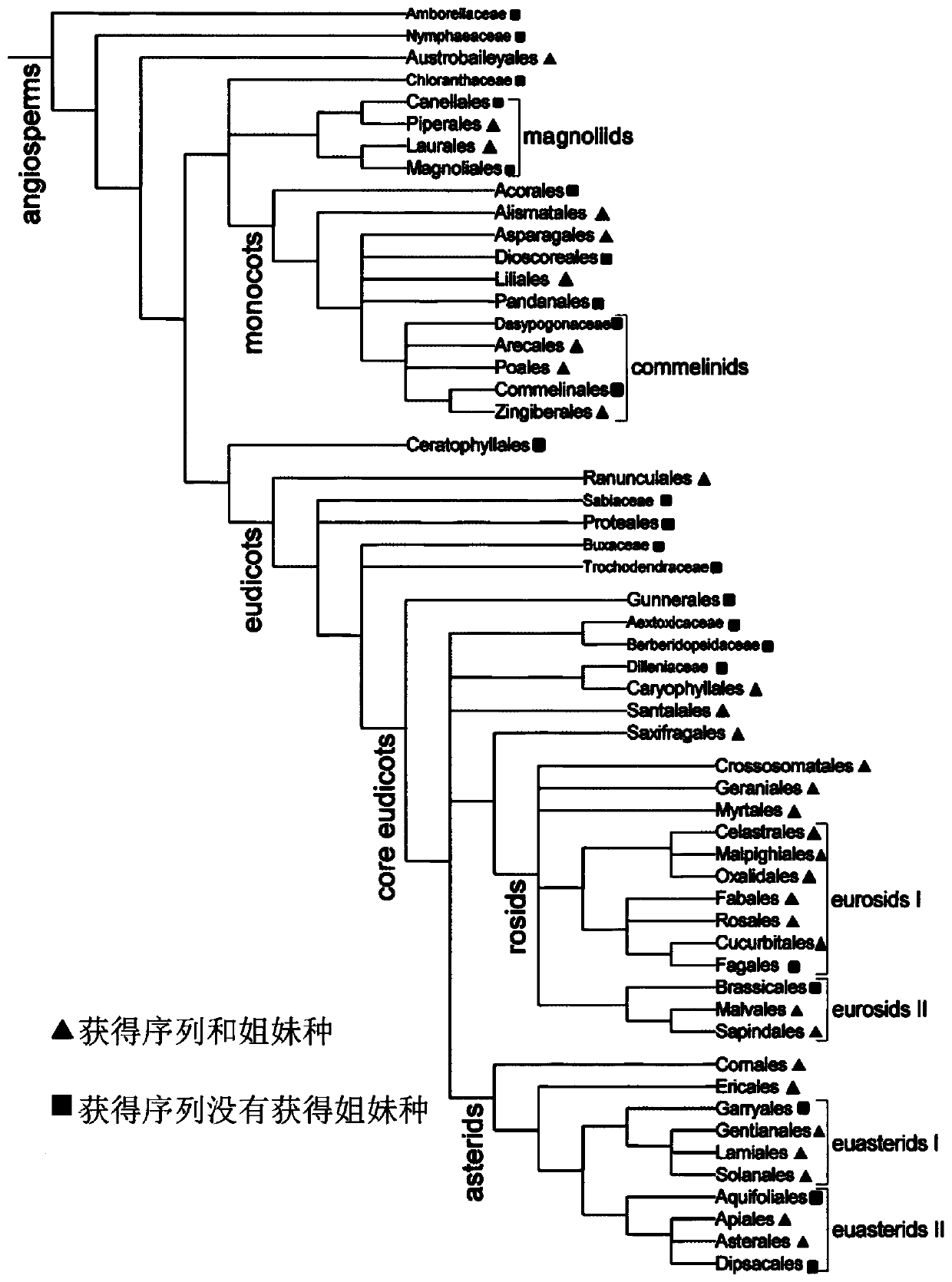
[0050] Determining molecular cut-off values: according to e.g. figure 1 The group relationship shown in the "Angiosperm APG II Classification System (Revised Edition)" and all representative classes of gymnosperms except the monotype (Ginkgophyla), selected 7866 species, including 99 angiosperms families, 179 genera, and 99 families, so that it basically covers the diversity of angiosperms, and the genera of the selected species meet the species coverage of more than 75%; download the ITS2 gene sequence of the group from GenBank, or download the group The ITS sequence of the selected species is intercepted according to the GenBank annotation to obtain the ITS2 gene sequence; the ITS2 gene sequence matrix of the selected species is imported into the MEGA software to build an evolutionary tree in units of genus. Multiple sequences of the same species must be input adjacently. According to the princi...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Determining the molecular threshold is consistent with the steps described in Example 1, so it will not be repeated in this example.
[0060] Determining the species category: a method for identification of a suspected medicinal plant yew, the specific implementation steps include:
[0061] Step 1. Sequencing of the species to be tested: extract the DNA of the species to be tested, perform PCR amplification, use ITS universal primers ITS4 and ITS5B as PCR amplification primers, and perform DNA sequencing on the PCR products. The sequence results of the species to be tested are shown as SEQ ID No: Shown in 4: the sequence of ITS4 is shown in SEQ ID No: 5; the sequence of ITS4 is shown in SEQ ID No: 6;
[0062] Step 2. Sequence alignment: Obtain the GenBank sequence numbers AF259300, AF259292, and AF259291 of the target species Taxus chinensis from GenBank, wherein the sequence of the GenBank sequence number AF259300 is shown in SEQ ID No: 2, The sequences of GenBank seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com