Cuttage propagation method for loropetalum chinense var.rubrum
A technology of safflower and cutting propagation, which is applied in botany equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, animal repellants, etc., can solve the problems of low survival rate and slow speed, and achieve high survival rate , simple technical operation and high reproductive efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The specific process of cutting propagation of safflower loropetalum is as follows:
[0025] 1. Management of the female parent of ear picking: Strong pruning of the ear picking nursery of Safflower safflower from February to March, keeping the height of the female parent at 50-60 cm, and performing stubble. After pruning, apply a compound fertilizer with a ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium of 10:15:20 at a distance of 40 to 50 cm from the root of the female parent as the base fertilizer to promote the germination of more and thicker spikes of the year. The amount of base fertilizer is 150 to 200 kg / hm 2 ;
[0026] 2. Cutting time: from mid-November to the end of March of the following year;
[0027] 3. Preparation of the slotting bed: spread 20cm thick clean river sand on the pre-built electric hotbed, the electric hotbed is 60-80cm wide, and the electric hotbed is set in a simple steel shed;
[0028] 4. Preparation of rooting agent: first dissolve 100-20...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A. Rooting agent screening experiment
[0036] Experimental method: preparation method of rooting agent: dissolve indole acetic acid or / and naphthalene acetic acid in 200 ml of ethanol with a volume concentration of 95%, add water to 1 kg and mix evenly.
[0037] The rooting agent is provided with 14 kinds of treatments, and the specific treatments are shown in Table 1. The hormone unit in each treatment is mg / kg, no synergist is added in the rooting agent, and other steps are the same as in Example 1. Under different rooting agents and concentrations, the rooting rate of cuttings was also different, as shown in Table 1.
[0038] Table 1 Effects of different rooting agents on the rooting rate of the cuttings of P. safflower
[0039] Processing number
IAA+NAA(mg / kg)
Rooting rate (%)
1
0+0
38.4
2
0+200
43.5
3
0+400
44.0
4
200+0
41.1
5
400+0
40.8
6
100+50
54.5
7
50+100
52...
Embodiment 3
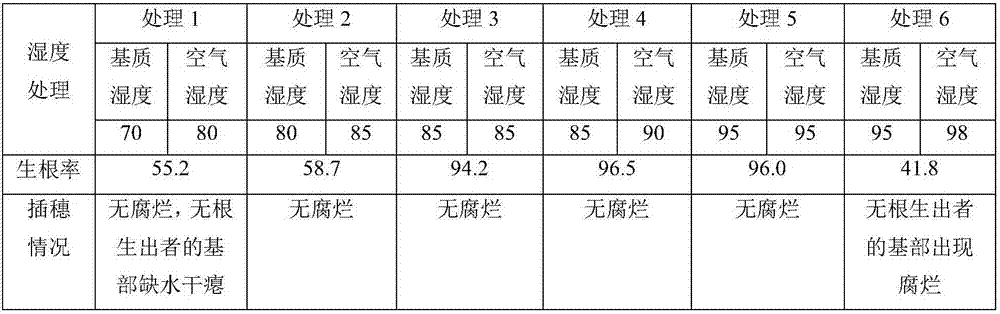
[0055] Experimental method-preparation of rooting agent: dissolve 100mg of indoleacetic acid (IAA) and 200mg of naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) in 200ml of ethanol with a volume concentration of 95%, add water to 1kg and mix evenly, then add vitamin B 1 2g and 1g of boric acid are mixed evenly for use. Dilute the base of the cuttings with 70% thiophanate-methyl wettable powder by 800-1500 times in a medium-speed dip for 1s-5s, then soak in the prepared rooting agent for 10-30 minutes, and insert the laid cuttings on the substrate. The cutting substrate was set to 9 treatments, see Table 4 for details. Other steps are with embodiment 1. Under different cutting substrate treatments, the rooting rate of cuttings is different, see Table 4:
[0056] Table 4 Effects of different cutting substrate treatments on the rooting rate of A. safflower cuttings
[0057] Processing number
Components of the cutting substrate
Volume ratio
Rooting rate (%)
1
Garden...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com