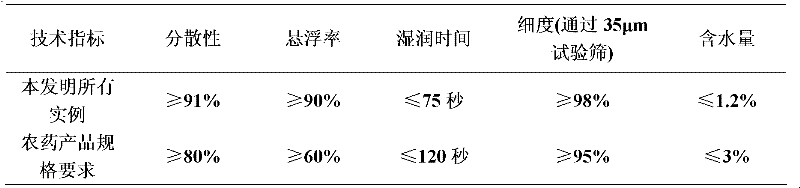
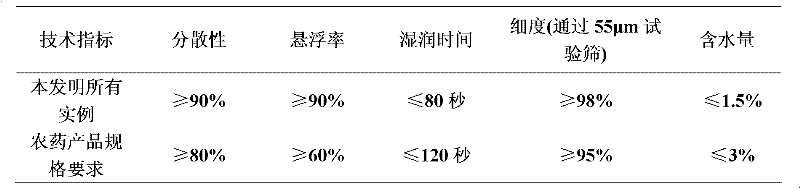
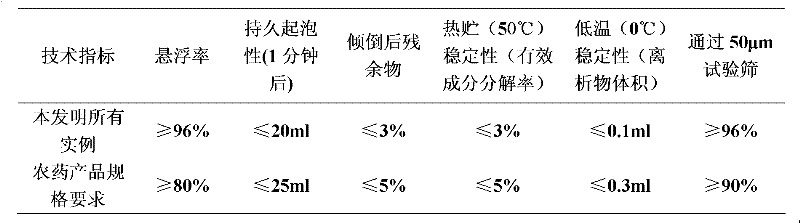
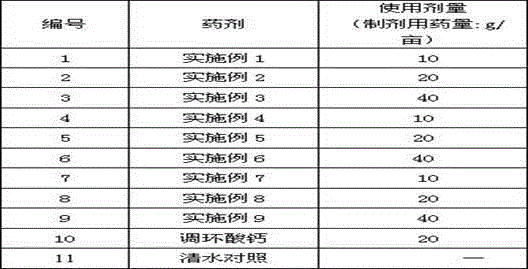
Patents
Literature
261 results about "Thiophanate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nematocide used in livestock; also has fungicidal properties.
Method for quick cultivation of long-stem standard rose using cutting with long shoots
ActiveCN102498905AImprove survival ratePromotes rapid rootingHorticultureThiophanate-methylRosa arvensis
The invention relates to a method for quick cultivation of long-stem standard rose using cutting with long shoots. A stock of the long-stem standard rose to be cultivated by the method is a shoot of rosa multiflora Thunb. var. carnea Thory, which is dipped with rooting powder for cuttage, the rooting powder is made of IBA (indole-3-butyric acid) 0.8-1.0% and thiophanate-methyl 2-5%, mass water content of substrate soil is maintained to be 60-65% after cuttage, relative humidity of air in a seed bed is 60-80%, the relative humidity of the air is reduced to 50-60% after a cutting seedling rootsand sprouts, daytime temperature is controlled to be 25-26 DEG C, night temperature is controlled to be 10-14 DEG C, a black shade with light transmittance 50% is used for covering from 11 O'clock to17 O'clock in two weeks after rooting and sprouting, the black shade is removed after two weeks, daytime temperature is then controlled to be 26-28 DEG C, and the rose shoot or bud is grafted to the stock. The stock has average height 120cm and only requires 135-150 days, and cultivation of the long-stem standard rose only requires 225-270 days, so that production cycle is short.
Owner:YUNNAN LANDSCAPING CO LTD
Method for cuttage propagation of rhododendron lapponicum
InactiveCN102498899ASolve the problem that the cuttings are not easy to take rootSolve the problem of low cutting propagation rateHorticultureThiophanate-methylDisease damage
The invention relates to a method for cuttage propagation of rhododendron lapponicum, which includes: making a mixture of peat and pearlite into cuttage substrate according to a volute ratio of from 1:3 to 1:4, cutting a stem of a current year growing semi-lignified branch of a rhododendron lapponicum plant which is under no pest and disease damage and 3-5 years old as a cutting, and retaining two to three complete leaves at the top of the cutting; dipping the base of the cutting into rooting reagent A or B prior to inserting into the substrate; and performing intermittent spray for subsequent water management, maintaining mass water content of soil to be 60-65%, and maintaining air humidity to be more than 80% during a period from cuttage to rooting of a cutting seedling. The rooting reagent A includes IBA (indole-3-butyric acid) 0.8-1.0% and thiophanate-methyl 2-4%. The rooting reagent B includes IBA 0.015-0.02% and thiophanate-methyl 1-2%. By the method, rooting rate can reach morethan 85%, rooting of the cutting only requires about 60 days, and production cycle is short.
Owner:YUNNAN YUNKE FLOWER
Intelligent rapid propagation method of tea tree
InactiveCN102405757AEasy to preparePermeableClimate change adaptationGreenhouse cultivationIntelligent control systemThiophanate
The invention discloses an intelligent rapid propagation method of tea tree. The method comprises the following steps: (1) growing environment: setting parameters of temperature, humidity and nutritional environment required for rapid growth of tea seedlings by using an intelligent control system; (2) seedling culture matrix: sufficiently and uniformly mixing sugar-free perlite and sandy yellow soil with soil pH value between 4.5 and 5.5 in a weight ratio of 1:(3-5); (3) seedling bed sterilization and disinfection treatment: spraying the seedling bed with 800-1,000 time mildothane or carbendazim solution before cuttage; (4) cuttage: ensuring that the cut is smooth and the upper cut is 0.2-0.3cm from the blastema; (5) seedling phase management: carrying out conventional short-ear cuttage management. The method has the advantages of short seeding period and high efficiency; moreover annual production can be performed, and breeding materials can be saved; and the original excellent properties of the tea tree can be maintained, and the cost is low.
Owner:周国兰 +2
A kind of bactericidal composition containing prothioconazole
The invention relates to a bactericidal composition containing prothioconazole, which contains active ingredient A and active ingredient B, wherein active ingredient A is selected from prothioconazole, and active ingredient B is selected from thiophanate-methyl, multibacterium One of Ling and prochloraz, wherein the weight ratio of active ingredient A to active ingredient B is 1:80 to 80:1, made into wettable powder, water dispersible granule, suspending agent, suspoemulsion, water emulsion, Microemulsion, used to control powdery mildew, sheath blight, fusarium wilt, leaf spot, rust, sclerotinia, viral disease, anthracnose, gray mold, ring spot, bakanae disease, rice blast, early blight, Diseases such as green mold, pedicle rot, penicillium, flax spot, scab, blight, etc. have the characteristics of small dosage, resistance to rain erosion, and obvious synergistic effects.
Owner:SHAANXI MEIBANG PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Composition of prohexadione calcium and fungicide
ActiveCN103814901ALower drug costsIncrease productionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideCarboxylic acidHexaconazole
The invention discloses a composition of prohexadione calcium and a fungicide. The composition includes 5 to 50 parts by weight of the prohexadione calcium and 5 to 60 parts by weight of the fungicide; the bactericide is a triazole fungicide such as epoxiconazole, tebuconazole, hexaconazole and difenoconazole, or a carboxylic acid amide fungicide such as thifluzamide and fenoxanil, or a benzimidazole fungicide such as carbendazim and thiophanate-methyl, or an imidazole fungicide such as prochloraz and prochloraz-manganese chloride complex. The composition of the prohexadione calcium and the fungicide provided by the invention can achieve the purposes of vigorous growth control, disease resistance and yield increase, has no effect on next-stubble crops, reduces the pesticide costs of farmers, and increases the crop yield, so as to increase the income of farmers, and create enormous economic and social values.
Owner:郑州郑氏化工产品有限公司
Method for planting anoectochilus formosanus in northern area
InactiveCN103766113ARegulating light, temperature and humidity conditionsAvoid heat damageFertilising methodsHorticultureSoil humusSoil texture
The invention discloses a method for planting anoectochilus formosanus in the northern area. The method comprises the following steps: (1) woodland selection, (2) seedling selection, (3) seedbed preparation, wherein the northern area with the temperature in spring, summer and autumn ranging from 15 DEG C to 30 DEG C is selected as the cultivation field, soil under chestnut trees is selected, soil texture is required to be loose, breathable and good in moisture retention, the matrix on the ridge surface is formed by adopting and evenly stirring and mixing 1 / 2-2 / 3 of organic fertilizer and 1 / 3-1 / 2 of under-wood fine soil humus, before plantation, spraying and sterilizing are carried out through carbendazim or thiophanate, plastic films cover the matrix for 2-3 days and then are uncovered, and the matrix is prepared for use, (4) transplantation, (5) management after plantation, and (6) harvest. According to the method, a complete set of the technology for planting the anoectochilus formosanus under woods in the northern area is formed. The wild environment is imitated, local natural products are explored and utilized for mixing preparation to form the matrix for transplantation, and therefore the production cost is low; the cultivation technology for improving the plantation survival rate of the anoectochilus formosanus is formed, and therefore the stable yield is achieved easily; by the adoption of the method, the anoectochilus formosanus grows normally, and the net weight of a single plant is increased.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Alfalfa seed obducens agent and production process thereof
InactiveCN104496662AThe production application effect is remarkableReduce applicationsAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersMonopotassium phosphateGibberellin
The invention discloses an alfalfa seed obducens agent which is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 1.5-5% of carboxymethylcellulose, 0.5-3% of rhizobium of alfalfa, 0.5-7% of biological humic acid, 0.2-3% of urea, 0.2-3% of monopotassium phosphate, 0.1-0.7% of ammonium molybdate, 0.1-0.5% of borax, 2-6% of sulfur powder, 0.15-0.7% of ferrous sulfate, 5-8% of sodium polyacrylate, 0.01-0.05% of indolebutyric acid, 0.01-0.05% of gibberellin, 0.01-0.05% of lysine acetate, 1.0-8.0% of thiram, 2.0-8.5% of thiophanate-methyl and the balance of alfalfa seeds. Aiming to the characteristics that alfalfa in the seedling stage is not saline-alkaline tolerant, draught tolerant, susceptible to diseases and the like, anti-salt and alkali, anti-drought and soil sterilizing factors are respectively added into the obducens agent disclosed by the invention, and moreover, the alfalfa seed obducens agent is obvious in production and application effects and is deeply welcomed by farmer households.
Owner:酒泉大业种业有限责任公司
Method for planting Anoectochilus formosanus
InactiveCN102696465ALow survival rateSurvival rate maintained or increasedCultivating equipmentsPlant protectionPeatFarmyard manure
The invention provides a method for planting Anoectochilus formosanus. The method is characterized by preparing a planting matrix by mixing peat, humus soil, carbonized rice hull and river sand in a ratio of 1:1, and comprising the following steps of: (A), exposing matrix soil to the sun for 4 to 6 hours, spraying a thiophanate solution diluted by water in an amount which is 800 times the volume of thiophanate or a carbendazim solution diluted by water in an amount which is 600 to 1,000 times the volume of carbendazim, paving on a planting seedling bed, and controlling the thickness to be 15 to 20cm; (B), selecting strong Anoectochilus formosanus seedlings which have the plant height of 2cm and have more than two roots and branches, and planting in the matrix according to the plant row distance of 5*10-15cm; and (C), watering, spraying a nutrient solution and applying a compound fertilizer or farmyard manure according to the circumstances after plantation, spraying a bactericide or a pesticide, and harvesting after 5 to 7 months. The matrix is easy in material selection, low in cost and high in compactness, has a long using period and a good water and fertilizer retention effect, and is applicable to the healthy growth of the Anoectochilus formosanus, the survival rate is high, the labor intensity is low, and good social and economic benefits can be achieved.
Owner:陈洪堤
Chinese yew seedling cultivation technology
InactiveCN101773031AEarly resultsImprove survival rateSeed and root treatmentHorticultureComing outWax
The invention relates to a Chinese yew seedling cultivation technology which comprises the steps of: retting seeds, washing flesh and peeling off, removing wax coat; disinfecting; drying in the sun; storing in a big stone mortar with holes for 12 months; when the seeds crack and expose white parts, dipping the seeds in 0.05% potassium permanganate liquid for disinfecting; washing with clean water; drying in the air and then seeding after the beginning of winter and before the beginning of spring; after seedlings come out, applying 800 multiple thiophanate to stems, leaf backs and leaf surfaces of the seedlings; sun shading; outplanting when the seedlings are 20-30 cm in height, and have ground diameter of 0.3cm and 3-5 lateral branches. The Chinese yew seedling cultivation technology has the advantages of high seedling yield, strong seedling, fast growth and early fruiting; in addition, space among Chinese yew seedlings can be used to plant soybeans to increase grain income, moreover, roots of soybeans can increase biological nitrogen and improve soil for the rooting of Chinese yew, and the soybean seedlings can shade the Chinese yew seedlings for resisting high temperature, thereby improving the survival rate of the Chinese yew seedlings. The invention combines agriculture and forestry, develops ecological agriculture, and achieves both agriculture benefits and forestry benefits.
Owner:株洲市神舟红豆杉苗圃
Drug liquor composition for cutting and reproducing macadimia nut, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101606528AImprove the survival rate of cuttingsHarm reductionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyThiophanate-methyl
The invention discloses a drug liquor composition for cutting and reproducing macadimia nut, a preparation method and an application thereof. The drug liquor composition consists of thiophanate methyl, gibberellin, indolebutyric acid and vitamin B1. The cutting is dipped by the drug liquor composition for cutting seedlings of macadimia nut, so as to promote the cutting to grow roots; and the average cutting planting rate is 96.2% and the cutting planting rate is improved by 144.3% to 164.1%. In addition, the invention can realize strong and regular seedlings and strong root systems, and has low cost, convenient operation and easy scale promotion.
Owner:SOUTH SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Loquat tree organic cultivation method
InactiveCN105638350APlanting is simplePlanting method is simpleCultivating equipmentsDiseaseTrapping
The invention relates to a loquat tree organic cultivation method. The invention relates to the technical field of agriculture, forestry, husbandry, hunting, trapping and fishing, and especially relates to a loquat tree cultivation method. The invention provides a large-volume, high-yield and high-disease-resistance loquat tree organic cultivation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) girdling, branch stretching and injured branch bending are carried out, such that flower bud differentiation is promoted and controlled; wherein a main trunk is girdled by 2-3 strips, and the wound is smeared with a 1:50 solution of 50% thiophanate wettable powder for preventing germ infection; (2) reasonable close planting is carried out, wherein a red soil, loess or loam land with deep soil, good drainage and rich humus is selected for planting; (3) a base fertilizer is heavily applied, wherein 0.5-0.75kg of lime, and 1-1.5kg of a calcium, magnesium and phosphorous fertilizer are filled in each pit; (4) flower bud differentiation is promoted and controlled through fertilizer and water management; through June to August, no nitrogen fertilizer is applied, and phosphorous and potassium fertilizes are approximately added; and (5) trimming and pruning are carried out, wherein after field planting of the loquat trees, topping is carried out on a main trunk at a place 50cm from the ground for determining the height of trunk.
Owner:申茂军
Bactericide compsns, with synergistic effect
A composite bactericide with synergistic action for preventing and eliminating the diseases and pests of fruit tree, grapevine, vegetables, watermelon, wheat and rice is prepared from tebuconazole (2-25 Wt%), thiophanate-methyl (10-75), assistant (3-25) and filler (10-70).
Owner:日曹达贸易(上海)有限公司
Preserving method of bananas
InactiveCN103004953AImprove corrosion resistanceExtended shelf lifeFruits/vegetable preservation by heatingFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingThiophanateBiology
The invention discloses a preserving method of bananas. The method comprises the steps of (1) selecting banana fruit which is fresh and green in fruit color and free from diseases and pests, wherein the mechanically damaged fruit does not exceed 30%, and the maturity is 8-9; and placing the fruit in hot water to clean; (2) placing the cleaned bananas in a preservative liquid and soaking for 5-10min, wherein the preservative liquid comprises 2-5 parts of thiophanate and 20-50 parts of encalyptus robusta liquid; and (3) after drying, packaging and sealing with a preservative bag, and placing in an environment at 10-15 DEG C and storing. The preservative liquid provided by the invention is a mixed liquid of thiophanate and the encalyptus robusta liquid, so that not only is bacteria on the banana eliminated, but also the corrosion resistance of the bananas is improved, and the preservative period of the bananas is prolonged.
Owner:高鑫
Method of transplanting camphor tree
InactiveCN107114188APrevent drynessPromote hydrationFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsDeltamethrinObserved Survival
The invention discloses a method of transplanting a camphor tree. The technical solution thereof has the following key points: the method comprises the process of preparation before transplanting, digging the seedlings, trimming before transplanting, seedling transportation, digging planting holes, sterilization and insecticidal treatment on the planting holes, transplanting, management after transplanting, and spraying of mixed thiophanate and deltamethrin in one week after the transplanting. A straw rope can maintain sufficient water of the seedlings in the seedling digging process, thereby avoiding the problem of dry roots due to lack of water in the transportation process; the seedlings can be protected well, and then the survival rate after transplanting is high.
Owner:浙江天地环境建设有限公司
Polygonum multiflorum cultivating method
InactiveCN104303782AImprove survival rateIncrease productionPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsDry weightLolium multiflorum
The invention discloses a polygonum multiflorum cultivating method and belongs to the technical field of plant cultivation. The polygonum multiflorum cultivating method includes steps of selecting and preparing land soil, selecting cuttage twigs with 2-4 knots, soaking rooting agent and cutting the cuttage, fertilizing respectively when seedlings grow to the next May and the next September, putting up a support when the seedlings grow to certain height, spraying 800-times solution of 50% of thiophanate wettable powder and 800-1000-times solution of 50% of carbendazim wettable powder when plants have leaf spot diseases; spraying 800-1000-times solution of 70% of thiophanate wettable powder to stems when the roots have root rot; harvesting finally. By the polygonum multiflorum cultivating method, yield of polygonum multiflorum is remarkably increased to 1200-1500kg / mu (dry weight). Besides, the polygonum multiflorum cultivating method is simple and low in production cost.
Owner:郭燕平
Taipei fritillary bulb planting method
InactiveCN103597987AReduce pests and diseasesAvoid harmFertilising methodsPlant protectionChlordaneMonopotassium phosphate
The invention relates to a Taipei fritillary bulb planting method. The Taipei fritillary bulb planting method comprises selecting and leveling sandy soil at the altitude of 2000 to 5000 m, making beds, planting, disinfecting, timely covering soil after the Taipei fritillary bulbs damp off and starting digging four years after seeding. The Taipei fritillary bulb planting method has the advantages of reducing diseases and insect pests of the Taipei fritillary bulbs; avoiding rust diseases and avoiding plants from being damaged by wireworms due to the fact that the organic fertilizer and the soil in the planting region are sterilized through carbendazim and added chlordane emulsifiable concentrate and 50 % of the thiophanate 1000 times liquid is sprayed in the planting region during the growing process of the Taipei fritillary bulbs; improving yield and quality of seed and commodity bulbs.
Owner:巫溪县瑞雪药材种植有限责任公司
Germicide composition containing thiophanate and tricyclazole
ActiveCN101103726AExpanded bactericidal spectrumChemically stableBiocideFungicidesBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTPlant disease
The invention relates to a germicide combination which comprises thiophanate-methyl and tricyclazole, which has strong antibacterial and germicidal activity, and is applicable for the agricultural chemical protection field. The invention is mainly used for various diseases prevention and cure of the rice and has protection and cure functions to the rice, and the germicide combination is different from the prior other germicide combinations. The active ingredients of the invention are made from thiophanate-methyl and tricyclazole; the percentage of the weight distribution of the raw materials of the germicide combination is that: the thiophanate-methyl is from 20 percent to 50 percent; the tricyclazole is from 10 percent to 45 percent; the additive agent is ranged from 5 percent to 70 percent. The germicide combination can be made into wettable powder and suspension. The invention can be applicable for the various diseases prevention and cure of the rice.
Owner:日曹达贸易(上海)有限公司
Lychee preservative
InactiveCN101766211AReasonable formulaGood fresh-keeping effectFruit and vegetables preservationSulfatePreservative
The invention discloses a lychee preservative which is mixed with lime, activated clay, potassium sorbate, calcium stearate, thiophanate, houttuynia, ferrous sulfate, tea polyphenols, potassium sorbate and water. The preservative has the advantages of reasonable prescription, good preservation effect, long preservation time and low production cost. When in use, fruit is put into the preservative of the invention for 3 to 5min.
Owner:蒋进军
Thiophanate methyl inclusion complex pesticide preparation
InactiveCN1448053AGood water solubilityReduce usageBiocideAnimal repellantsThiophanate-methylCyclodextrin Derivatives
The farm chemical preparation of thiophanate-methyl clatherate features that thiophanate-methyl molecules are included inside cyclodextrin with cyclic molecular structure. The said cyclodextrin may be any one kind of cyclodextrins or derivatives or their mixture. Cylcodextrin has many hydroxyl groups distributed in the outer part and thus high hydrophilicity and water solability, so that including water insoluble thiophanate-methyl with cyclodextrin can raise the water solability, stabilization, emulsifying capacity and germicidal effect of the farm chemical.
Owner:西安敬业生物药物科技有限公司
Insect control method for improving yield of Cuiguan pears
InactiveCN103404395AIncrease productionIncrease incomeCultivating equipmentsPlant protectionPest controlHorticulture
The invention relates to an insect control method for improving the yield of Cuiguan pears. The method comprises the following steps that (1) after Cuiguan pear blossoms fall, leave spraying is continuously carried out three to five times every five to ten days. The leave spraying medicament forming method comprises the steps that after 15% triadimefon and 50% carbendazim are mixed according to the proportion of 3:1, 1000-fold to 1500-fold water is used for attenuation to obtain leave spraying medicaments; (2) before the Cuiguan pears are sleeved with bags, 500-fold captan is applied to the Cuiguan pears once, 2000-fold pyrethroid pesticides are applied to the Cuiguan pears once five days later, and 1000-fold thiophanate is applied to the Cuiguan pears once three days later. The insect control method effectively carries out comprehensive insect control, improves the yield of the Cuiguan pears by 5-10%, and greatly increases incomes of fruit growers.
Owner:JURONG CITY HOUBAI TOWN YUQIN FRUIT COOP
Medicine for silkworm and its preparation method
InactiveCN1353933AGreat efficacyNo pollution in the processBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyDisease
The present invention discloses a silkworm medicine for preventing and curing commonly encountered diseases of silkworm and its preparation method. Said invented medicine preparatino contains (by weight portion) 6-8 portions of carbendazim powder and 2-4 portions of thiophanate-methyl powder. The above-menioned materials can be made into powder dosage form. Also, they can be respectively dissolved in dilute acetic acid and ethyl alcohol so as to obtain liquid dosage form. Said invented medicine is low in toxicity, harmless and pollutionless, and possesses the unique killing action for curing white muscardine, grasserie and others.
Owner:唐永琦
Method for controlling diseases and pests of peach trees
The invention discloses a method for controlling diseases and pests of peach trees. The method comprises the following steps: using nano sulfur powder before germination; using a mixture of captan-tebuconazole, imidacloprid and cyhalothrin before blossom; using a mixture of butyl sulfur imidacloprid, abamectin bifenthrin, fluorine aliette and flower tanghinin after blossom; using a mixture of thiophanate methyl, quinolinone, carbosulfan, cyhalothrin and flower tanghinin in the young fruit period; using a mixture of PBO (penicillin in beeswax) (fruit tree chemical promotive and control agent), flower tanghinin, captan-tebuconazole and chlorantraniliprole before fruit picking; using a mixture of abamectin bifenthrin, fluorine aliette and carbosulfan after fruit picking and trimming; and performing final-period management. The method for controlling the diseases and pests of the peach trees, provided by the invention, is good in control effect and strong in pertinence and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:ZHENYUAN ZUIMEI FRUIT IND CO LTD +1
Tree wound treating agent
InactiveCN108522563AImprove frost resistanceNot easy to freezeBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant hormoneVitamin C
The invention relates to the technical field of landscaping, in particular to a tree wound treating agent. The tree wound treating agent is prepared from the following components: activated aloe dry powder, activated clay, algin, rapin, vitamin C, a preservative, chitosan quaternary ammonium salt, glycerinum, plant hormones, a bactericide and a permeable regulator, wherein potassium sorbate is used as the preservative; the plant hormones are prepared from gibberellins, heteroauxin and cytokinin; the bactericide is prepared from streptomycin, thiophanate methyl and difenoconazole of which the content ratio is 4:3:3; glucose or sodium chloride is used as the permeable regulator. The tree wound treating agent disclosed by the invention adopts biogel prepared from aloe as a drug carrier, is capable of providing a good moisturizing and air-permeable environment for a wound, and is convenient to stably and sustainably release a drug; healing of a tree wound is promoted, and the healing timeis shortened.
Owner:合肥谦尧建筑装饰工程有限公司
Tissue-culture rapid propagation method for arundina graminifolia
InactiveCN105475129AImprove regenerative abilityMaintain genetic stabilityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsArundinaThiophanate-methyl
A tissue-culture rapid propagation method for arundina graminifolia is characterized by comprising step 1, selecting and disinfecting explant materials, concretely selecting a high bud as an explant, and performing disinfection for usage; step 2, performing inducing culture to obtain adventitious bud, concretely, cutting the top of the high bud, inoculating an adventitious bud culture medium with the high bud, so as to obtain the adventitious bud through inducing; step 3, performing propagation culture to clustered buds, concretely, inoculating a clustered-bud induction medium with the adventitious bud, so as to obtain the clustered buds, and then inoculating a propagation medium with the clustered buds, so as to obtain a clustered-bud block mass; step 4, performing seedling strengthening and rooting culture, concretely, cutting the large clustered-bud block mass obtained in the step 3 into small block masses, then inoculating the seedling-strengthening rooting medium with the small clustered-bud block masses obtained in the step 3, wherein the small clustered-bud block mass grow vigorously and new roots are grown; and step 5, performing seedling hardening and domestication transplanting, when a seedling grows to 4-8 cm and has 1-3 roots, performing seedling-hardening culture, then taking the seedling out, immersing in a thiophanate methyl solution, and finally transplanting by using moss. The variation probability of arundina graminifolia during subculture proliferation is reduced.
Owner:三明市农业科学研究院
Ochrobactrum and biological agent thereof, preparation method and application
ActiveCN105238729AEfficient degradationEasy to useBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses ochrobactrum and a biological agent thereof, a preparation method and application. The ochrobactrum is ochrobactrum intermedi. The biological agent with the ochrobactrum as an active ingredient is prepared by conducting test tube culture and liquid fermentation culture on the ochrobactrum intermedi. The preparing method of the biological agent with the ochrobactrum as the active ingredient comprises the steps of test tube culture and liquid fermentation culture. The application refers to the application of the biological agent with the ochrobactrum as the active ingredient in repairing polluted soil with thiophanate methyl residues and in degrading and removing the thiophanate methyl residues in crops. The thiophanate methyl residues degrading bacteria prepared through fermentation of strains TP206 can be widely used for eliminating thiophanate methyl residue pollution in the soil, can also be directly sprayed to the surface of the soil or surfaces of the crops in agricultural production, can effectively degrade and remove the thiophanate methyl residues and are convenient to use and low in cost.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Novel disinfectant containing organic copper
InactiveCN102318628ANo pollution in the processHas a systemic bactericidal effectBiocideFungicidesSide effectDisinfectant
The invention relates to a novel disinfectant containing organic copper, which comprises the components in percentage: 40% to 50% of thiediazole copper, 20% to 30% of thiophanate-ethyl, 20% to 30% of DA-6 (diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate), and 10% to 20% of sodium phenoxyacetate. The novel disinfectant overcomes the defects of the traditional disinfectant, has improved disinfection efficiency and small toxic or side effect and can be mixed with an insecticide. The novel disinfectant containing organic copper has the disinfection and insecticidal actions and the function of plant hormone and can be used for enhancing yield and the content of nutrient components such as protein, amino acids, vitamins, sugar, carotene and the like of products and improving product quality.
Owner:韦文礼
Single-bud planting method of sugarcane
InactiveCN105103834ALess susceptible to infectionImprove germination ratePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsFertilizerThiophanate
The invention discloses a single-bud planting method of sugarcane. The single-bud planting method comprises the steps of (1) selecting seeds; (2) peeling sugarcane leaves: peeling leaf sheaths of sugarcane seeds first before the seeds are chopped after the seeds are selected, chopping off tails of lower parts from growing points for 4 to 5 cm and old stems away from the ground for 80 to 100 cm, and using most middle sugarcane stems as the sugarcane seeds; (3) chopping the seeds: removing bad buds and wormy buds; (4) soaking the seeds and disinfecting: soaking the seeds with 800 to 1000 times thiophanate liquid, completely soaking seed surfaces for one minute, and then taking out; (5) placing the seeds: placing four buds per meter for the seeds with strong tillering ability, i.e. placing one bud every 25 cm, and placing five buds per meter for the seeds with weak tillering ability, i.e. placing one bud every 20 cm, wherein the sugarcane buds are placed upwards or towards both sides when the seeds are placed, and the sugarcane buds cannot be placed downwards; (6) applying base fertilizers; (7) covering mulching films; (8) inspecting seedlings. The single-bud planting method of the sugarcane has the advantages of high budding rate and difficulty in disease infection, and the yield of the sugarcane can reach more than eight tons per mu in normal years.
Owner:GUANGXI KANGFENG TECH DEV CO LTD
Cultivation method for purple sweet potatoes and method for processing purple sweet potato powder
InactiveCN104335811APromote expansionImprove processing qualitySeed and root treatmentSoil-working equipmentsThiophanate-methylHorticulture
The invention relates to a cultivation method for purple sweet potatoes and a method for processing purple sweet potato powder and belongs to the technical fields of sweet potato cultivation and processing. A new cultivation method is obtained by changing the concentration of thiophanate methyl water solution for soaking seeds, sweet potato seedling planting time and density, fertilizer types and consumption, and types and concentration of inhibitors. According to the cultivation method, acre yield of fresh potatoes is more than 2,200kg, the large medium sized tuber rate is higher than 90.3 percent, anthocyanin content is more than 120mg / 100g, and starch content is more than 31.1 percent; the yield for preparing the purple sweet potato powder from the purple sweet potatoes harvested by the cultivation method is higher than 41.6 percent. Methods of cooking, mashing, drying and pulverizing are adopted, sweet potatoes are sliced, and the sliced sweet potatoes are blanched, cooled, cooked, mashed, dried, pulverized and screened to form the purple sweet potato powder, the defect of poor cluster caused by improper color protection in the traditional process is overcome, and the processed product is bright in color, high in dispersibility and high in water absorption.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Sweet potato southern blight prevention method
InactiveCN103340123AHas a therapeutic effectEffective controlBiocideFungicidesMetalaxylThiophanate-methyl
The invention discloses a sweet potato southern blight prevention method. Metalaxyl hymexazol 800-1000 times liquid with the mass percent concentration of 30% is adopted to carry out pesticide spraying on the periphery of a damaged plant, and the spraying is carried out for 2-3 times and is carried out every 5-7 days; or triadimefon with the mass percent concentration of 25%, 600-800 times diluted root rot germicide and root-irrigation thiophanate with the mass percent concentration of 50% are utilized alternately for 2-3 times, and application of the three pesticides is carried out every 7-15 days; or 800 times thiophanate-methyl with the mass percent concentration of 70% is adopted to irrigate the root, and root irrigation is carried out for 2-3 times and is carried out every 10 days. Proper pesticides and a using method are screened out, plants where sweet potato southern blight is generated can obtain effective prevention, and loss of the plants can be greatly reduced. According to the sweet potato southern blight prevention method, sources of materials are wide, the materials are easy to obtain, the using method is simple and easy to achieve, cost is low, and using effects are good.
Owner:贵州省生物技术研究所
Agricultural bactericidal composition
The invention relates to a bactericidal composition comprising the effective components of (A) and (B), wherein the (A) is ethirimol or bupirimate, the (B) is one of sanmate, benomyl, thiophanate-methyl or thiabendazole, and the mass proportion of the A to the B is 50:1-1:50. The composition has an obvious synergistic action and can be used for preventing and treating diseases on crops, such as fruit trees, cotton, paddy, wheat, vegetables and the like, especially for preventing and treating fungoid diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com