Light emitting diode
A technology of light-emitting diodes and light-emitting surfaces, applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems of weakening light-emitting efficiency and low light-extraction efficiency, and achieve the effects of reducing lateral propagation, increasing light output, and increasing forward efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
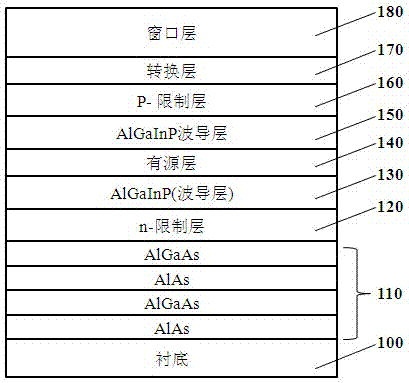
[0051] Please see attached figure 2 The quaternary light-emitting diode of the first preferred embodiment of the present invention may include, from top to bottom: a substrate 100, a combined DBR structure 220, an n-type confinement layer 120, a waveguide layer 130, an active layer 140, waveguide layer 150, p-type confinement layer 160, Al a Ga (1-a) In b P gradient layer 190 , GaP window layer 180 .
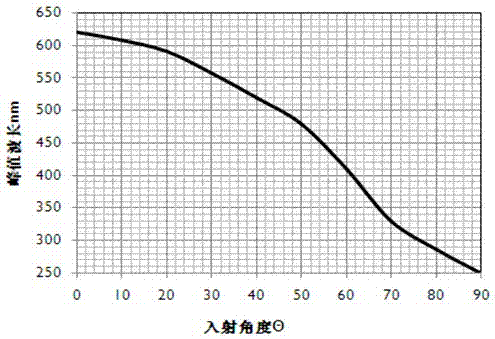
[0052] Wherein, the substrate 100 may be a GaAs substrate. The combined DBR structure 220 is composed of N groups of DBR sub-layers, where N≥3 is better, and the preferred value is 3~5. The corresponding wavelength of each DBR sub-layer is adjusted to lengthen the central reflection wavelength to obliquely incident the active area. Light is reflected efficiently. The active layer 140 is a multi-quantum well structure, wherein the barrier layer is Al a1 Ga 1-a1 InP (0.1≤a1≤0.3), the well layer is Al a2 Ga 1-a2 InP, where a1>a2, the materials of the n-type confinement l...
Embodiment 2
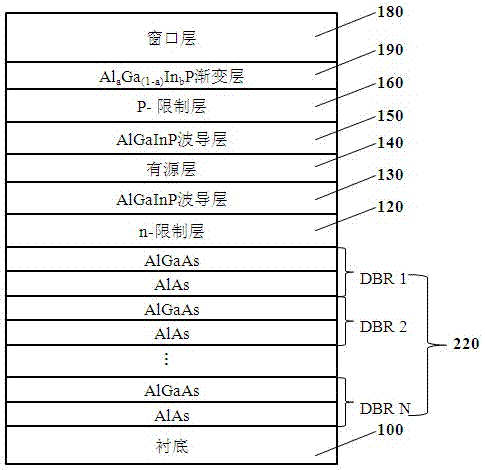
[0064] Please see attached Figure 5 , the quaternary light-emitting diode of the second preferred embodiment of the present invention may include, from top to bottom: a substrate 100, a DBR structure 110, an n-type confinement layer 120, an Al y Ga (1-y) InP graded dielectric waveguide layer 200, waveguide layer 130, active layer 140, waveguide layer 150, Al y Ga (1-y) InP graded dielectric waveguide layer 210, p-type confinement layer 160, Al a Ga (1-a) In b P gradient layer 190 , GaP window layer 180 .
[0065] In this embodiment, conventional materials for the DBR structure 110 , n-type confinement layer 120 , active layer 140 , and p-type confinement layer 160 are selected as required. Form Al y Ga (1-y) InP graded dielectric waveguide layer, Al is formed between the p-type confinement layer and the window layer a Ga (1-a) In b The P graded layer 190 forms a graded refractive index interface so as to reduce the lateral propagation of obliquely incident light an...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Please see attached Figure 6 , the quaternary light-emitting diode of the third preferred embodiment of the present invention may include, from top to bottom: a substrate 100, a combined DBR structure 220, an n-type confinement layer 120, an Al y Ga (1-y) InP graded dielectric waveguide layer 200, waveguide layer 130, active layer 140, waveguide layer 150, Al y Ga (1-y) InP graded dielectric waveguide layer 210, p-type confinement layer 160, Al a Ga (1-a) In b P gradient layer 190 , GaP window layer 180 .
[0070] The combined DBR structure 220 can refer to the method disclosed in Embodiment 1, and set the central reflection wavelength of each DBR sub-layer according to the specific light emission wavelength λ of the active layer and the refraction layer of the material of the DBR layer. al y Ga (1-y) InP graded dielectric waveguide layers 200, 210 and Al a Ga (1-a) In b The P gradient layer 190 can refer to the second embodiment.
[0071] In this embodiment,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com