150°C heat-resistant cross-linked low-smoke halogen-free electronic wire material and manufacturing method thereof
An electronic wire, heat-resistant technology, applied in the field of 150 ℃ heat-resistant cross-linked low-smoke halogen-free electronic wire and its production, can solve the problem that tensile strength and elongation at break cannot meet the requirements of practical applications, elongation at break and The problems such as the unsatisfactory elongation rate under load, the reduction of tensile strength and elongation at break, etc., are beneficial to commercial promotion, low cost, and improved stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-18
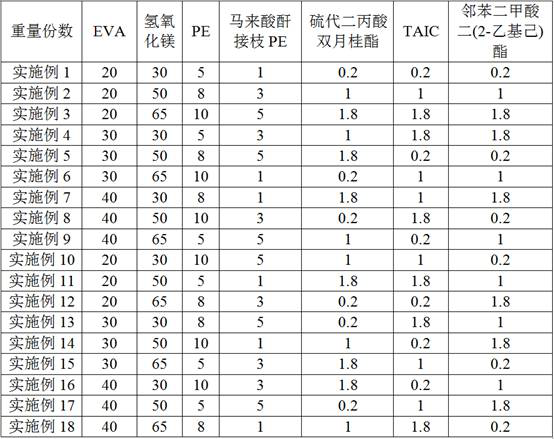
[0077] 150°C heat-resistant cross-linked low-smoke halogen-free electronic wire material, 18 sets of experiments were carried out according to the orthogonal experiment method, in which the components and weight ratios included in Example 1-Example 18 are listed in Table 1.
[0078] Table 1 Components and weight ratios included in Examples 1-18, wherein the particle size of magnesium hydroxide is 0.8 micron-1.2 micron, and the magnesium hydroxide is produced by chemical synthesis, and the purity is analytically pure.
[0079]
Embodiment 19
[0112] The method for making 150°C heat-resistant cross-linked low-smoke halogen-free electronic wire material, the method for preparing implementation 1 includes the following steps:
[0113] S1 Weigh each component according to the weight ratio and pour it into a high-speed mixer for stirring and preheating, and fully mix the components; the host speed is set at 340 rpm, and the preheating is divided into three stages. The stage temperature is 110°C, the second stage temperature is 120°C, and the third stage temperature is 130°C.
[0114] S2 Plasticize at constant temperature first, and then gradually lower the temperature to enter the next process; the plasticizing process is divided into six stages, the fourth to sixth stages maintain a temperature of 140°C, the seventh stage temperature drops to 130°C, and the second stage Eight stages are at 120°C and the ninth stage is at 110°C.
[0115] S3 Raise the temperature to form, granulate, and sieve to obtain the white electro...
Embodiment 20-36
[0120] The method for making 150°C heat-resistant cross-linked low-smoke halogen-free electronic wire material, Examples 20-36 are the preparation methods of Examples 2-18 respectively, the difference from Example 19 lies in the weight of each component weighed different.
[0121] The preparation method of Comparative Examples 1-3 is the same as that of Example 19, except that the weight of each component is different.
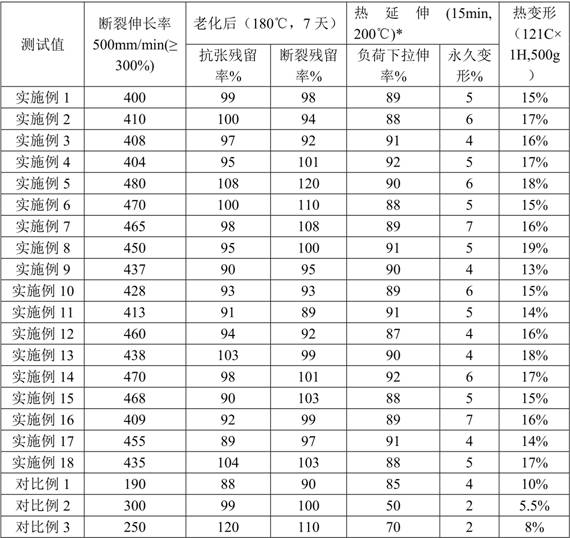
[0122] Examples 1-18 and Comparative Examples 1-3 were tested to obtain the following data.
[0123]
[0124] *Sample after cross-linking
[0125] Among them, the test method for elongation at break is ASTM D638, the test method for tensile residual rate, residual rate at break and thermal deformation after aging is UL1581, and the test method for thermal elongation is IEC 60811-2-1.
[0126] Can find by above test, in the mechanical performance test of the present invention, tensile residual rate and fracture residual rate are all obviously higher than 8...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com