Electric driving device
一种电动驱动、电动机的技术,应用在机电装置、电动组件、冷却/通风装置等方向,能够解决磁传感器磁检测误差等问题,达到减小检测误差、抑制性能的下降、提高自由度的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
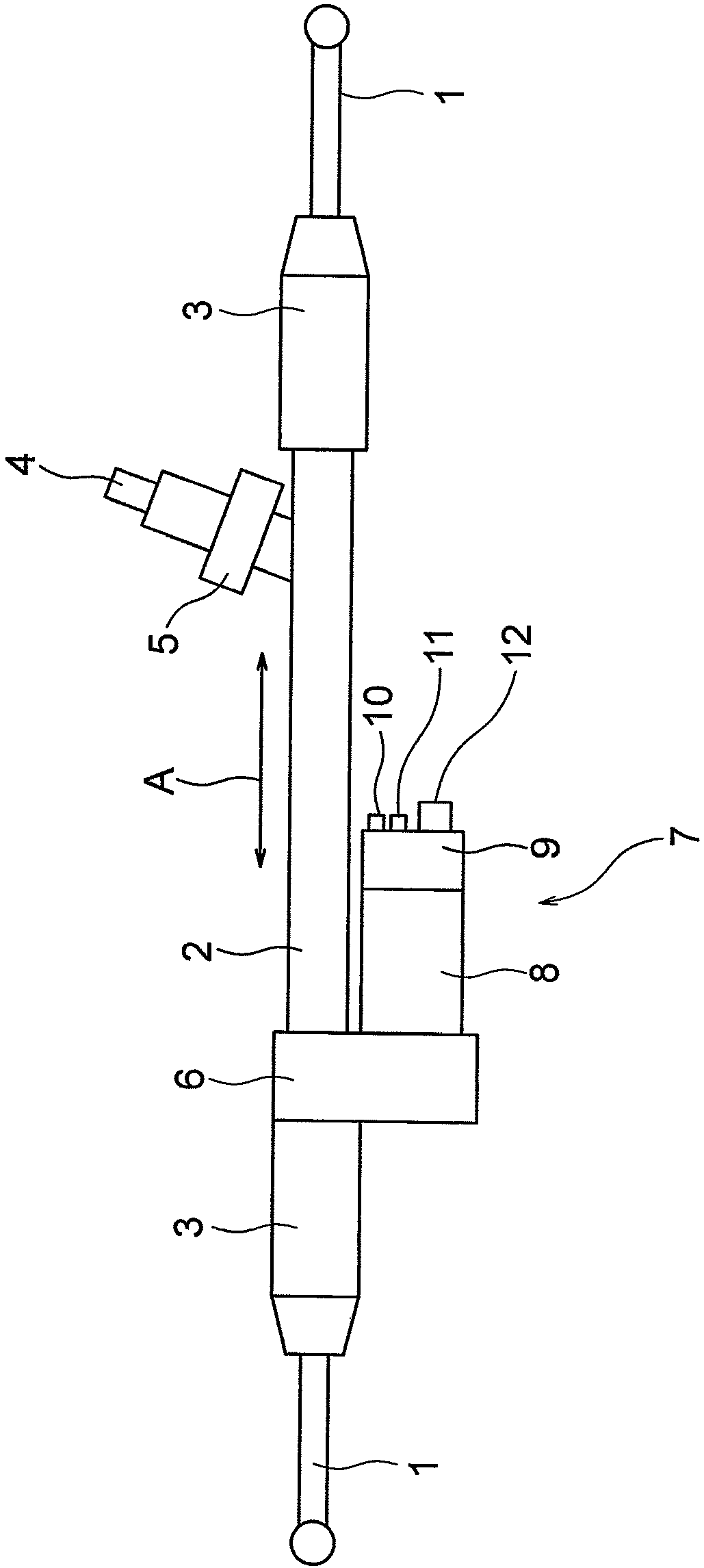
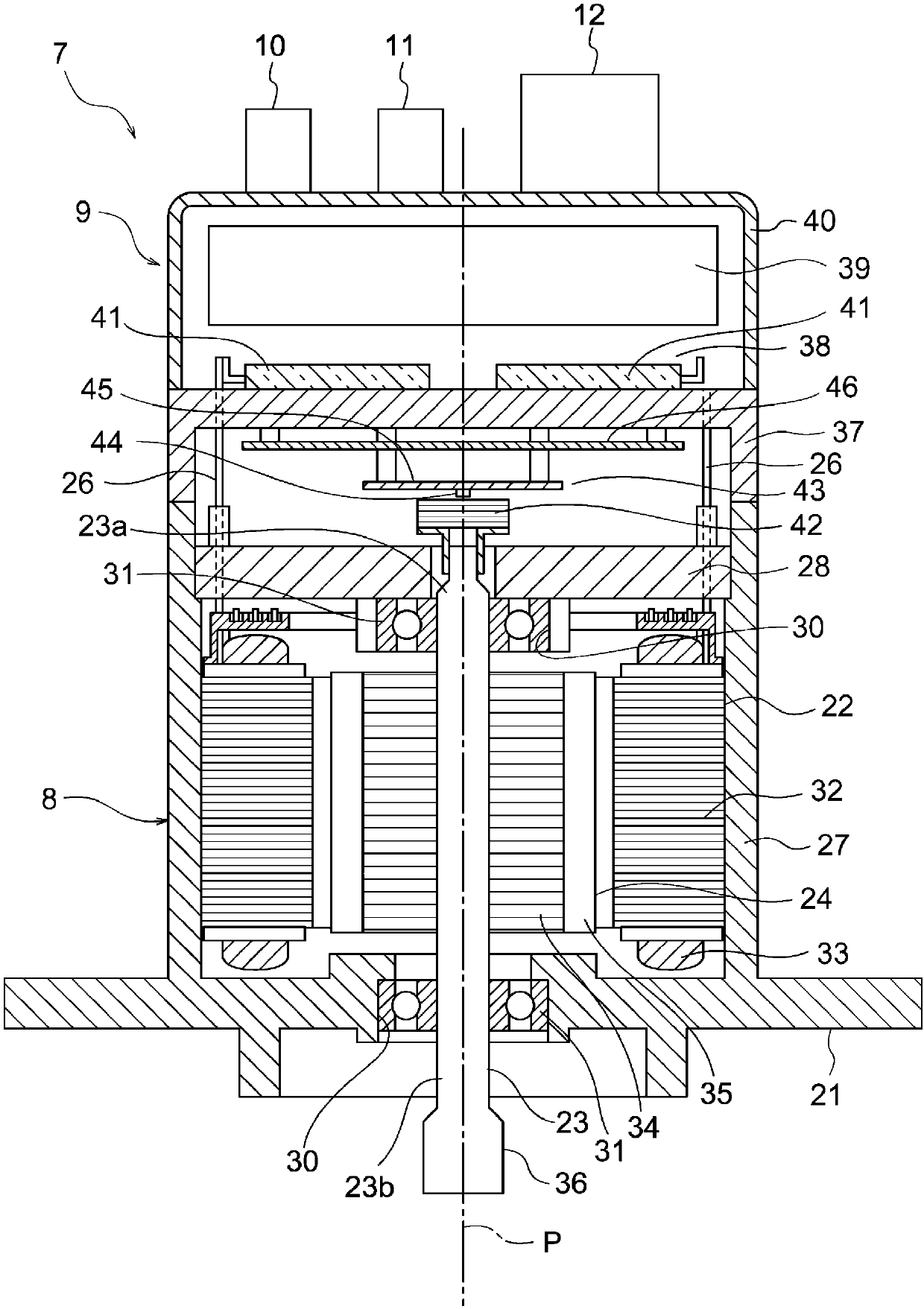
[0034] figure 1 It is a configuration diagram showing the electric power steering device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The electric power steering device according to the present embodiment is, for example, a vehicle electric power steering device mounted on a vehicle such as an automobile. A rack shaft (not shown) accommodated in the case 2 is connected between the pair of link rods 1 . The joints between the respective connecting rods 1 and the rack shafts are accommodated in rack boots 3 that prevent foreign matter from entering the electric power steering apparatus. The rack shaft is connected to shaft 4. When the driver turns the steering wheel (not shown), the torque generated by the steering is transmitted to the rack shaft via the steering shaft (not shown) and the shaft 4 . The shaft 4 is provided with a torque sensor 5 that detects a torque generated by turning the steering wheel. Furthermore, an electric drive 7 is arranged on the rack shaf...
Embodiment approach 2
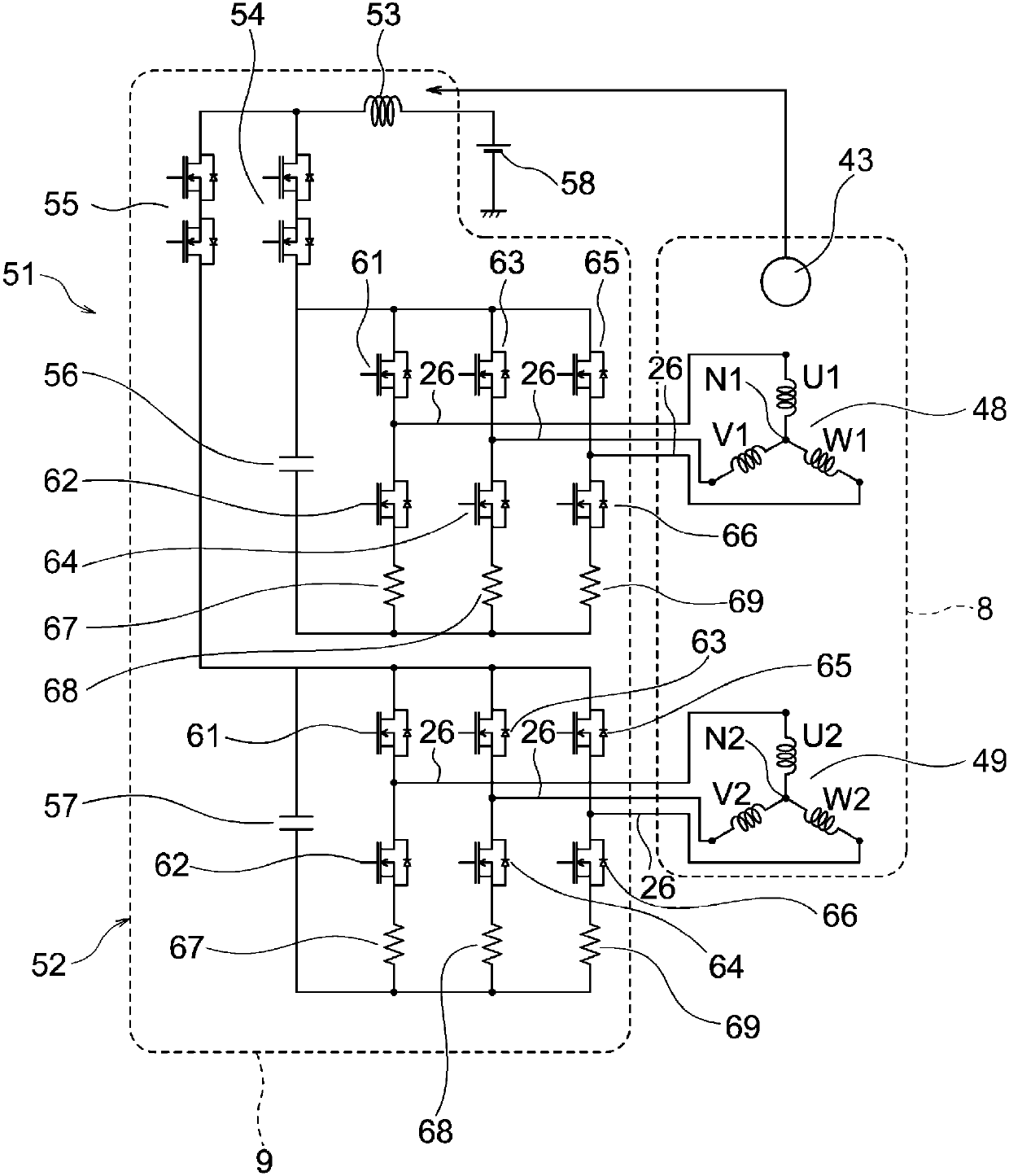
[0092] In Embodiment 1, the current phase difference of each power supply line 26 is 0° between the U1 phase and the U2 phase, between the V1 phase and the V2 phase, and between the W1 phase and the W2 phase. However, it may also be between the U1 phase and the U2 phase Between phases, between V1 phase and V2 phase, and between W1 phase and W2 phase, the current phase difference of each power supply line 26 is set to 30°. That is, in the present embodiment, the current phases of the power supply lines 26 differ by 30° between the U1 phase and the U2 phase, between the V1 phase and the V2 phase, and between the W1 phase and the W2 phase. Other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0093] Next, in this embodiment, the positional relationship between each power supply line 26 and the rotation sensor 44 is Figure 7 The influence of the magnetic field from each power supply line 26 on the rotation sensor 44 at the time of the positional relationship will be describe...
Embodiment approach 3
[0101] In Embodiment 1, electric current flows through each feeding line 26 , but only a part of the current flowing through each feeding line 26 may always be stopped. In this embodiment, among the currents flowing through the power supply lines 26 of the U1 phase, V1 phase, W1 phase, U2 phase, V2 phase, and W2 phase, the current flows through the power supply lines 26 of the U1 phase, V1 phase, and W1 phase, And only the current flowing through the power supply lines 26 of the U2 phase, the V2 phase, and the W2 phase is always stopped. That is, in the present embodiment, in the first and second three-phase AC coils 48 and 49, only the inverter circuit 38 supplies three-phase power to the first three-phase AC coil 48, and the slave inverter circuit 38 The power supply to the second three-phase AC winding 49 is always stopped. Other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0102] Next, in this embodiment, the positional relationship between each power supply line ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com