Method for guiding a crack in the peripheral region of a donor substrate
A substrate and donor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, fine working devices, etc., can solve problems such as edge effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
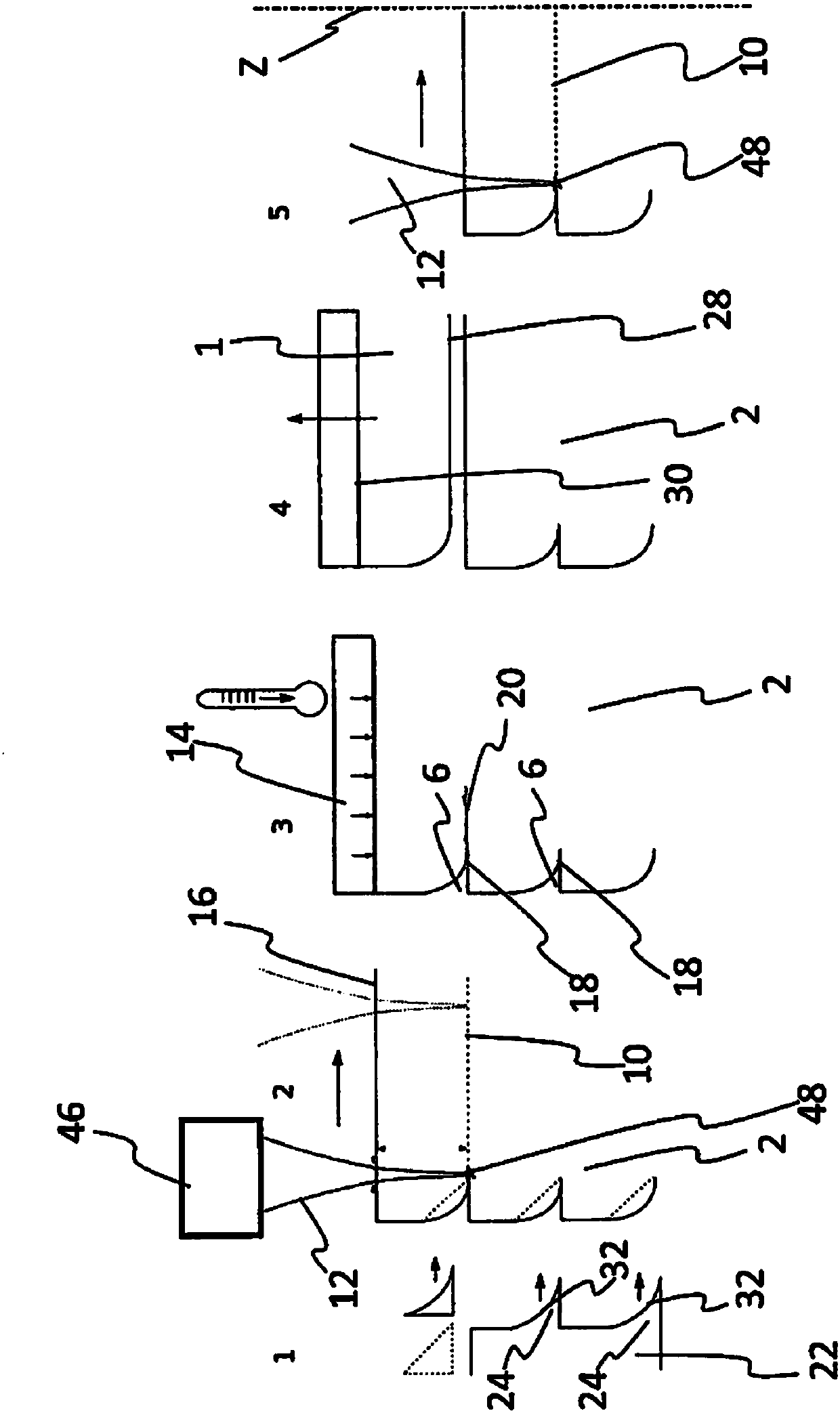
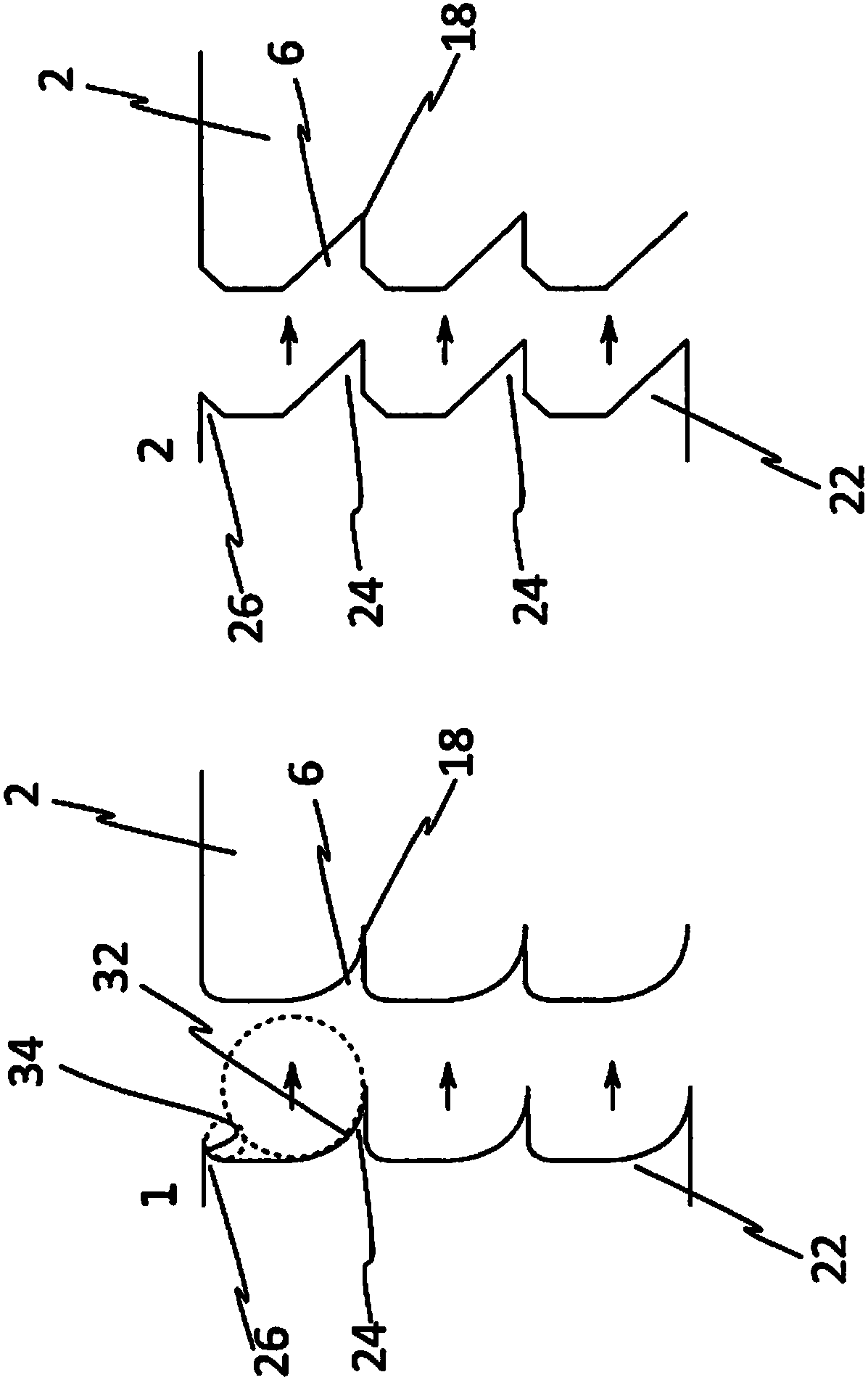
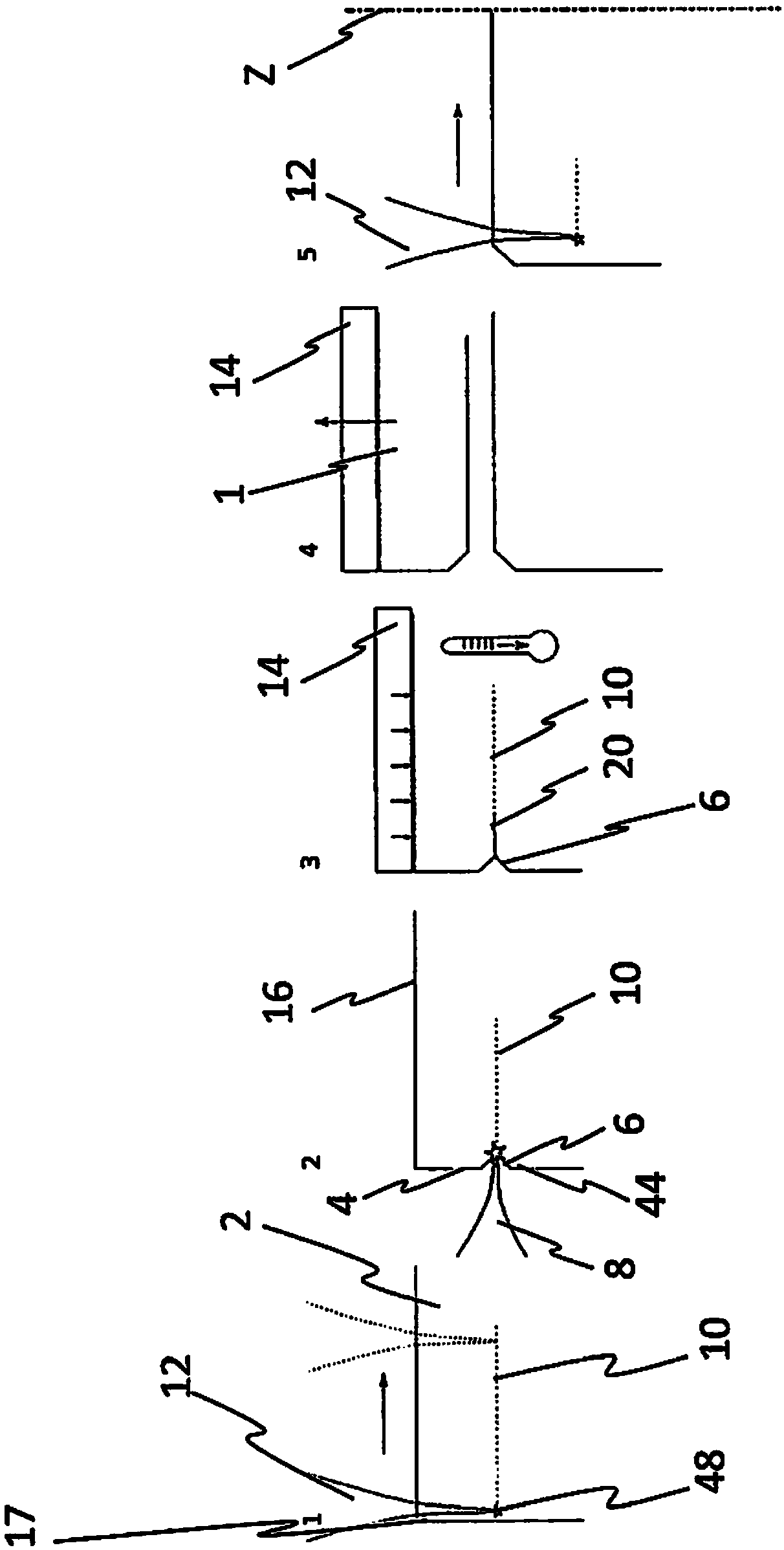
[0048] figure 1 Shown are 5 views by which an example of solid sheet fabrication or wafer fabrication according to the invention is shown. See figure 1 A grinding tool 22 is shown here, which has two machining parts 24 spaced apart from one another, which each form a main grinding surface 32 . The main grinding surface 32 is designed in such a way that it produces a recess 6 in the donor substrate 2 . The grinding tool 22 is preferably designed as a rotary grinding tool or as a belt grinding tool.
[0049] figure 1 view of figure 2 A donor substrate 2 is shown in which a recess 6 has been produced by means of a grinding tool 22 . In this case, the recesses 6 are preferably evenly spaced apart from one another in the longitudinal direction of the donor wafer 2 , wherein it is also conceivable for the distances to be of different sizes. according to figure 2 In the second view in FIG. 1 , modification 10 is also produced in donor substrate 2 by means of laser device 46 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com