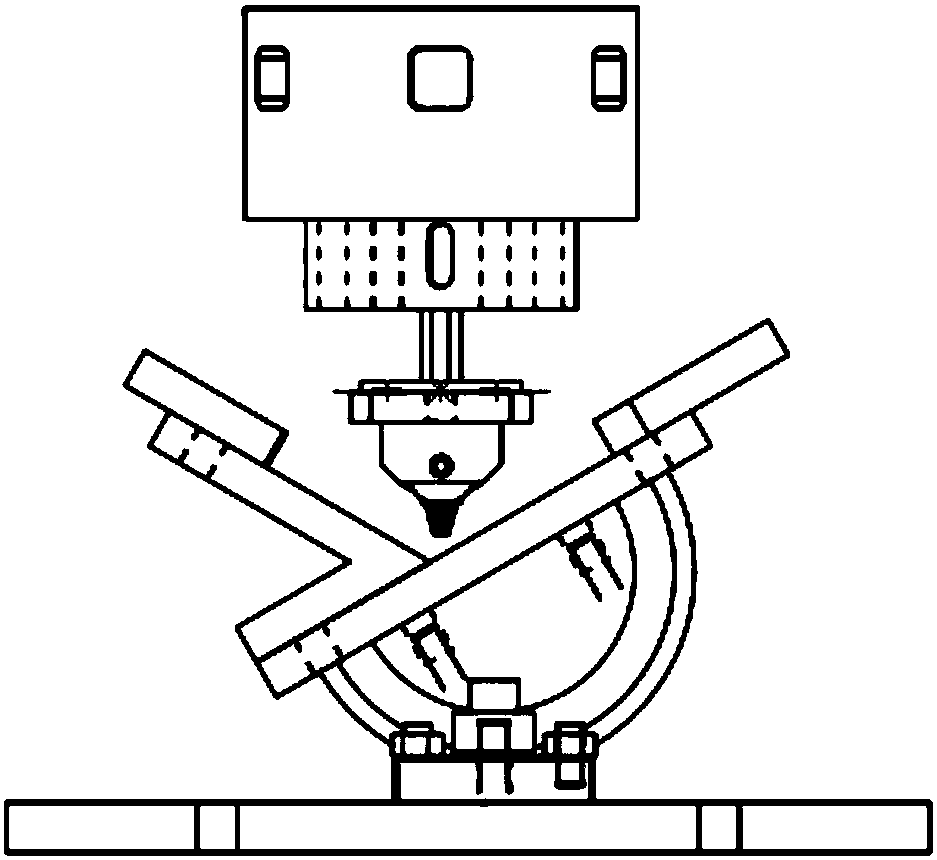
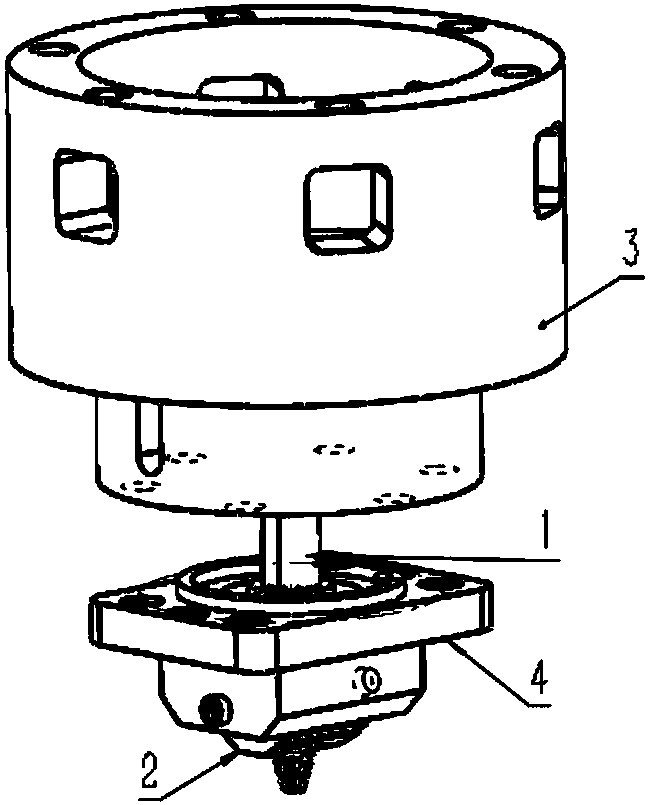
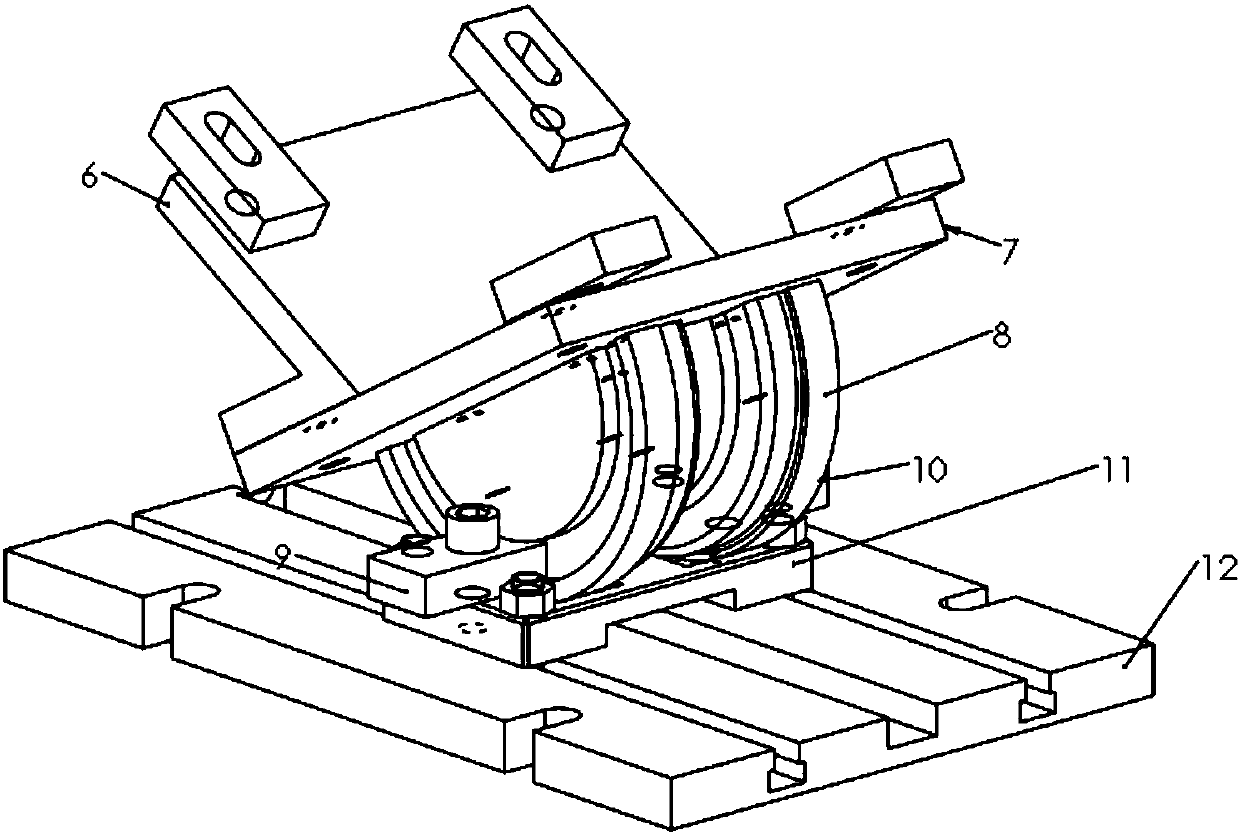
Stationary shoulder friction stir welding device and method for variable-angle fillet joints
A static shoulder and fillet joint technology, applied in the field of friction stir welding, can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining defect-free welded joints, uneven temperature along the plate thickness, overheating of the weld surface, etc., to achieve repeated use and easy installation Sealing stack rings and post-weld cleaning, performance-enhancing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0054] Based on the above device, a static shoulder friction stir welding method for fillet joints is provided.
[0055] In the welding example, the thickness of the aluminum alloy plate is 17mm, and the angle joint is 120°. The static shoulder stirring head is designed as follows: the static shoulder transition fillet radius is 8mm, the root diameter of the stirring needle is 16mm, the length is 16mm, the cone angle is 30°, and the root is strengthened. The shoulder diameter is 22mm and the length is 6mm.
[0056] Step 1, use set screws to assemble and fix the stirring needle 1 on the knife handle of the machine head, then assemble and fix the first rigid connection device 3 and the second rigid connection device 4 in sequence, and then install the sealing stack ring 5 into the static The installation groove 22 of the shaft shoulder 2, then put the stationary shaft shoulder 2 into the rigid connection device 4, tighten the set screw, and press into the round holes 19, 20 on t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com