Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, production method and applications
An ultra-high molecular weight, polyethylene technology, applied in the field of copolymerized ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, can solve the problem that it is difficult to obtain ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene with good chain transfer characteristics, does not reach the conventional level of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, and the height is only 8.72 dl and other problems, to achieve the effect of easy molding, processing and application, insignificant activity attenuation, low loss of wear resistance and impact strength performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0092]According to the Chinese patent CN200910210988.3, the preparation method of the preferred supported non-metallocene catalyst used in the present invention is disclosed, which includes the following steps: dissolving the magnesium compound and the non-metallocene ligand in a solvent to obtain the magnesium compound solution steps; mixing the porous carrier optionally subjected to thermal activation treatment with the magnesium compound solution to obtain a mixed slurry; drying the mixed slurry to obtain a composite carrier; and chemical treatment selected from group IVB metal compounds The step of treating the composite carrier with an agent to obtain the supported non-metallocene catalyst.
[0093] The steps for obtaining the magnesium compound solution are specifically described below.
[0094] Specifically, the magnesium compound (solid) and the non-metallocene ligand are dissolved in an appropriate solvent (ie, a solvent for dissolving the magnesium compound), there...
Embodiment 1
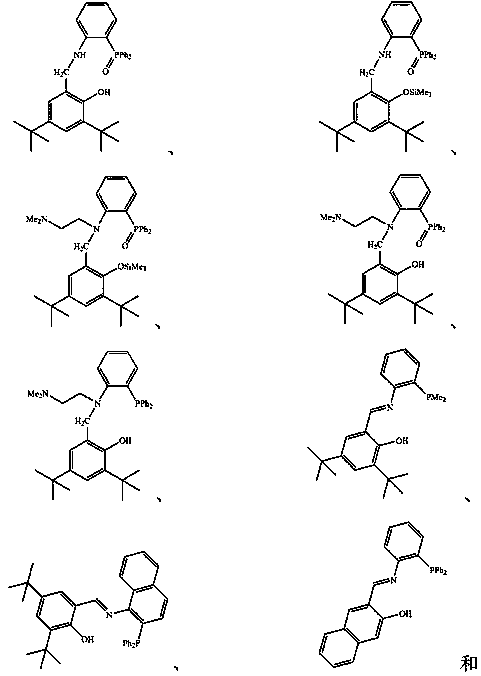
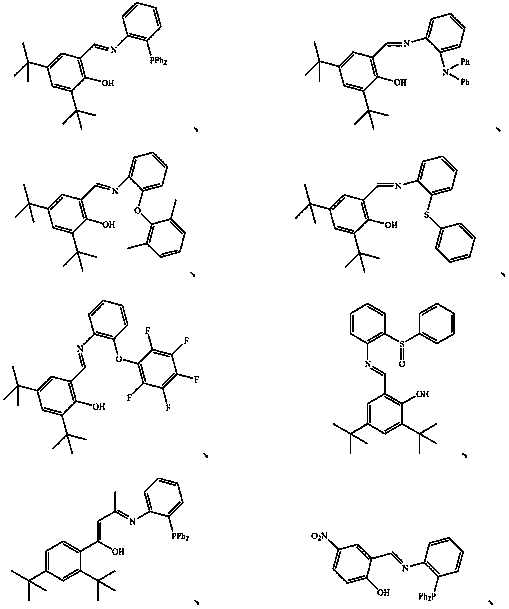
[0296] The magnesium compound adopts anhydrous magnesium chloride, the solvent for dissolving the magnesium compound and the non-metallocene ligand adopts tetrahydrofuran, and the chemical treatment agent adopts titanium tetrachloride. The porous carrier adopts silicon dioxide, that is, silica gel, the model is ES757 of Ineos Company, and the non-metallocene ligand adopts the structure of compound of.
[0297] Firstly, the silica gel was continuously fired at 600° C. under nitrogen atmosphere for 4 hours to thermally activate it.
[0298] Weigh 5g of anhydrous magnesium chloride and non-metallocene ligands, add tetrahydrofuran solvent and dissolve completely at room temperature, then add heat-activated silica gel, stir for 2 hours, heat evenly to 90°C and directly vacuum-dry to obtain a composite carrier.
[0299] Then add 60ml of hexane to the composite carrier, add titanium tetrachloride dropwise for 30 minutes under stirring conditions, stir and react at 60°C for 4 hours...
Embodiment 1-2
[0303] Basically the same as Example 1, but with the following changes:
[0304] The porous carrier adopts aluminum oxide. Aluminum oxide was continuously calcined at 700°C for 6 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0305] The magnesium compound is changed to anhydrous magnesium bromide (MgBr 2 ), the non-metallocene ligand adopts , the solvent for dissolving magnesium compounds and non-metallocene ligands was changed to ethylbenzene, and the chemical treatment agent was changed to titanium tetrabromide (TiBr 4 ).
[0306] Wherein the ratio is, the ratio of the magnesium compound to the solvent for dissolving the magnesium compound and the non-metallocene ligand is 1mol: 250ml; the molar ratio of the magnesium compound to the non-metallocene ligand is 1:0.20; the mass ratio of the magnesium compound to the porous carrier is 1:1; the molar ratio of magnesium compound to chemical treatment agent is 1:0.30.
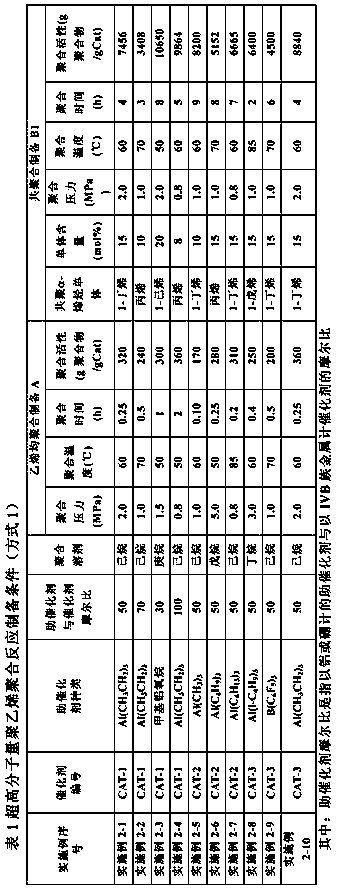
[0307] Supported non-metallocene catalysts are designated CAT-2. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com