High-efficiency extraction of bacterial polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites and identification of degradation pathways
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and pathway technology, applied in the field of biochemical analysis, can solve the problems of long time, no consideration of metabolites, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effects of complete peak shape, simple and efficient extraction method, and good resolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
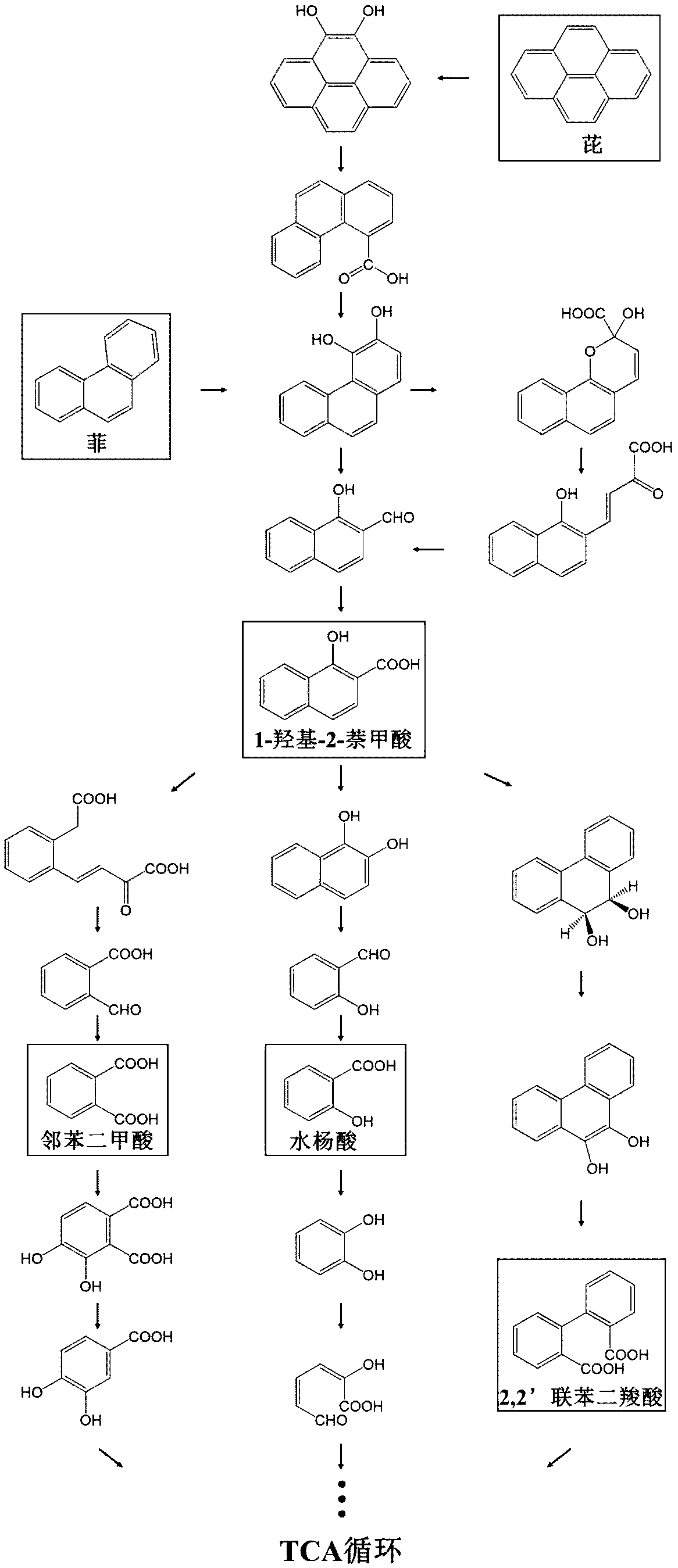
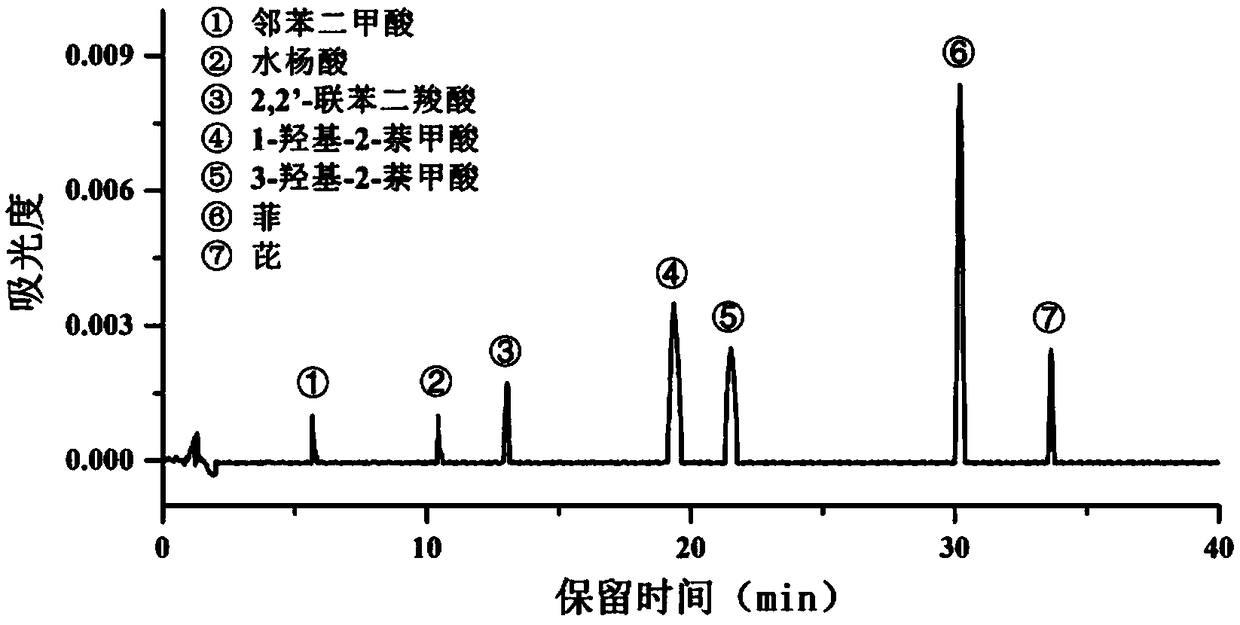
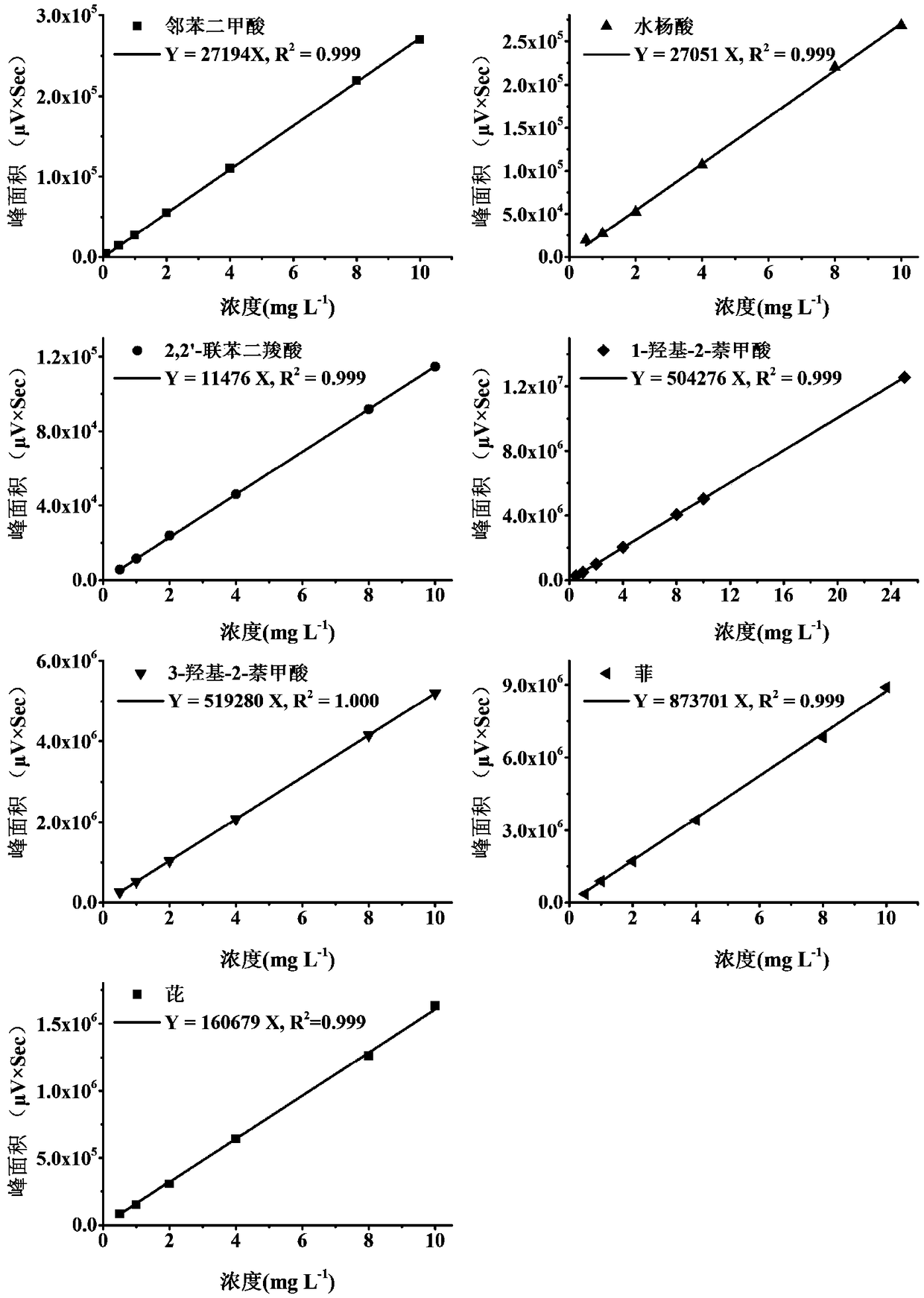
[0111] Embodiment 1, extract the degradation product of Mycobacterium sp.WY6 (CCTCC NO: M2017373) with pyrene as the only carbon source, and carry out the following steps successively:
[0112] 1) Draw 200 μL of 25% (V / V) glycerol to preserve the strains in 20 mL of LB medium, activate and culture at 28°C and 130 rpm for 12 hours; draw 200 μL of activated bacteria liquid into a new 20 mL of LB medium, Cultivate at 130 rpm for 14-16 hours to obtain the bacterial liquid.
[0113] 2) Centrifuge the bacterial liquid at 4°C and 5000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain degrading bacteria; vortex the obtained bacterial cells with sterile water, resuspend the bacterial cells in sterile water; centrifuge again, repeat this step twice, and finally Bacteria resuspended in sterile water to obtain bacterial suspension;
[0114] 3), adjust bacterial suspension in ultraviolet spectrophotometer OD 600nm =1.0 (at this time, the cell concentration is about 5×10 8 CFU mL -1 );
[0115] 4), draw 1m...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Example 2, extract the degradation product of Massilia sp.WG5 (CCTCC AB 2015362) with phenanthrene as the only carbon source, and perform the following steps in sequence:
[0135] 1) Take 200 μL of 25% glycerol to preserve the strains in 20 mL of LB medium, and culture at 28°C and 130 rpm for 12 hours; draw 200 μL of activated bacteria liquid and transfer it to a new 20 mL of LB medium, and culture at 28°C and 130 rpm for 14 to 16h to obtain the bacterial liquid.
[0136] 2) Centrifuge the bacterial solution at 4°C and 5000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain degrading bacteria; vortex the obtained bacterial cells with sterile water, resuspend the bacterial cells in sterile water; centrifuge again, repeat this step twice, and finally Body weight suspended in sterile water to obtain bacterial suspension;
[0137] 3) Regulate the bacteria suspension in the OD of the ultraviolet spectrophotometer 600nm =1.0 (at this time, the cell concentration is about 5×10 8 CFU mL -1 );
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com