Opposite irradiation type photoelectric sensor and target detection system
A photoelectric sensor and target detection technology, applied in the field of photoelectric sensors, can solve the problems of optical axis deviation, difficult alignment of light emitter and light receiver, and narrow installation space, achieve small installation spacing, overcome W/B shadows, and ensure consistency sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
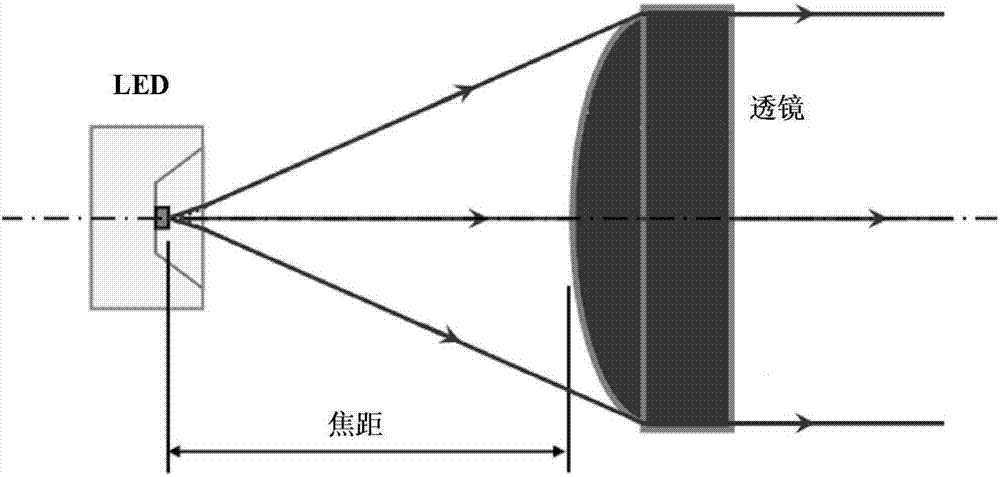
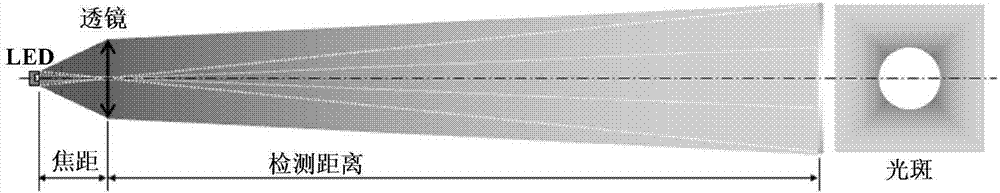
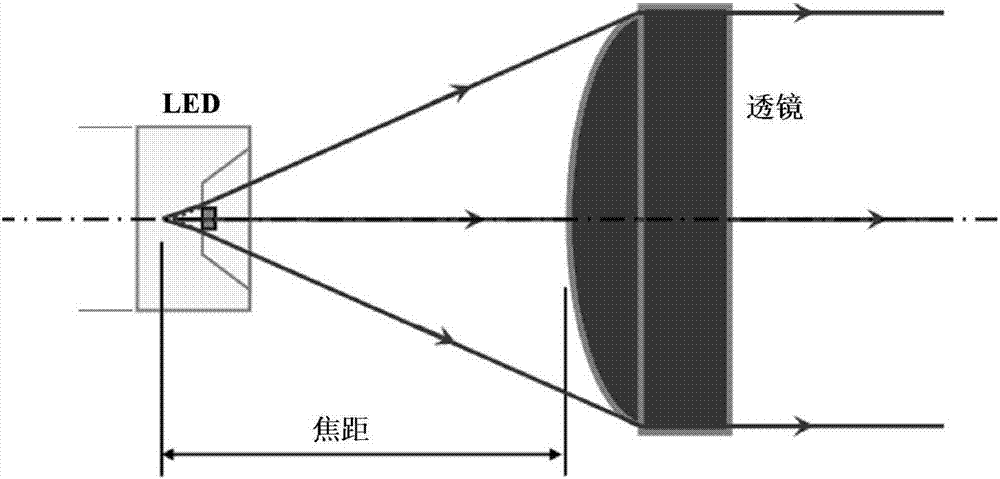
[0046] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a through-beam photoelectric sensor, Figure 5 It is a structural schematic diagram of the through-beam photoelectric sensor of Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the through-beam photoelectric sensor 50 includes a light projector 51 and a light receiver 52 . Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of the light path on the emitter side.
[0047] Such as Figure 5 and 6 As shown, the light projector 51 may include: a light emitting element 511 , a first lens 512 , and a first baffle 513 .
[0048]The light emitting element 511 emits light. The first lens 512 converts the light emitted by the light emitting element 511 into parallel light. The first baffle 513 is located between the light-emitting element 511 and the first lens 512, and a first through hole 5131 is provided on the first baffle 513. The center of the first through hole 5131 coincides with the focal point of the first lens 512....
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a target detection system, which has a plurality of through-beam photoelectric sensors described in embodiment 1. Since the through-beam photoelectric sensor has been described in embodiment 1, Its content is incorporated here, and will not be repeated here.
[0069] In this embodiment, the target detection system can detect whether there is a target (pedestrian or object) passing through the plurality of through-beam photoelectric sensors. In one embodiment, the target detection system can be applied to subway gates.
[0070] In this embodiment, the distance between every two through-beam photoelectric sensors may be less than or equal to 80 millimeters, so as to meet the requirements of parallel movement characteristics.
[0071] In this embodiment, all the projectors of the multiple through-beam photoelectric sensors can be installed on one side of the gate, and all the light receivers of the multiple through-beam photo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com