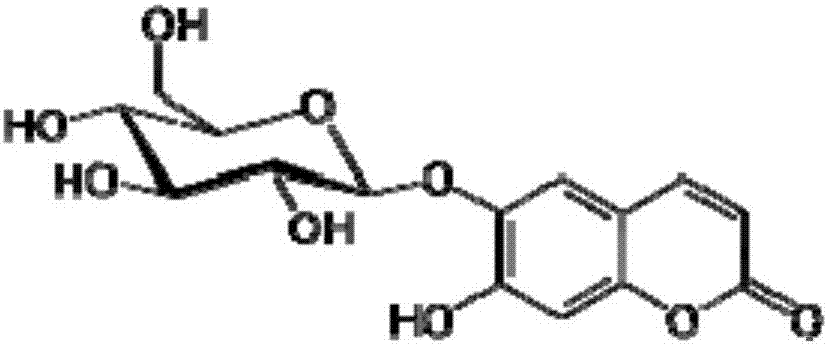
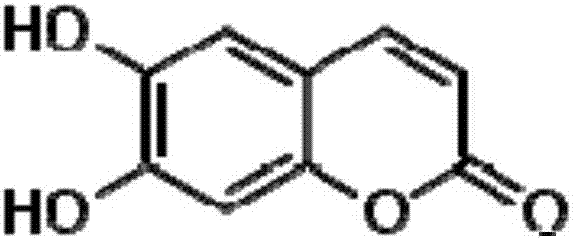
Composition for reducing inhibition of nucleic acid amplification
A technology of nucleic acid amplification reaction and composition, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism measurement/inspection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach AZ
[0162] Embodiments AZ are a kit comprising:
[0163] a plurality of zirconia particles;
[0164] nonionic surfactants; and
[0165] Organic iron chelating reagent;
[0166] Wherein the organic iron chelating reagent has a first affinity constant greater than or equal to 10 relative to ferric iron 4.2 and has a second affinity constant of less than 10 relative to magnesium 3.8 , where the first affinity constant and the second affinity constant were determined in deionized water at 20 °C at pH 8.45.
[0167] Embodiment BA is the kit of embodiments AZ, wherein the plurality of particles has an average particle size of less than about 1 μm.
[0168] Embodiment BB is the kit according to Embodiment AZ or Embodiment BA, wherein the organoiron chelating reagent comprises a plurality of carboxylate groups.
[0169]Embodiment BC is the kit according to any one of embodiments AZ to BB, wherein the organic iron chelating agent is selected from the group consisting of ethylene glyco...
Embodiment 1-8
[0197] Examples 1-8: Compositions comprising ferric ions and various amounts of zirconia particles .
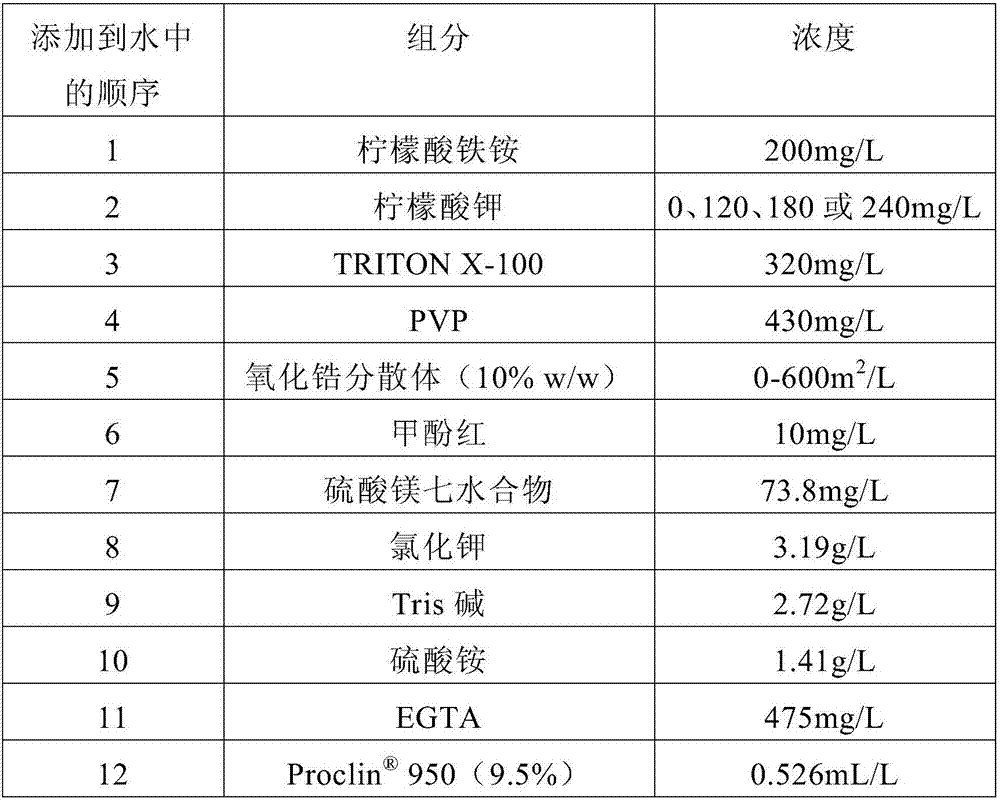
[0198] Zirconia nanoparticle dispersion (10% w / w in water; ≤ 100 nm average particle size (BET); surface area 11 m²) was obtained from Sigma Chemical Co. 2 / mL; part number 643025). The test compositions were prepared by adding the components in the order specified in Table 1 to deionized water. Comparative Example 1 was prepared as described in Example 1 except that no zirconia particles and no potassium citrate were added to the composition. Each composition of Examples 1-8 and Comparative Example 1 contained 200 mg / L ferric ammonium citrate and 320 mg / L TRITON X-100. The amounts of potassium citrate and zirconia dispersions used in each Example and Comparative Example 1 are shown in Table 2.
[0199] Table 1 : The test composition of Examples 1-8 and Comparative Example 1. The order of addition of the components of the composition is also shown.
[0200]
[020...
Embodiment 9-14
[0211] Examples 9-14: Compositions comprising zirconia particles and various concentrations of surfactants and ferric ions .
[0212] Test compositions were prepared with the components shown in Table 4 and their respective order of addition to deionized water. In these examples, ferric ion and nonionic surfactant concentrations were varied according to Table 5. Zirconia surface area kept constant at 20m 2 / L. Samples (600 μL) were prepared as described in Example 1 and Comparative Examples 2-7. Aliquots (20 μL) of the lysozyme solution were added to 580 μL of the test composition in Neptune (2600.X) lysis tubes.
[0213] Table 4 : Test compositions of Examples 9-14 and Comparative Examples 2-7. The order of addition of the components of the composition is shown.
[0214]
[0215] table 5 : The amount of ferric ammonium citrate, TRITON X-100 and zirconia particle dispersion added to each composition of Examples 9-14 and Comparative Examples 2-7.
[0216]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com