Steel rail flaw detection ultrasonic waveguide inclined probe and flaw detection method thereof
A technology of ultrasonic guided wave and oblique probe, which is applied to the analysis of solids using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, material analysis using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves, and measuring devices. Problems such as low guided wave mode recognition and inapplicability to production practice have achieved high flaw detection efficiency, easy promotion, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] This embodiment provides an ultrasonic guided wave inclined probe, which is used for rail head flaw detection. Compared with the traditional ultrasonic rail flaw detection technology, the single detection distance is longer, and the typical single detection distance can reach ten meters. To tens of meters, the flaw detection efficiency is high.
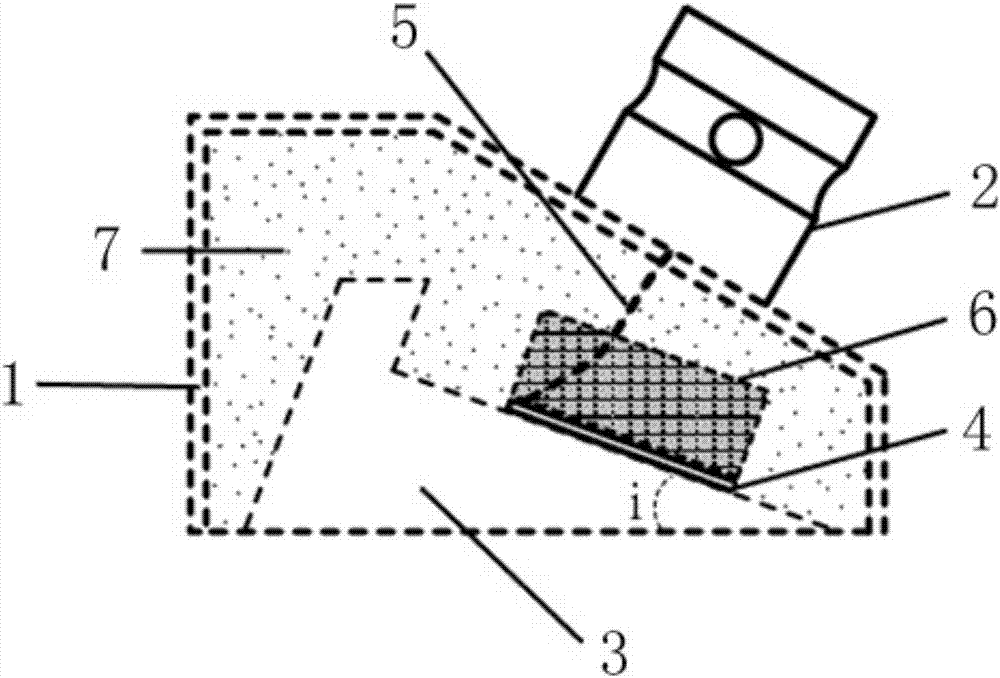
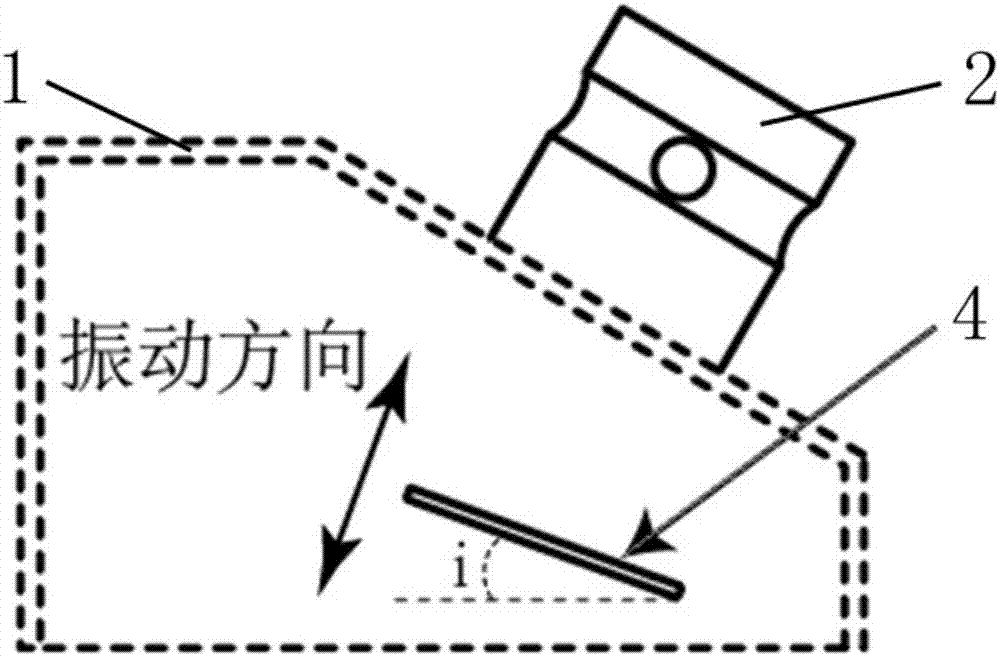
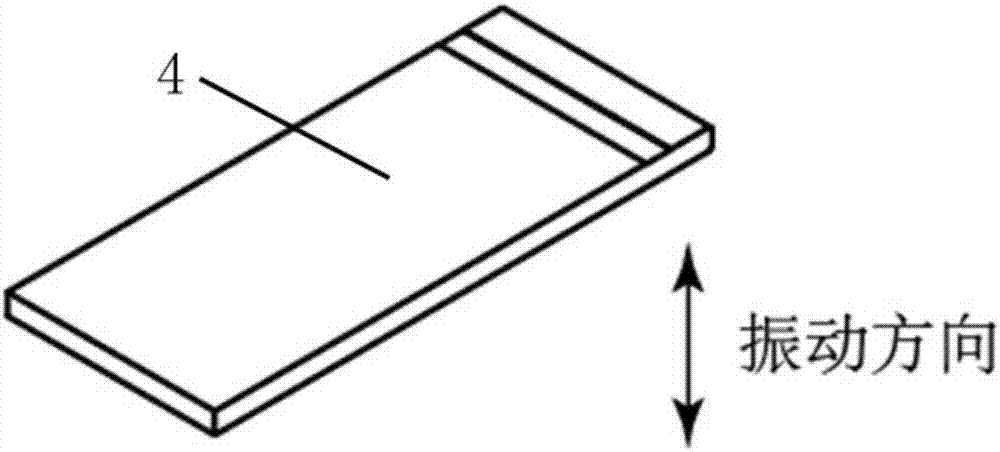
[0071] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, the ultrasonic guided wave angle probe of this embodiment includes a housing 1, a piezoelectric unit and an interface 2, and the piezoelectric unit includes a wedge 3, a piezoelectric wafer 4, a cable 5 and a damping block 6, for clarity See the position of the piezoelectric wafer 4 in the shell 1, in figure 2 Only the shell 1, the interface 2 and the piezoelectric chip 4 are shown in the figure, while other parts are omitted.
[0072] One surface of the wedge 3 forms an included angle i with the horizontal plane, and the included angle i in this embodiment is 41 degrees.
...
Embodiment 2
[0093] The main features of this embodiment are: the structure of the ultrasonic guided wave oblique probe is the same as that of Embodiment 1, such as Figure 11As shown, it is used for rail head flaw detection, but there are two ultrasonic guided wave oblique probes 8, and the two ultrasonic guided wave oblique probes 8 are placed longitudinally (along the length direction of the rail) on the upper surface of the rail head tread of the rail 9, and placed on the Ultrasonic detection couplant is used between the ultrasonic guided wave inclined probe 8 and the rail 9 to ensure the detection effect, and the interfaces 2 of the two ultrasonic guided wave inclined probes 8 are respectively connected to the excitation channel and the receiving channel of the external device 10, and the external device 10 The ultrasonic guided wave inclined probe 8 connected to the excitation channel, in the detection, the piezoelectric chip 4 realizes the excitation of the guided wave through the in...
Embodiment 3
[0095] The main features of this embodiment are: the structure of the ultrasonic guided wave oblique probe is the same as that of Embodiment 1, such as Figure 12 As shown, for rail head flaw detection, two ultrasonic guided wave angled probes 8 are placed longitudinally (along the length direction of the rail) in the center on the upper surface of the rail head tread of the rail 9, and between the ultrasonic guided wave angled probes 8 and the rail 9 Ultrasonic detection couplant is used to ensure the detection effect, but the external equipment includes external excitation equipment 11 and external receiving equipment 12, that is, the excitation and reception functions of the signal are realized by different external equipment, and the interface of two ultrasonic guided wave inclined probes 8 2 respectively connected to the external excitation device 11 and the external receiving device 12, the ultrasonic guided wave inclined probe 8 connected to the external excitation devic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com