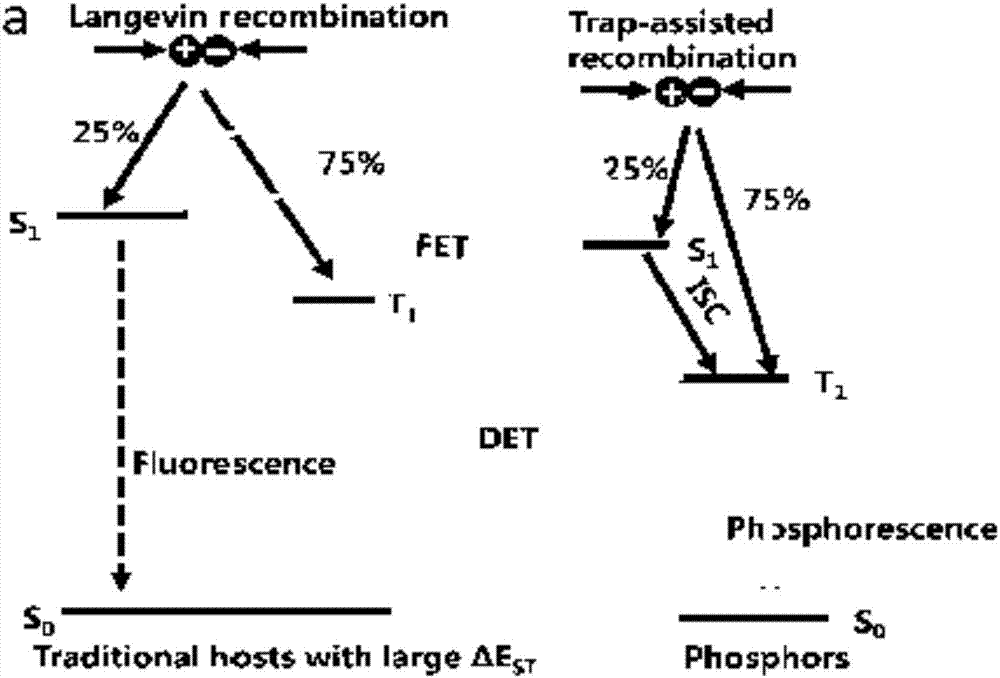
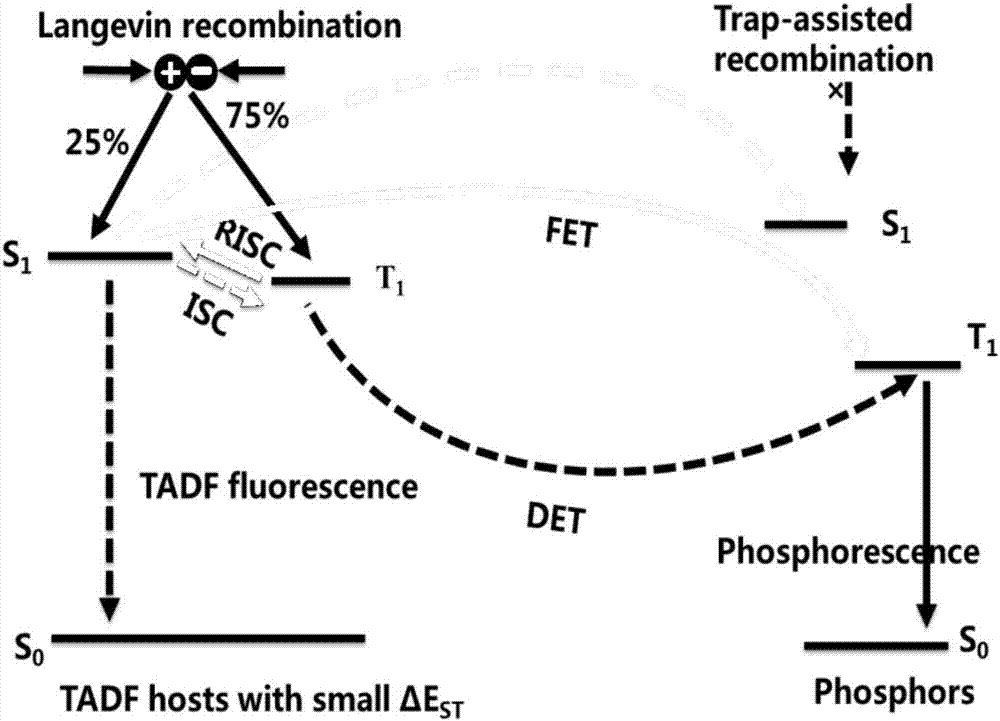
Red light organic electroluminescence device
A luminescent and electromechanical technology, applied in the field of red organic electroluminescent devices, can solve the problems of high doping concentration in the red OLED light-emitting layer, achieve the effects of reducing roll-off, improving efficiency, and ensuring full utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
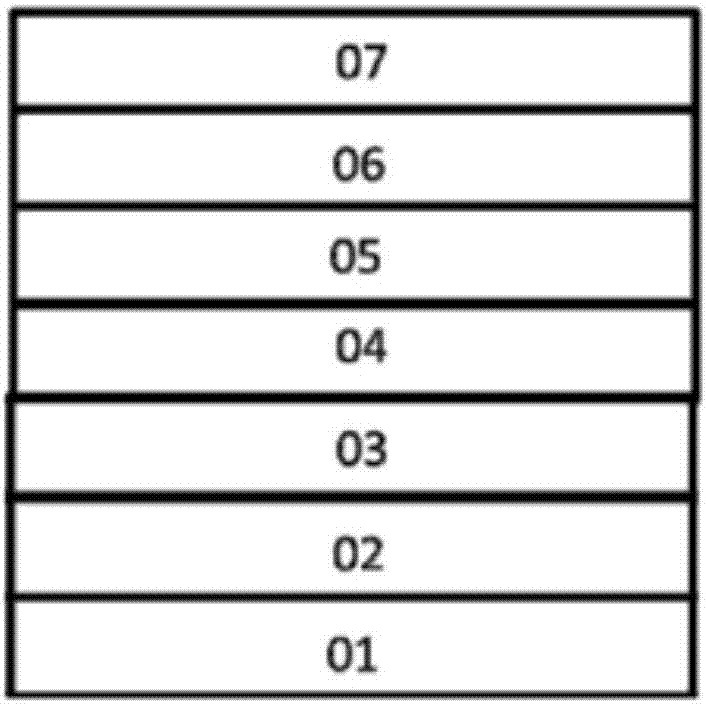
[0073] like image 3 As shown, a red light organic electroluminescent device provided by the present invention includes a substrate, and a first electrode layer 01, a light emitting layer 04 and a second electrode layer 07 sequentially formed on the substrate, the first electrode A first organic functional layer is arranged between the layer 01 and the light-emitting layer 04 , and a second organic functional layer is arranged between the light-emitting layer 04 and the second electrode layer 07 . The first organic functional layer is the hole injection layer 02 and / or the hole transport layer 03 , and the second organic functional layer is the electron transport layer 05 and / or the electron injection layer 06 .
[0074] The host material of the device in this embodiment includes a first host material and a second host material, and the dye is a red phosphorescent dye.
[0075] Device 1: ITO / NPB(40nm) / TCTA(10nm) / CBP:50wt%(1-37):3wt%Ir(piq) 2 (acac)(30nm) / Bphen(40nm) / LiF(5nm)...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The structure of the light-emitting device in Example 2 is the same as that of the light-emitting device in Example 1, the difference is that the host material of the light-emitting layer 04 is different, the doping concentration of the red phosphorescent dye is 1 wt%, and the structures of devices 2 to 8 are as follows:
[0085] ITO / NPB(40nm) / TCTA(10nm) / host material: 1wt%Ir(piq) 2 (acac)(30nm) / Bphen(40nm) / LiF(5nm) / Al
[0086] The performance test result of table 4 embodiment 2
[0087]
[0088] The performance of devices 2 to 8 was tested. As shown in Table 4, the red phosphorescent organic electroluminescent device of the present invention uses a hole-type transport material or an electron-type transport material as the first host material, and a heat-activated sensitized fluorescent material As the second host material, and the doping concentration of the host material is different, it can be seen from the table that this kind of red phosphorescent light emittin...
Embodiment 3
[0090] The structure of the light-emitting device in Embodiment 3 is the same as that in Embodiment 1, the difference lies in that the materials of the light-emitting layer are different, and the structures of devices 9 to 16 are as follows:
[0091] ITO / NPB(40nm) / TCTA(10nm) / luminescent layer / LiF(5nm) / Al
[0092] Table 5 embodiment 3 performance test results
[0093]
[0094]
[0095] The performance of devices 9 to 16 was tested. As shown in Table 5, the red phosphorescent organic electroluminescent device of the present invention uses a hole-type transport material or an electron-type transport material as the first host material, and a heat-activated sensitized fluorescent material As the second host material, and the doping concentration of the host material is different, it can be seen from the table that this kind of red phosphorescent light emitting device has high performance, which shows that the device structure protected by the present invention has universal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com