Improvement of microbial strains using the htp genome engineering platform
A microbial and genomic technology, applied in the field of high-throughput microbial genome engineering, can solve the problems of low efficiency of microbial strain improvement programs, stagnant mutation accumulation performance improvement rate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0613] The following examples are provided to illustrate various embodiments of the invention and are not intended to limit the invention in any way. Those skilled in the art will recognize that changes therein and other uses are encompassed within the spirit of the invention as defined by the scope of the claims.
[0614] A brief table of contents is provided below to assist the reader only. This list is not intended to limit the scope of the examples or disclosure of this application.
[0615] Table 5.1 - Table of Contents for Example Sections
[0616]
[0617]
example 1
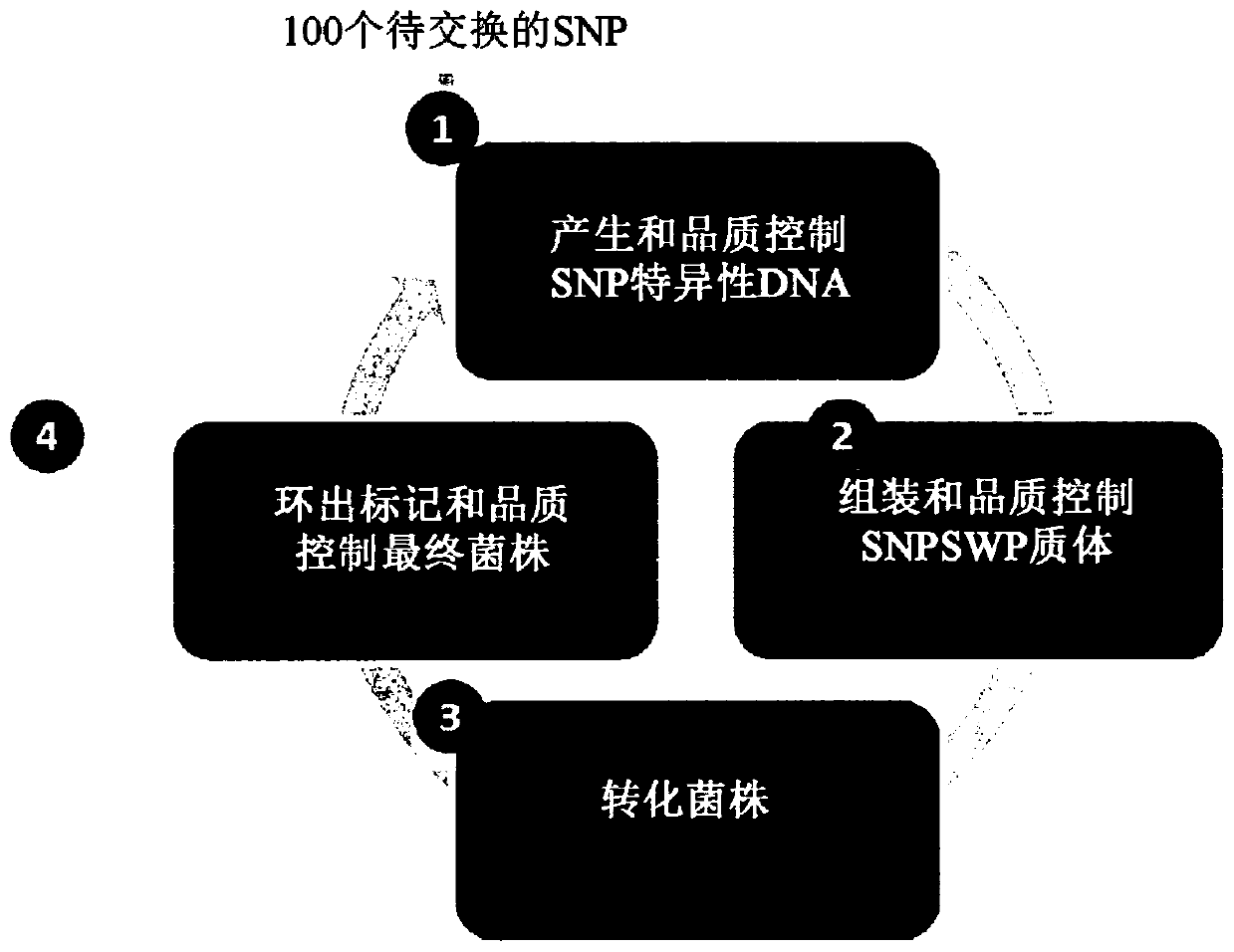
[0618] Example 1: Demonstration of HTP transformation and SNP library creation of coryneform bacteria
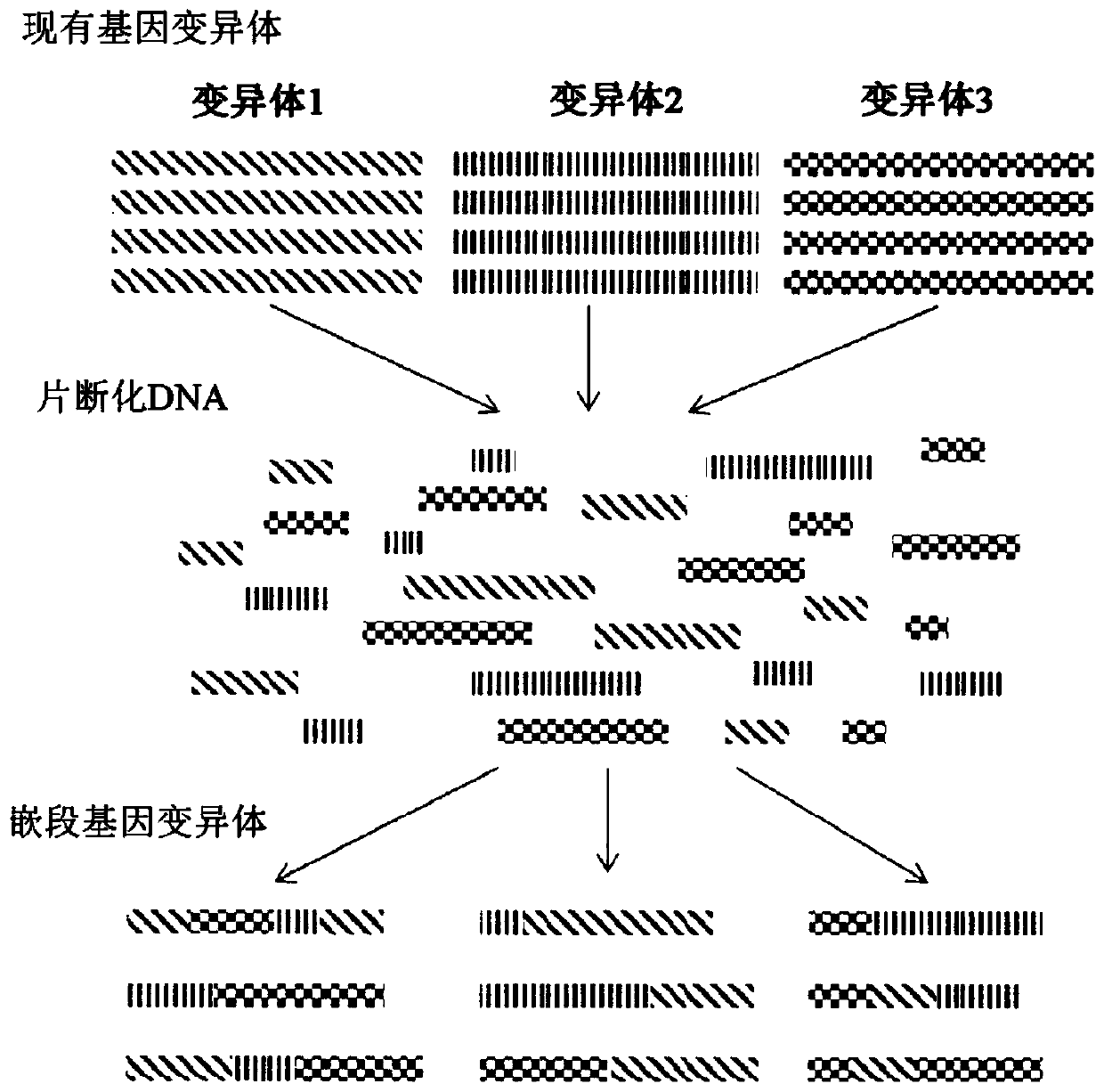
[0619] This example illustrates an embodiment of the HTP genetic engineering method of the present invention. Host cells are transformed with multiple SNP sequences of different sizes, all targeting different regions of the genome. The results demonstrate that the method of the present invention is capable of producing any kind of rapid genetic change across the entire genome of the host cell.
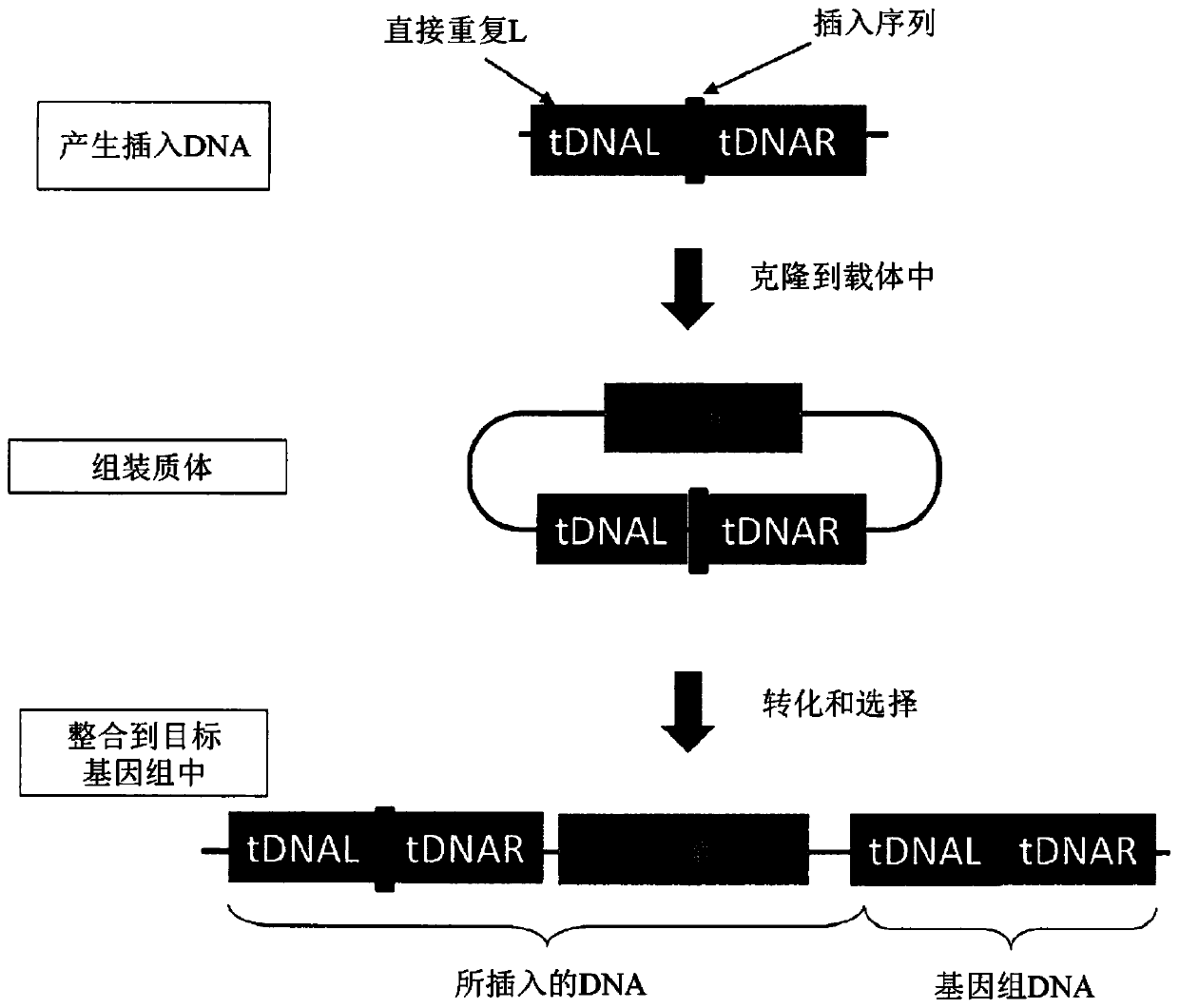
[0620] A. Cloning of Transformation Vectors
[0621] A variety of SNPs were randomly selected from Corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC21300) and cloned into a Corynebacterium cloning vector using yeast homologous recombination cloning technology to assemble the vector, wherein each SNP is flanked by a direct repeat region, as described above in "Assembly / Cloning of custom plastids" section and as described in image 3 described in.
[0622] The SNP cassette used in this example was...
example 2
[0643] Example 2: HTP Genome Engineering - Construction of SNP Libraries to Repair / Improve Industrial Microbial Strains
[0644] This example illustrates several aspects of the SNP exchange library in the HTP strain improvement program of the present invention. In particular, the examples illustrate several conceived approaches to rehabilitate currently existing industrial strains. This example describes up-swing and down-swing approaches to explore the phenotypic solution space arising from multiple genetic differences that may exist between "basic", "intermediate" and industrial strains.
[0645] A. Identification of SNPs in Diversity Pools
[0646] An exemplary strain improvement program using the methods of the invention is performed on an industrial microorganism strain (referred to herein as "C"). The diversity pool strains used in this procedure are indicated by A, B and C. Strain A represents the original production host strain prior to any mutagenesis. Strain C re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com