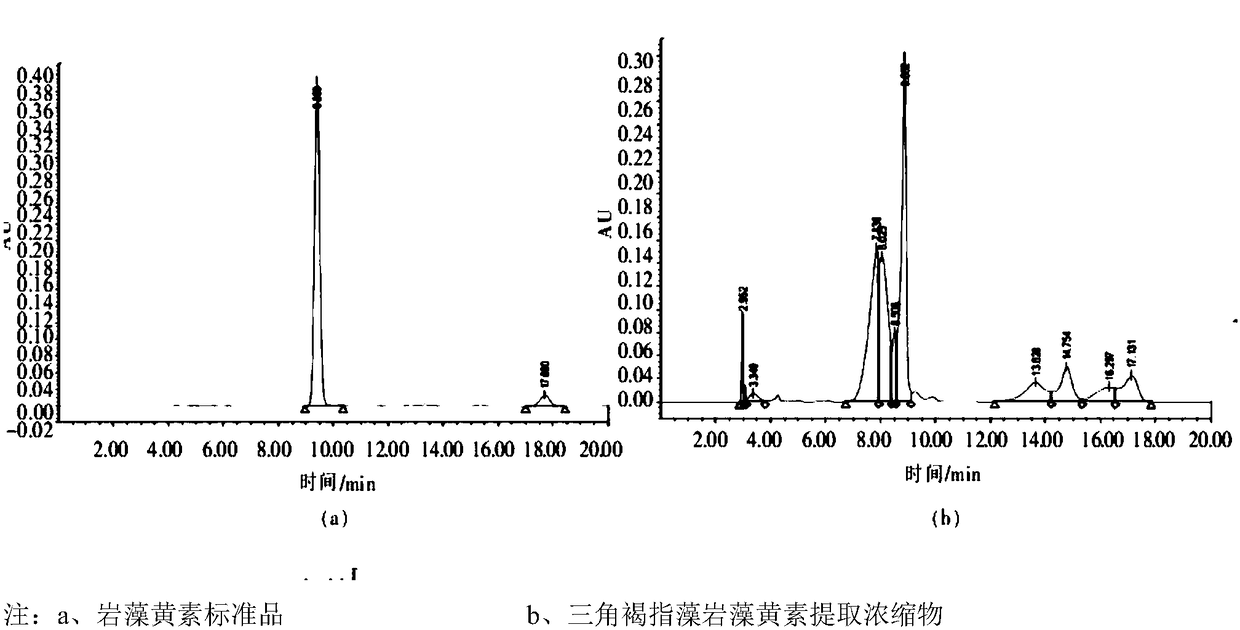
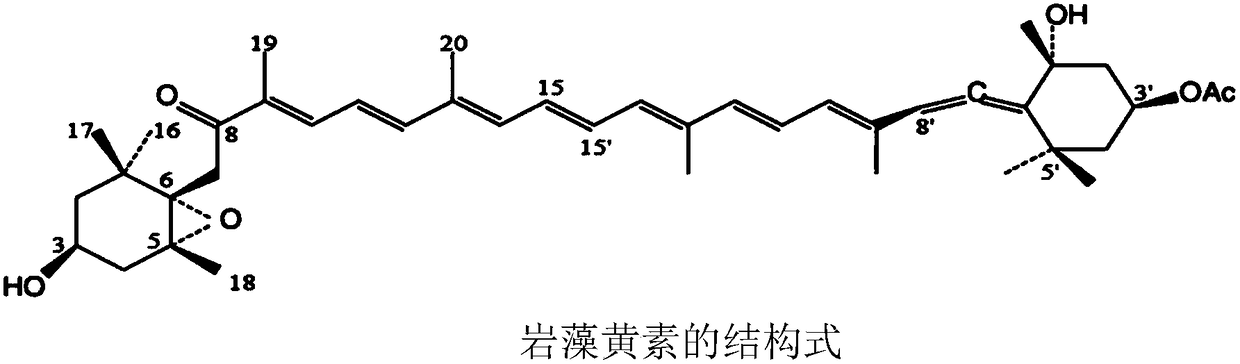
Method for extracting fucoxanthin from phaeodactylum tricornutum with dimethyl ether fluid
A technology of Phaeodactylum tricornutum fucoxanthin and dimethyl ether, which is applied in the field of microalgae cultivation, can solve the problems that do not involve the extraction of Phaeodactylum tricornutum fucoxanthin, the destruction of Phaeodactylum tricornutum fucoxanthin, the extraction solvent and High energy consumption and other problems, to achieve the effect of reliability and safety, reduce energy consumption, and reduce consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] A method for extracting fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum with dimethyl ether fluid, comprising steps:
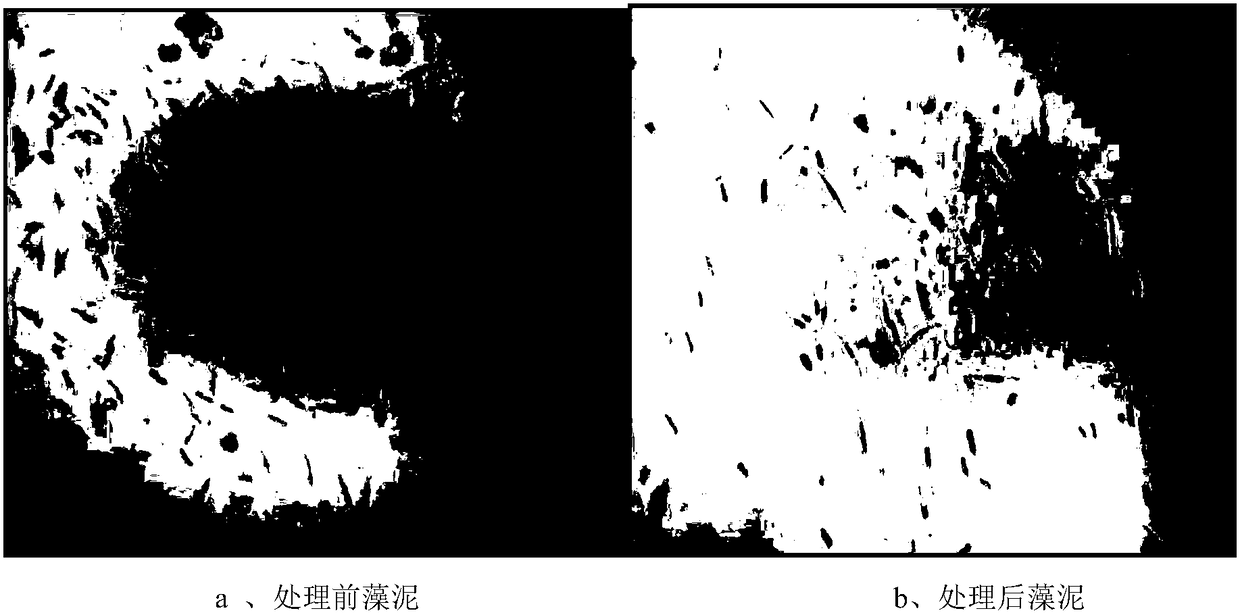
[0051] 1) Freezing and thawing fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum;
[0052] 2) Dimethyl ether fluid dynamic gradient countercurrent extraction of broken algae mud;
[0053] 3) The extract solution is precipitated to separate the fucoxanthin.
[0054] The fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in the step 1) is the fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum dried by a high-speed centrifuge, and the water content mass percentage is 65.0%.
[0055] The fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum are first quick-frozen, then refrigerated, and finally thawed to achieve freeze-thaw wall breaking. The quick-freezing temperature is -70°C, the quick-freezing time is 8.0h, the cold storage temperature is -20°C, the thawing temperature is 20°C, and the thawing time is is 0.5, and the number of freeze-thaw cycles is 1 time.
[0056] The dimethyl ether fluid in the...
Embodiment 2
[0063] A method for extracting fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum with dimethyl ether fluid, comprising steps:
[0064] 1) Freezing and thawing fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum;
[0065] 2) Dimethyl ether fluid dynamic gradient countercurrent extraction of broken algae mud;
[0066] 3) The extract solution is precipitated to separate the fucoxanthin.
[0067] The fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in the step 1) is the fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum dried by a high-speed centrifuge, and the water content mass percentage is 70.0%.
[0068] The fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum are first quick-frozen, then refrigerated, and finally thawed to achieve freeze-thaw breaking. The quick-freezing temperature is -55°C, the quick-freezing time is 102.0h, the cold storage temperature is -15°C, the thawing temperature is 25°C, and the thawing time 1.0h, freeze-thaw times 23 times.
[0069] The dimethyl ether fluid in the step 2) is a subcritical fl...
Embodiment 3
[0076] A method for extracting fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum with dimethyl ether fluid, comprising steps:
[0077] 1) Freezing and thawing fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum;
[0078] 2) Dimethyl ether fluid dynamic gradient countercurrent extraction of broken algae mud;
[0079] 3) The extract solution is precipitated to separate the fucoxanthin.
[0080] The fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in the step 1) is the fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum dried by a high-speed centrifuge, and the water content mass percentage is 5.0%.
[0081] The fresh algae of Phaeodactylum tricornutum are first quick-frozen, then refrigerated, and finally thawed to achieve freeze-thaw breaking. The quick-freezing temperature is -40°C, the quick-freezing time is 12.0h, the cold storage temperature is -10°C, the thawing temperature is 30°C, and the thawing time is 1.5h, freeze-thaw times 3 times.
[0082] The dimethyl ether fluid in the step 2) is a subcritical fl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com