In vitro artificial lymph node for sensitization and expansion of t cells for therapy and epitope mapping
A technology of cells and cell groups, which is applied in the field of sensitization and expansion of T cells used in artificial lymph nodes in vitro for treatment and epitope mapping, and can solve problems such as insufficient expansion level and loss of specific function of cell death antigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
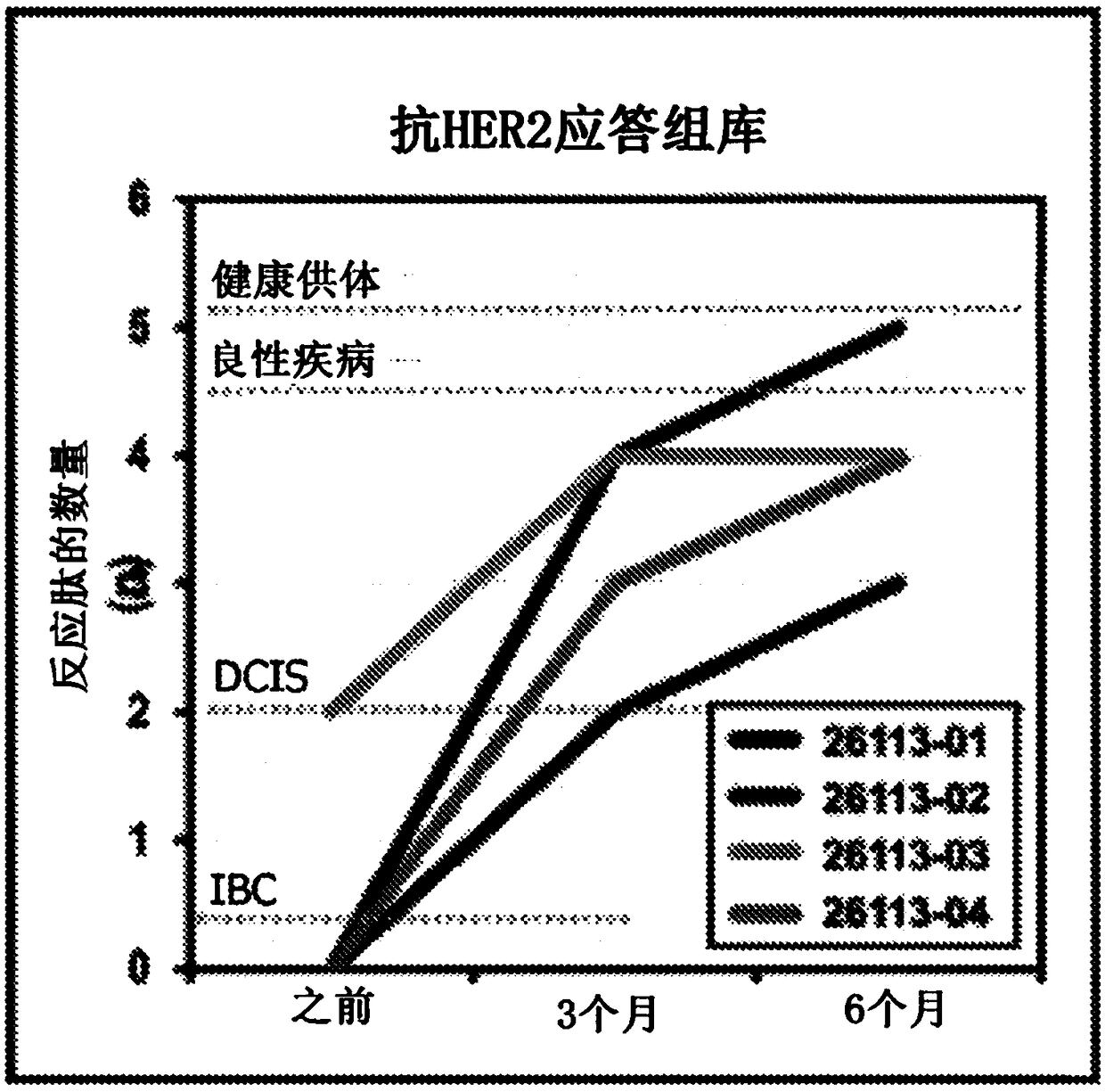
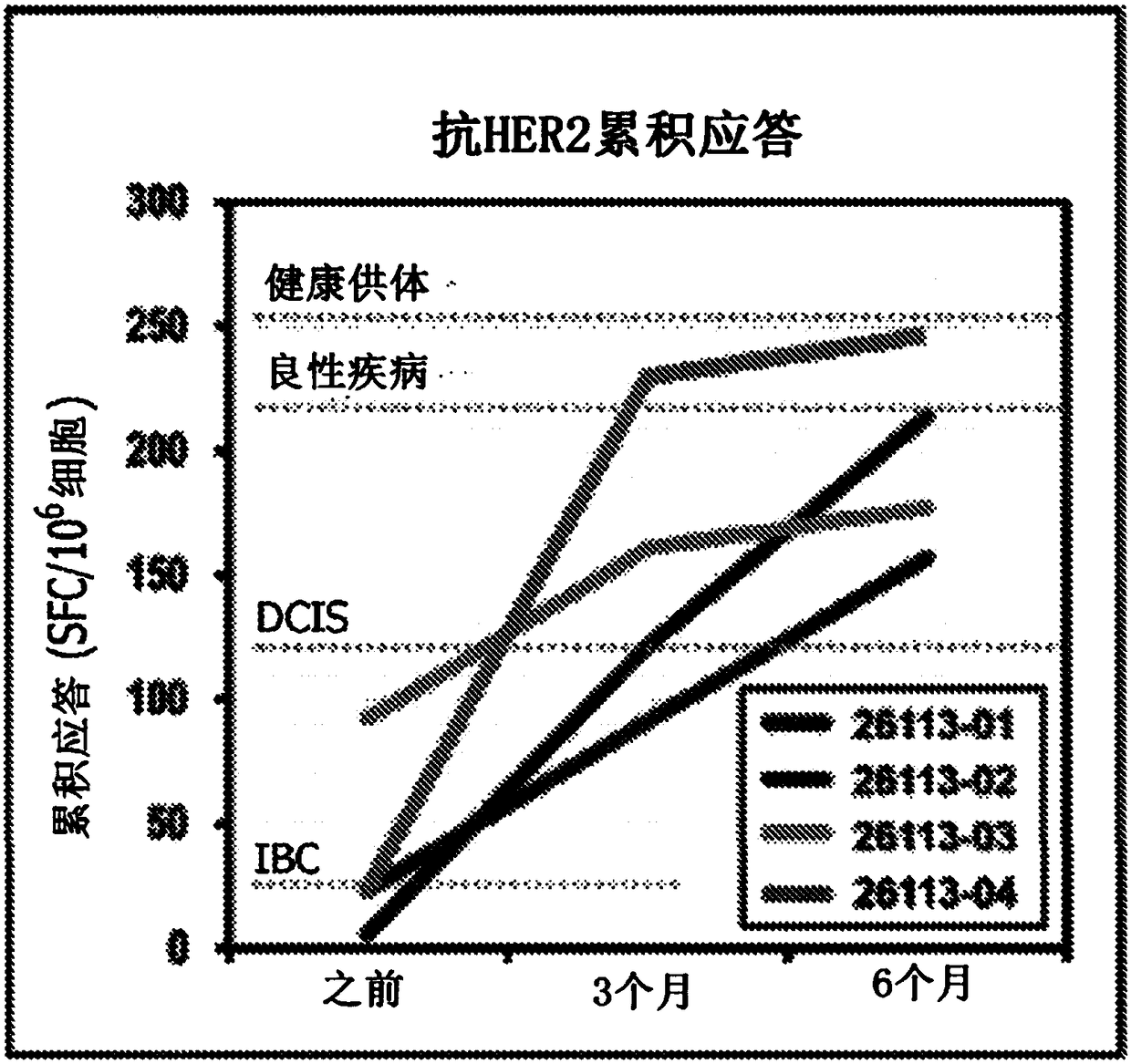
[0255] Example 1: Anti-HER2 CD4 in breast cancer patients inoculated with type I dendritic cells + Restoration of Th1 responses
[0256] The following study was designed to explore the role of helper type 1 polarized dendritic cell ("DC1") seeding.
[0257] Type I dendritic cell vaccination with HER2 with residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy + IBC patients
[0258] Four HER2 patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy + IBC patients receive adjuvant HER2-pulsed type I dendritic cell vaccine. The Th1 immune response of each patient was determined before type I dendritic cell inoculation, 3 months after dendritic cell inoculation and 6 months after inoculation, and obtained from six HER2 class II peptides (SEQ ID NO: 1-6 ) pulsed patient PBMC production by measuring IFNγ production by ELISPOT as described above. Autologous type I dendritic cell vaccines were prepared as previously described. (1) overall anti-HER2 response rate (response rate >1 pepti...
Embodiment 2
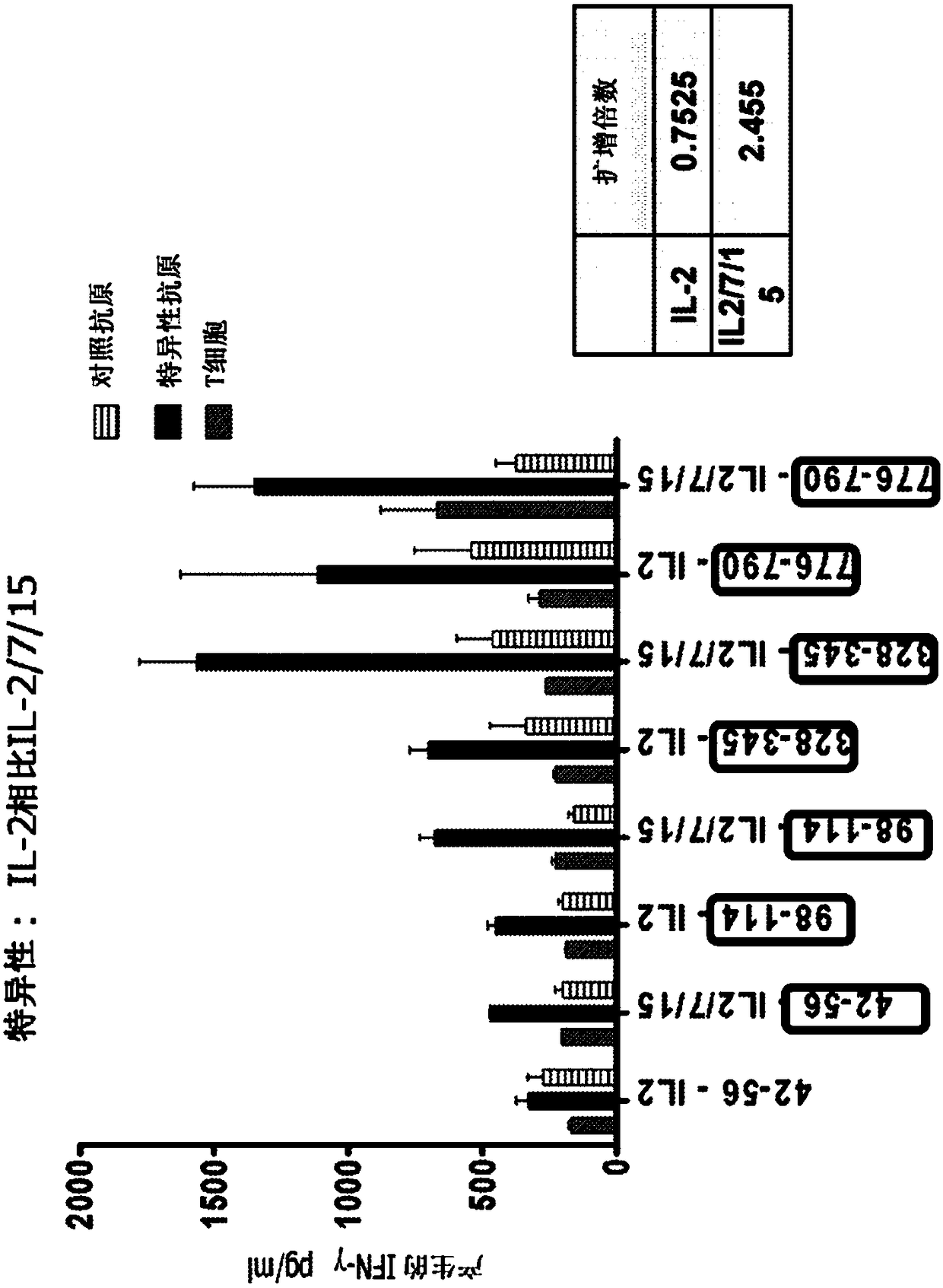
[0266] Example 2: In vitro expansion of HER2-specific Th1 cells
[0267] The following study was designed to interrogate the role of adoptive T cell transfer in restoring anti-HER2 Thl immunity. T cell expansion to levels required for adoptive therapy and epitope mapping studies while maintaining antigen specificity and cellular function. Briefly, in vitro, HER2-specific Th1 cells were generated by co-culture with HER2 peptide-pulsed type I dendritic cells and expanded using IL-2 alone or IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 . Th1 cells were subsequently expanded by repeated HER2-peptide pulses of type I dendritic cell co-culture or by anti-CD3 / CD28 stimulation. The expansion factor was defined as: (the number of T cells after expansion / the number of T cells before expansion); the specificity of antigen-specific IIγ production was determined by ELISA.
[0268] As shown in this paper, CD4 + Repeated co-culture of T cells with HER2 peptide pulsed with type I dendritic cells stimulated wi...
Embodiment 3
[0325] Example 3: Anti-HER2 CD4 can be restored in DC1 vaccinated breast cancer patients + Th1 response
[0326] Expansion of T cell subsets is an essential step to obtain sufficient T cells for adoptive therapy or to recognize epitopes on target antigens for peptide-based vaccines. Expansion of T cells is in principle a simple process. However, in practice, there are many technical problems including insufficient levels of expansion, premature activation-induced cell death (apoptosis) or loss of antigen specificity and / or function.
[0327] Part of the problem is the inability to replicate in vitro the expansion of antigen-specific T cells that occurs in lymph nodes in vivo. These are specialized tissues that contain many different cell types besides T cells, including antigen-presenting dendritic cells, stromal cells such as epithelial cells. Each of these cell types plays a different role by providing contact-dependent (surface receptors) and soluble signals (cytokines...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com