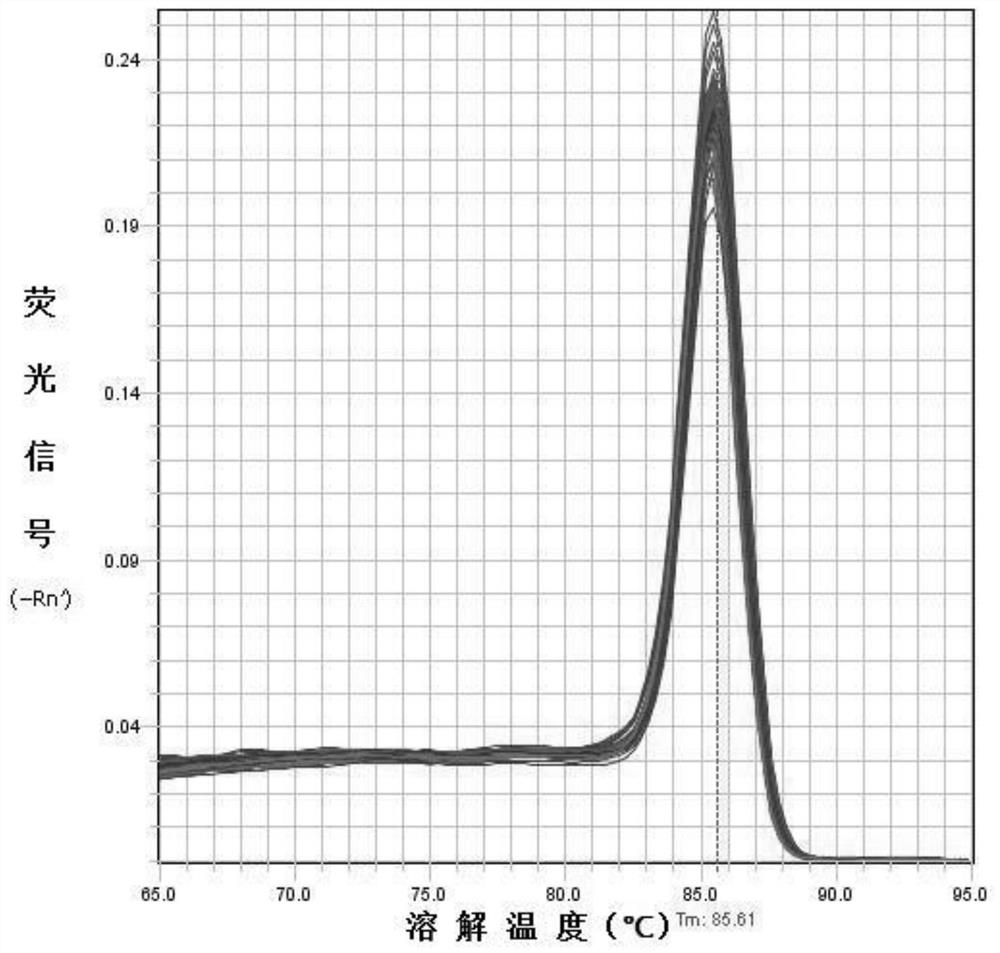
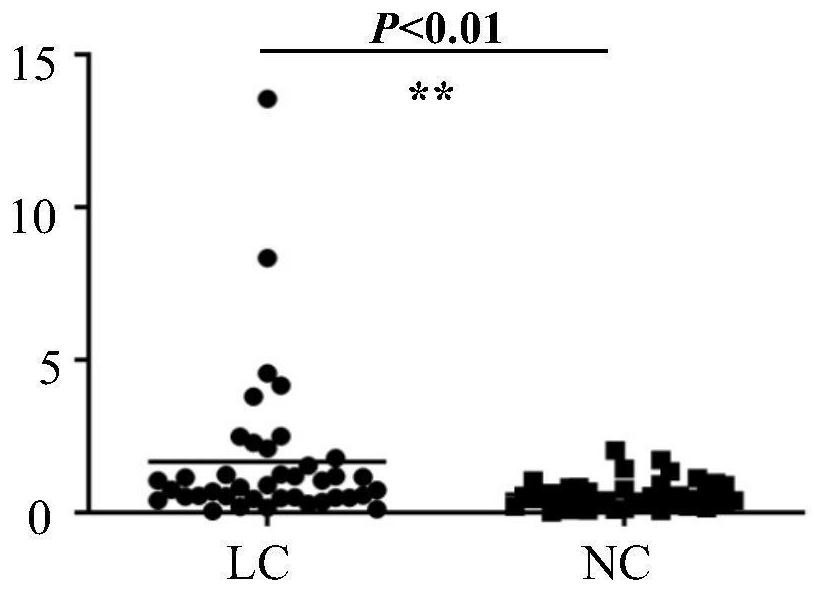
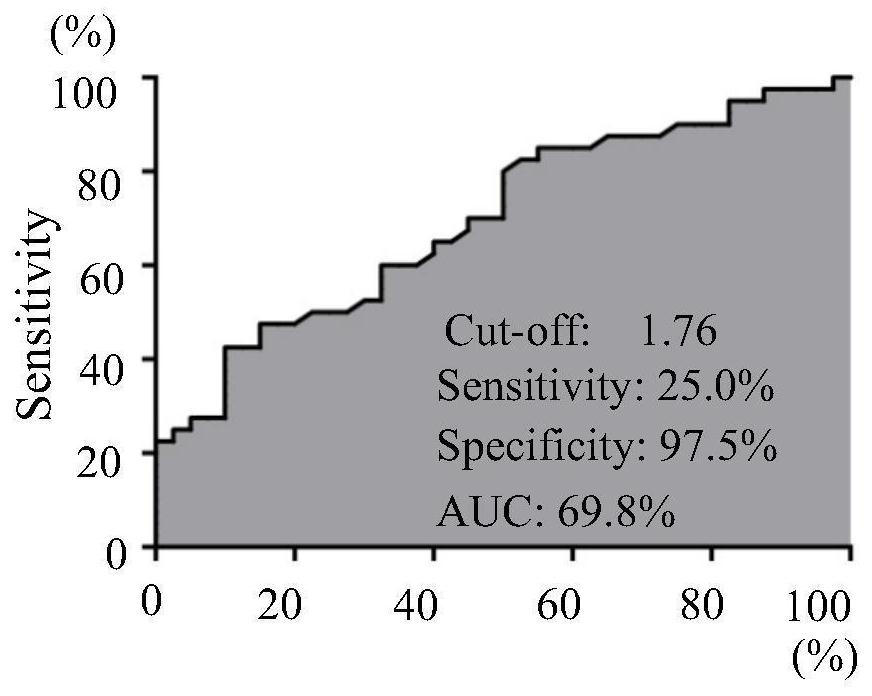
Patents
Literature
52 results about "Benign disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In human disease: Disease: signs and symptoms The terms benign and malignant, most often used to describe tumours, can be used in a more general sense. Benign diseases are generally without complications, and a good prognosis (outcome) is usual. A wart on the skin is a benign tumour caused by a virus; it produces….
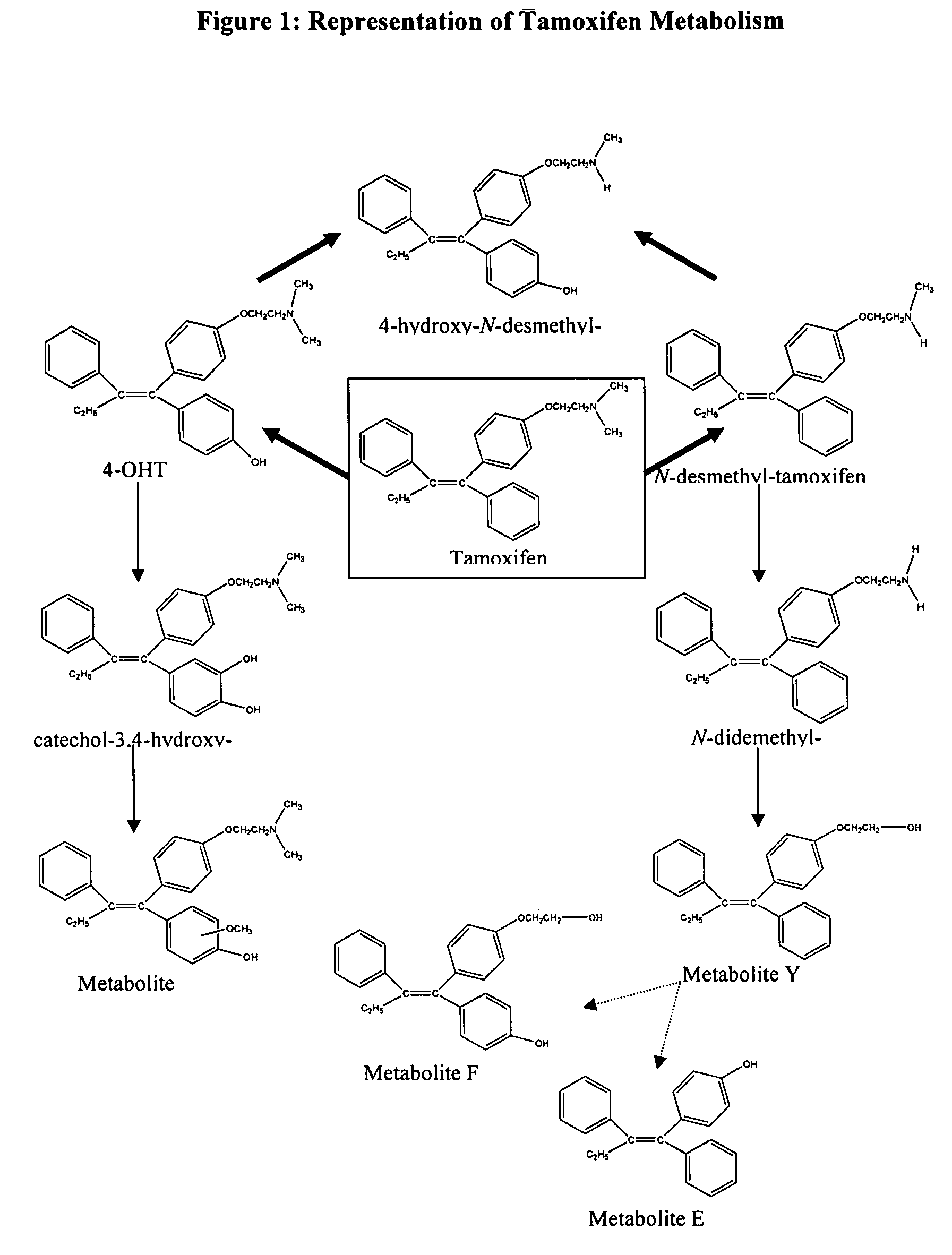
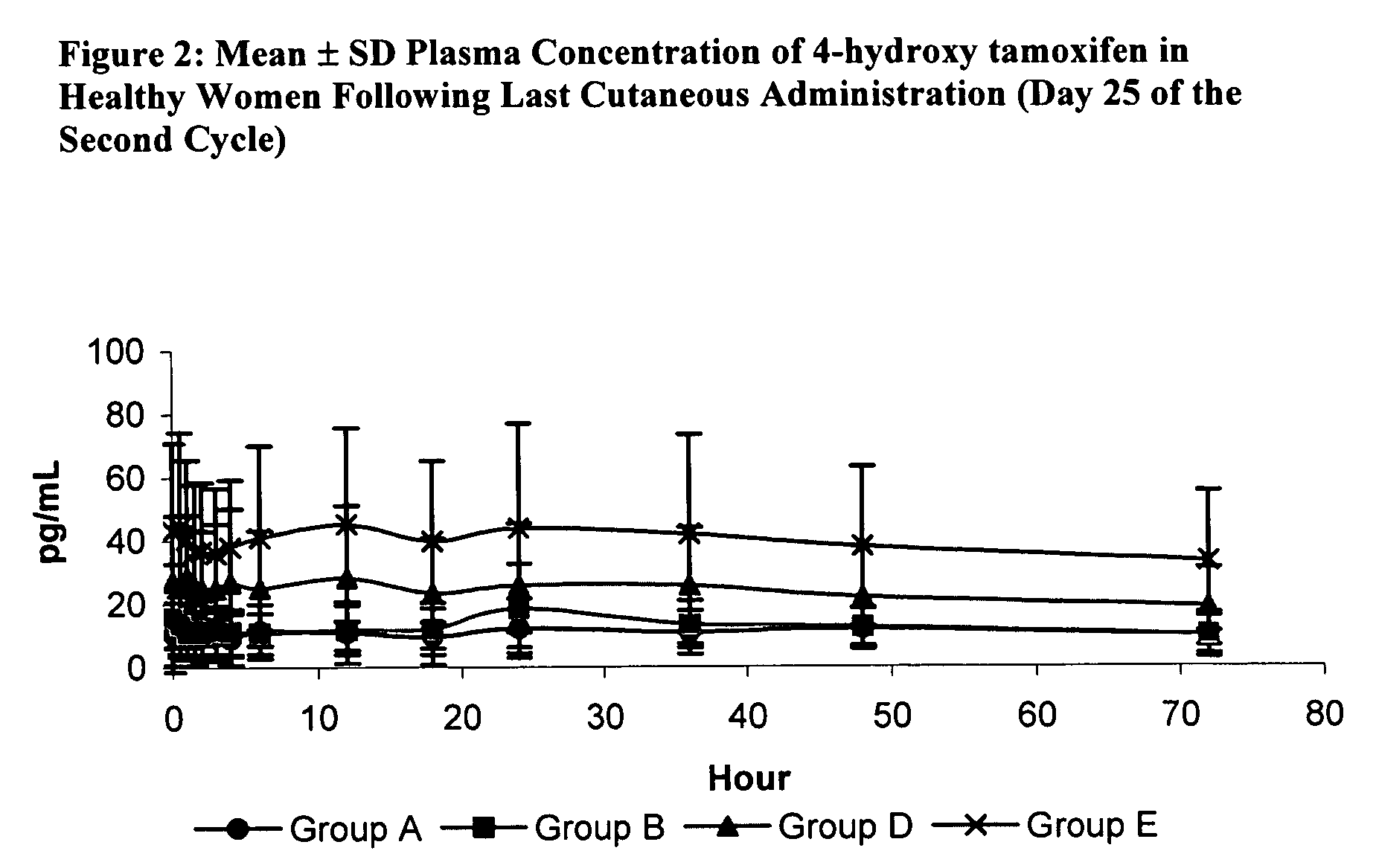
Treatment and prevention of benign breast disease with 4-hydroxy tamoxifen
The present invention provides methods for treating and preventing benign breast disease by administering 4-hydroxy tamoxifen to a patient. When percutaneously administered to a patient's breasts, 4-hydroxy tamoxifen concentrates locally, and exerts an anti-estrogenic effect. In patients with benign breast disease, this effect induces disease regression. In patients at risk for developing breast cancer, the anti-estrogenic effect prevents formation of benign breast conditions that can lead to cancer.
Owner:BESINS HEALTHCARE LUXEMBOURG (LU)
Plasma-depleted, non-red blood cell-depleted cord blood compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20060275271A1Better clinical outcomeMaximize recoveryBiocideEpidemiological alert systemsDiseaseCord blood stem cell
The umbilical cord blood (UCB) compositions of the present invention possess the unique features of having plasma that is substantially depleted from the UCB unit and red blood cells (RBC) that are not depleted from the UCB unit. Such UCB units can be prepared by a process that combines plasma depletion with cryopreservation, selection, thawing, and / or transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells to provide superior clinical outcome by maximizing post-processing cell recovery and post-thaw infusion cell dose. Methods for treating a wide variety of malignant diseases and benign diseases associated with the hematopoietic system by administering the UCB compositions of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:STEMCYTE
Suprametallogels and uses thereof
ActiveUS9447129B2Novel material propertiesHigh modulusPalladium organic compoundsNickel organic compoundsBovine respiratory diseaseGenitourinary diseases
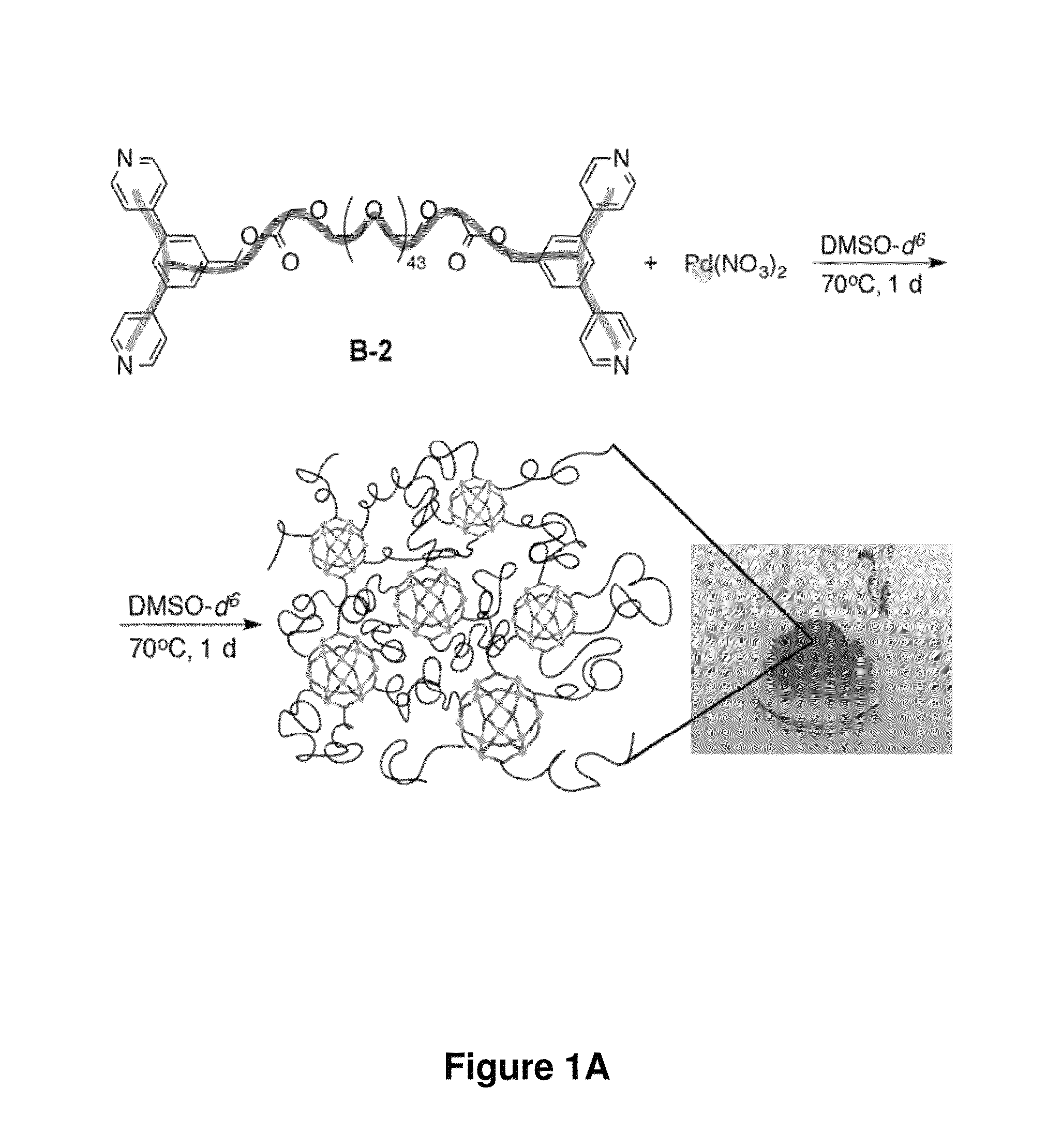
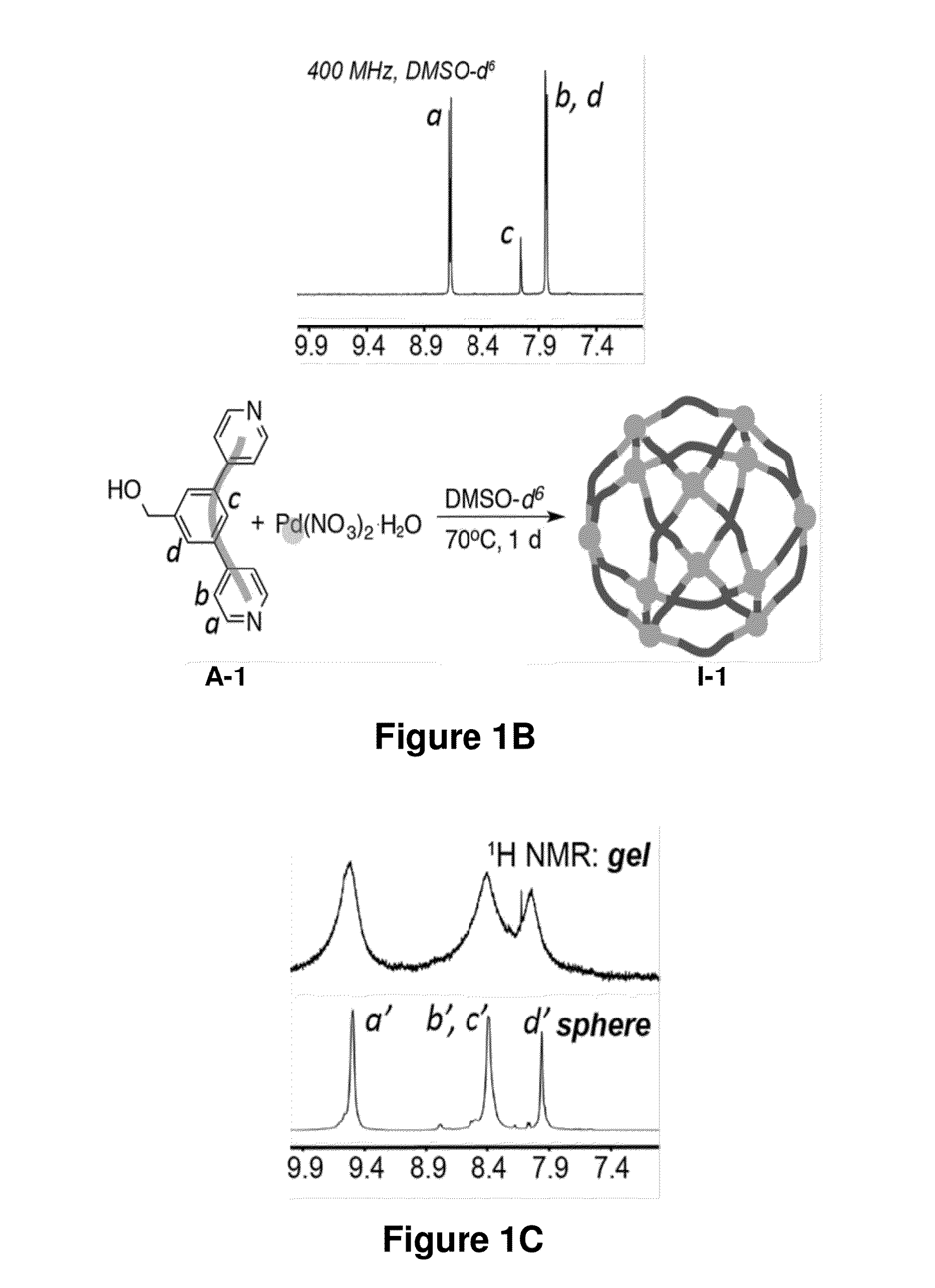
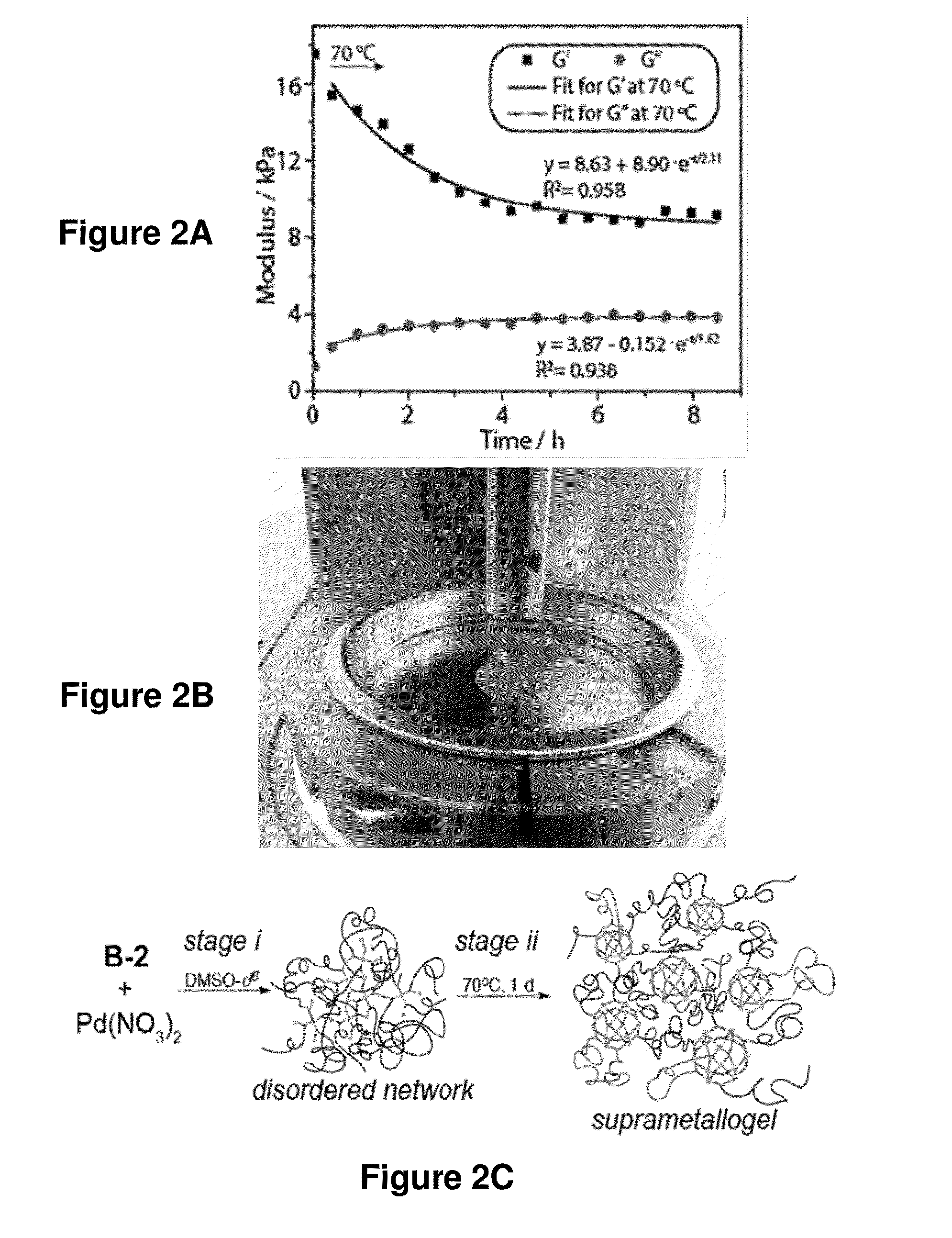
The disclosure provides nanostructures (e.g., nanospheres and nano-paddlewheels) formed through transition metal-ligand (e.g., Pd(II)-, Ni(II)-, or Fe(II)-ligand of Formula (A)) coordination and junction self-assembly. The disclosure also provides supramolecular complexes that include the nanostructures connected by divalent linkers Y. The provided supramolecular complexes are able to form gels (e.g., hydrogels). The gels are suprametallogels and exhibited excellent mechanical properties without sacrificing self-healing and showed high robustness and storage modulus. The present disclosure further provides compositions (e.g., gels) that include the nanostructures or supramolecular complexes and optionally an agent (e.g., small molecule), where the nanostructures and the nanostructure moieties of the supramolecular complexes may encapsulate and slowly release the agent. The nanostructures, supramolecular complex, and compositions may be useful in delivering an agent to a subject, tissue, or cell, as super-absorbent materials, and in treating a disease (e.g., a genetic diseases, proliferative disease (e.g., cancer or benign neoplasm), hematological disease, neurological disease, gastrointestinal disease (e.g., liver disease), spleen disease, respiratory disease (e.g., lung disease), painful condition, genitourinary disease, musculoskeletal condition, infectious disease, inflammatory disease, autoimmune disease, psychiatric disorder, or metabolic disorder).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
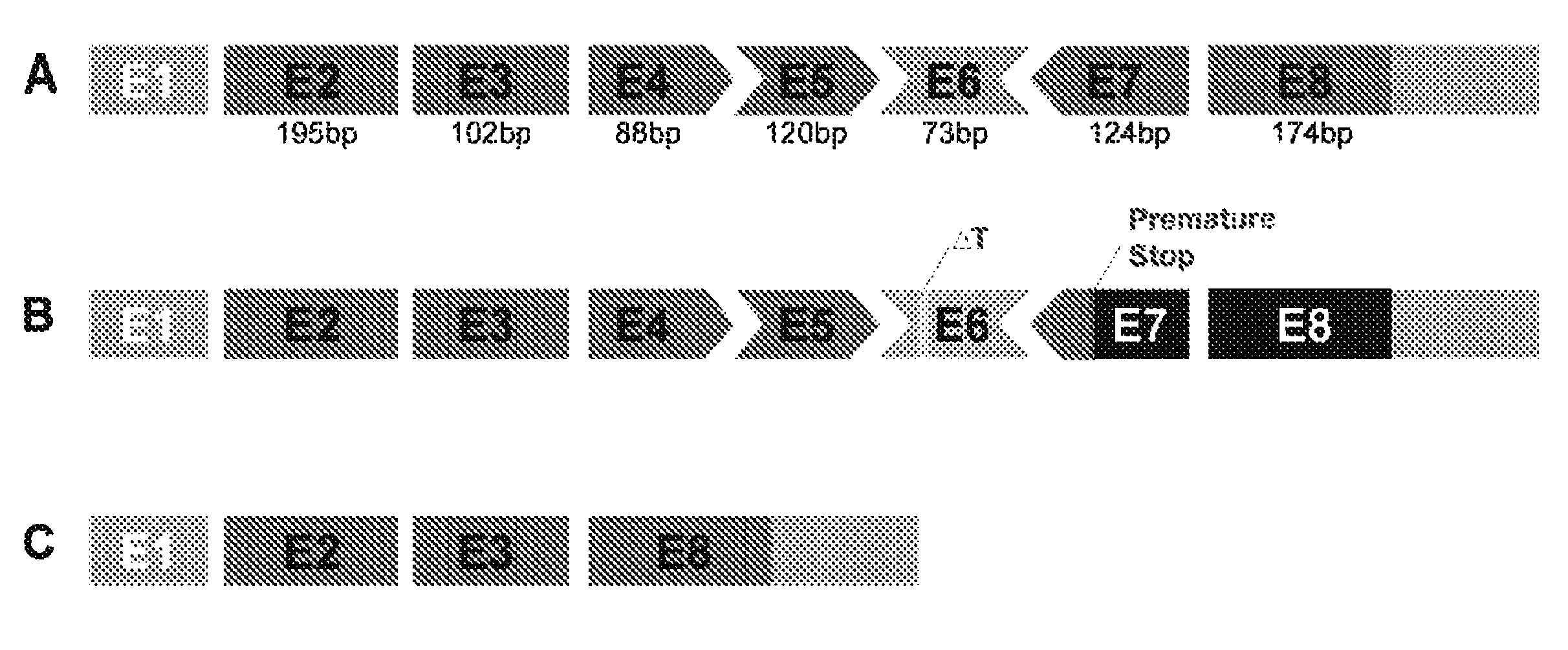
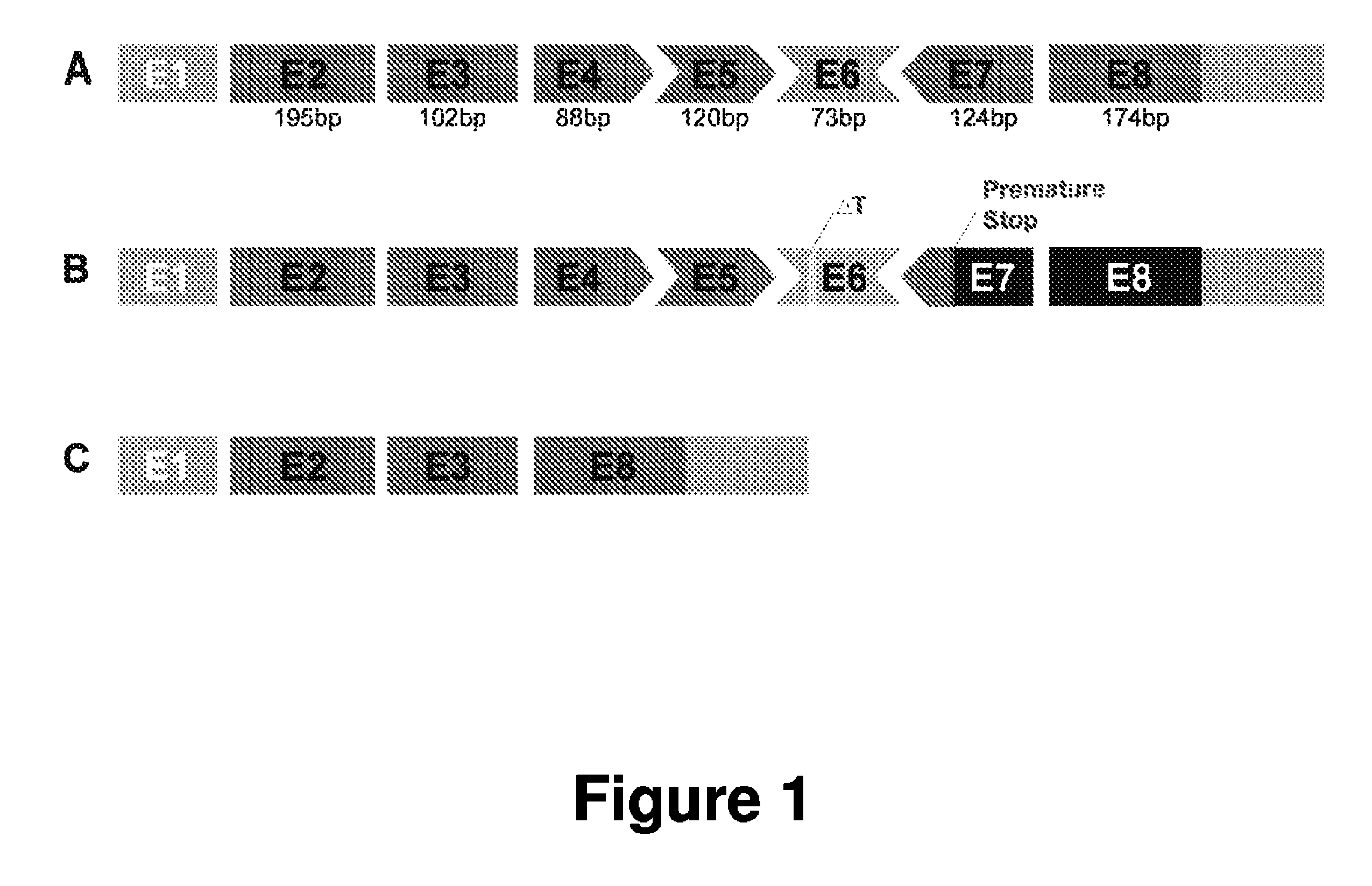
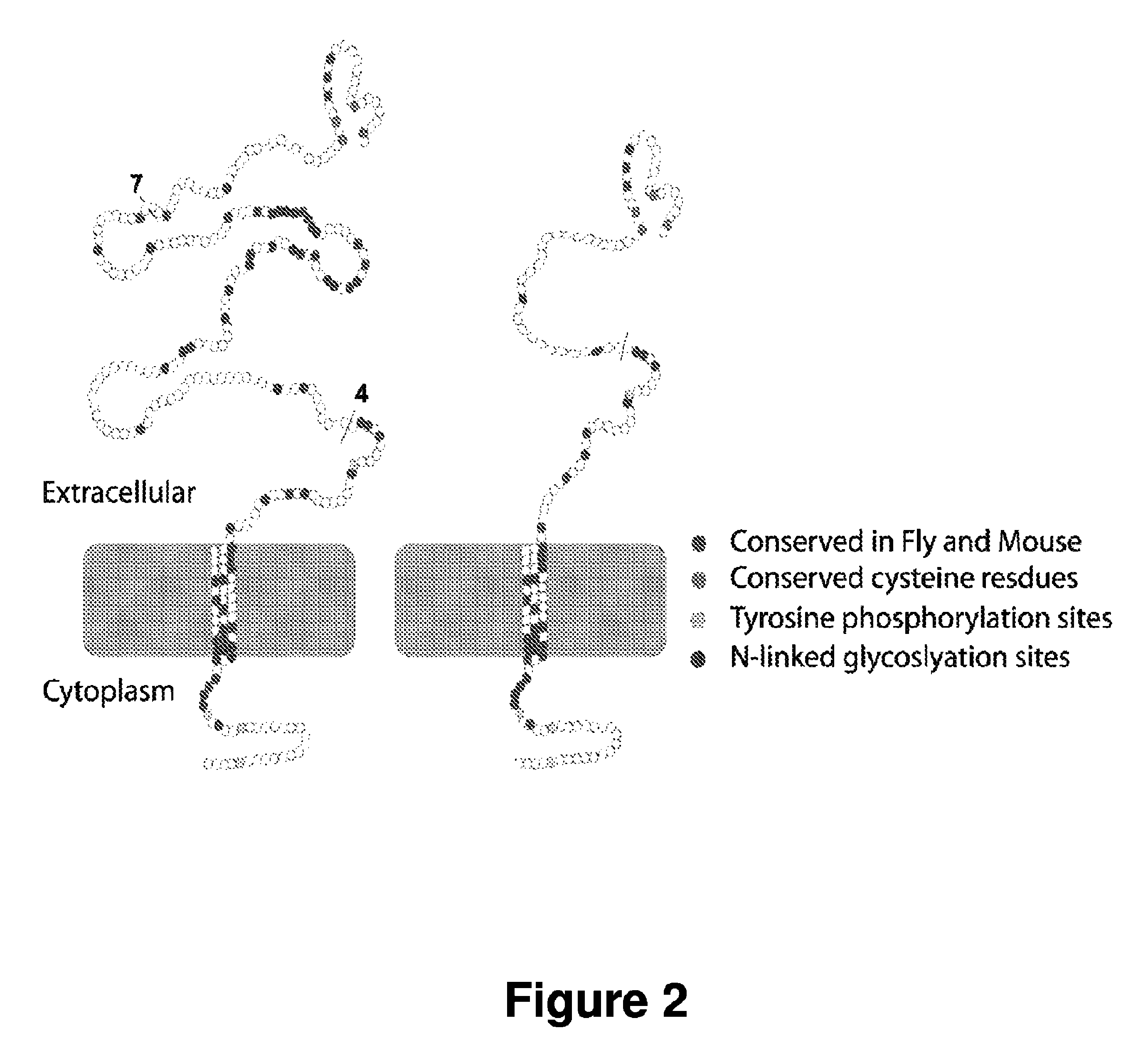
Antisense Polynucleotides to Induce Exon Skipping and Methods of Treating Dystrophies
ActiveUS20150225718A1Inhibit progressImprove muscle functionSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDiseasePolynucleotide
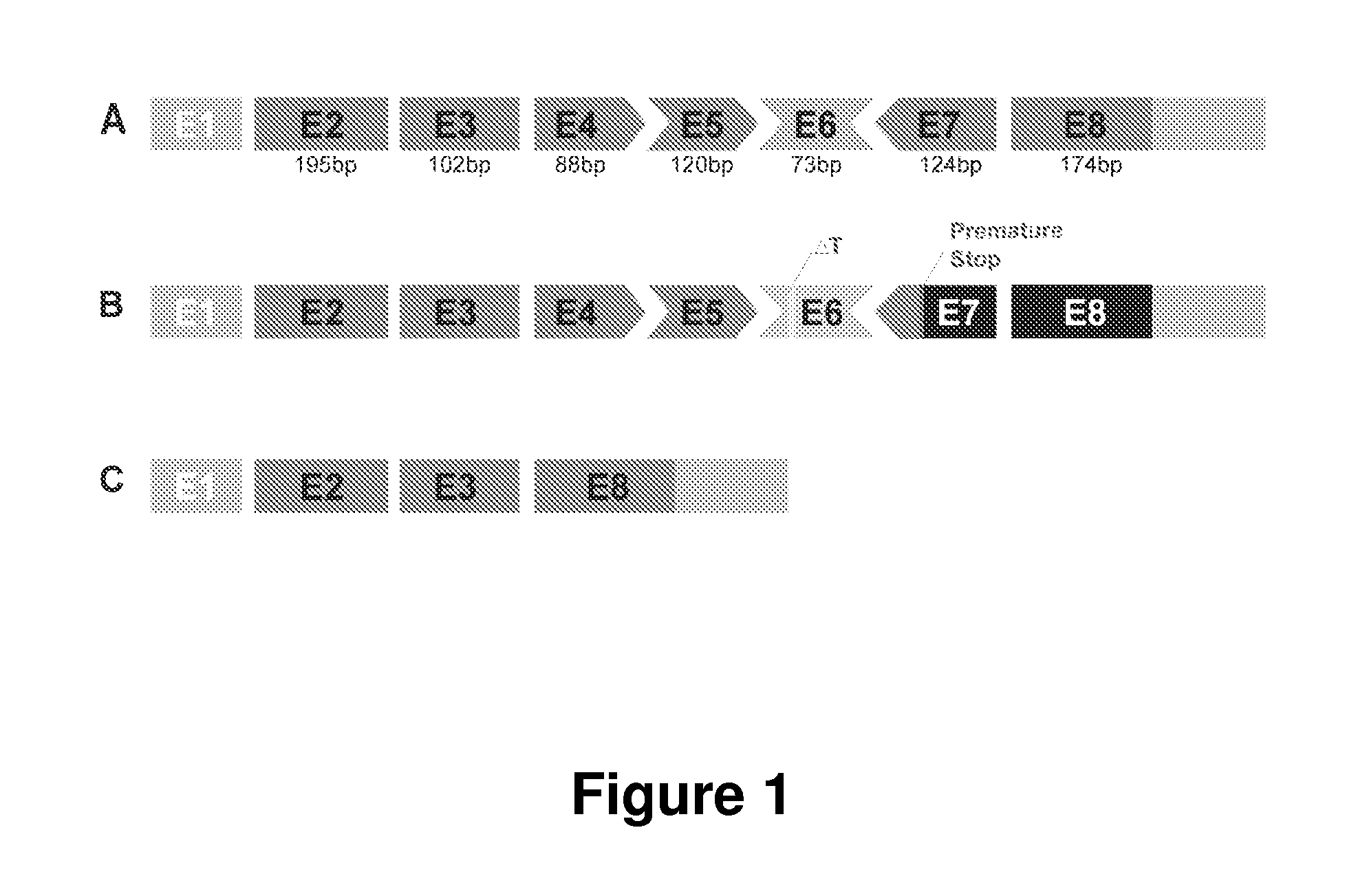
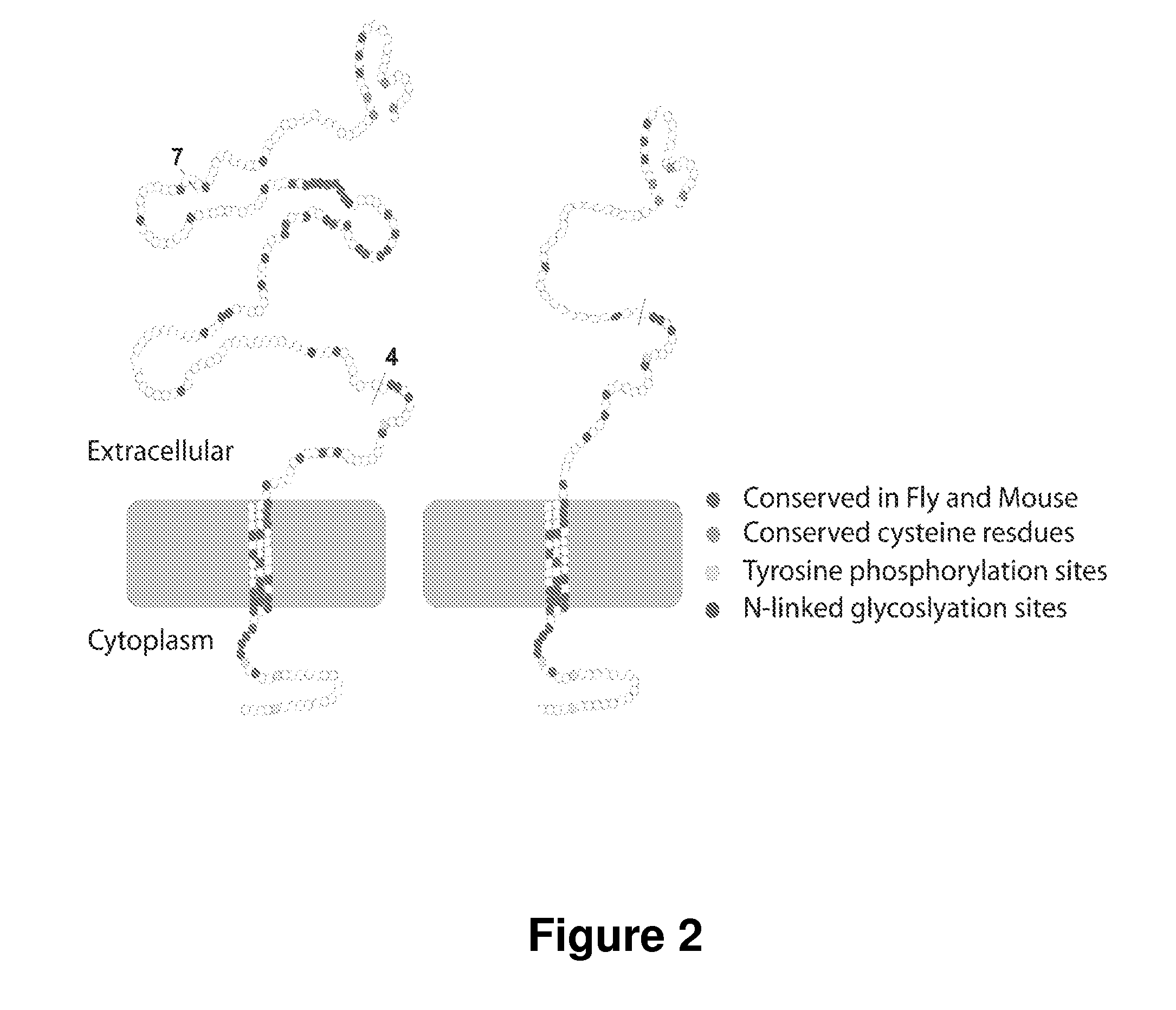
Antisense polynucleotides and their use in pharmaceutical compositions to induce exon skipping in targeted exons of the gamma sarcoglycan gene are provided, along with methods of preventing or treating dystrophic diseases such as Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. One aspect the disclosure provides an isolated antisense polynucleotide wherein the polynucleotide specifically hybridizes to an exon target region of a gamma sarcoglycan RNA, wherein the exon is selected from the group consisting of exon 4 (SEQ ID NO:1), exon 5 (SEQ ID NO: 2), exon 6 (SEQ ID NO: 3), exon 7 (SEQ ID NO: 4) and a combination thereof. In some embodiments, the antisense polynucleotide cannot form an RNase H substrate, and in further embodiments the antisense polynucleotide comprises a modified polynucleotide backbone.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
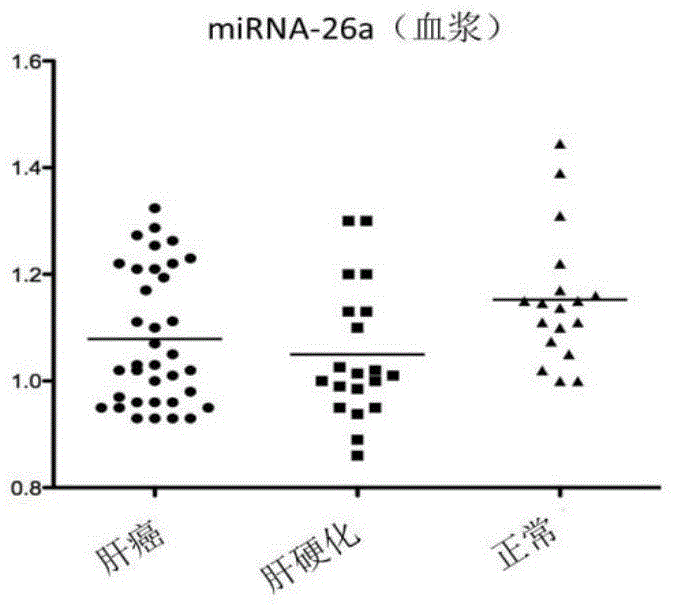
Blood miRNA marker related to liver cancer and application thereof
InactiveCN104152452AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseMirna microarray
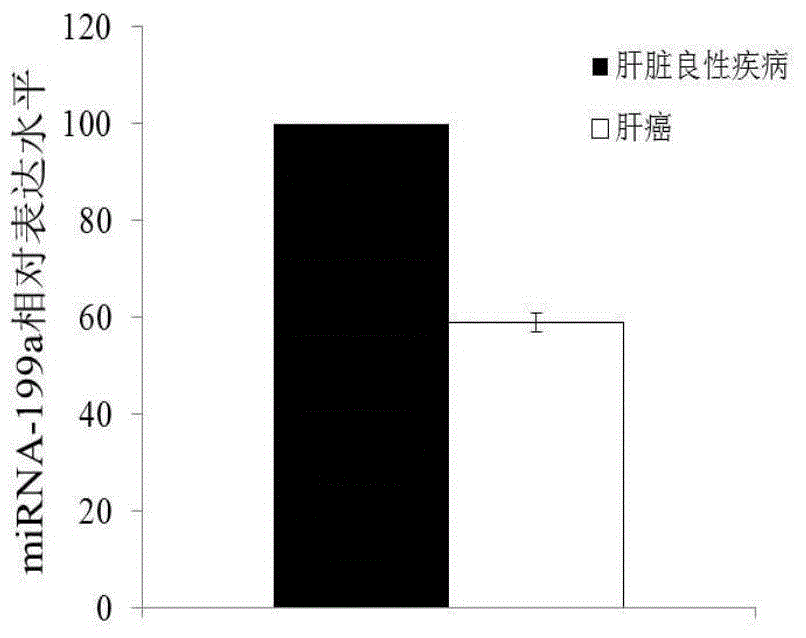
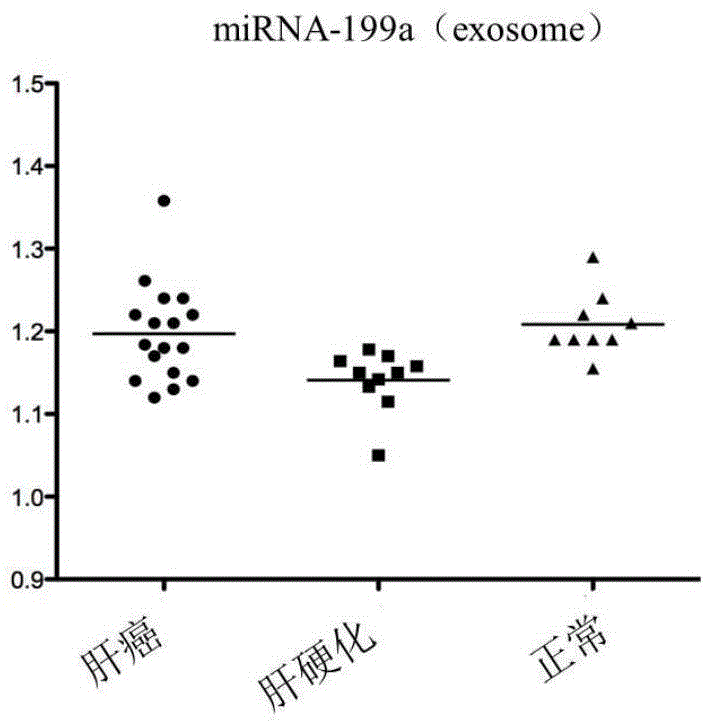
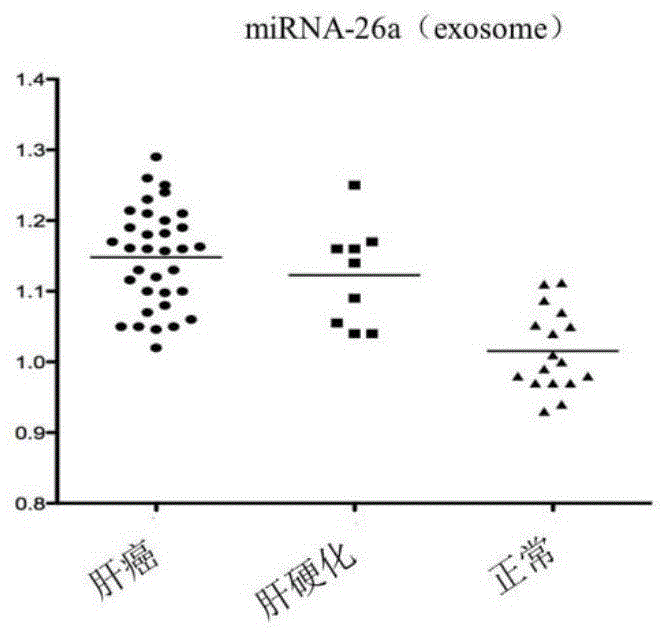
The invention discloses a blood miRNA marker related to liver cancer and an application thereof. The marker is the combination of tumor-induced exosome sourced miRNA-26a and miRNA-199a in human blood. According to the invention, tumor-induced exosome in peripheral blood of liver cancer patient and liver benign disease patient can be separated and purified, miRNA of two expression difference can be analyzed and screened by a miRNA chip, and the above conclusion is passed by a QPCR verification. The marker and its detection reagent can be used for preparing a diagnostic kit, which can be used for early diagnosis of liver cancer.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method of treating a hematopoietic associated disease or disorder with plasma-depleted, but not erythrocyte-depleted cord blood compositions
ActiveUS8048619B2Address bad outcomesMaximize recoveryBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCord blood stem cell
The umbilical cord blood (UCB) compositions of the present invention possess the unique features of having plasma that is substantially depleted from the UCB unit and red blood cells (RBC) that are not depleted from the UCB unit. Such UCB units can be prepared by a process that combines plasma depletion with cryopreservation, selection, thawing, and / or transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells to provide superior clinical outcome by maximizing post-processing cell recovery and post-thaw infusion cell dose. Methods for treating a wide variety of malignant diseases and benign diseases associated with the hematopoietic system by administering the UCB compositions of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:STEMCYTE
Plasma-depleted, non-red blood cell-depleted cord blood compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20080166324A9Address bad outcomesMaximize recoveryBiocideEpidemiological alert systemsDiseaseCord blood stem cell
The umbilical cord blood (UCB) compositions of the present invention possess the unique features of having plasma that is substantially depleted from the UCB unit and red blood cells (RBC) that are not depleted from the UCB unit. Such UCB units can be prepared by a process that combines plasma depletion with cryopreservation, selection, thawing, and / or transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells to provide superior clinical outcome by maximizing post-processing cell recovery and post-thaw infusion cell dose. Methods for treating a wide variety of malignant diseases and benign diseases associated with the hematopoietic system by administering the UCB compositions of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:STEMCYTE
Method of analyzing non-complexed forms of prostate specific antigen in a sample to improve prostate cancer detection
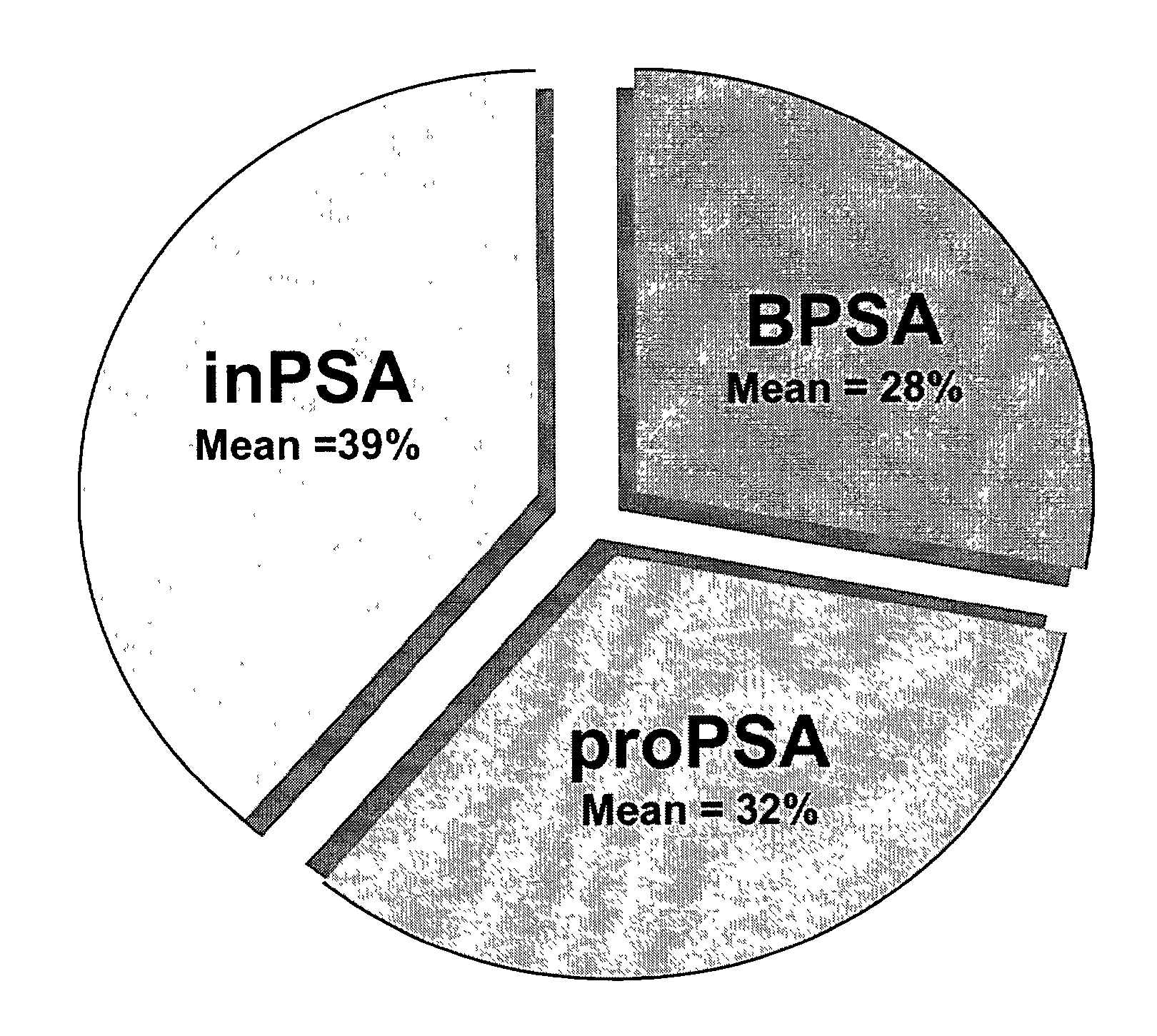
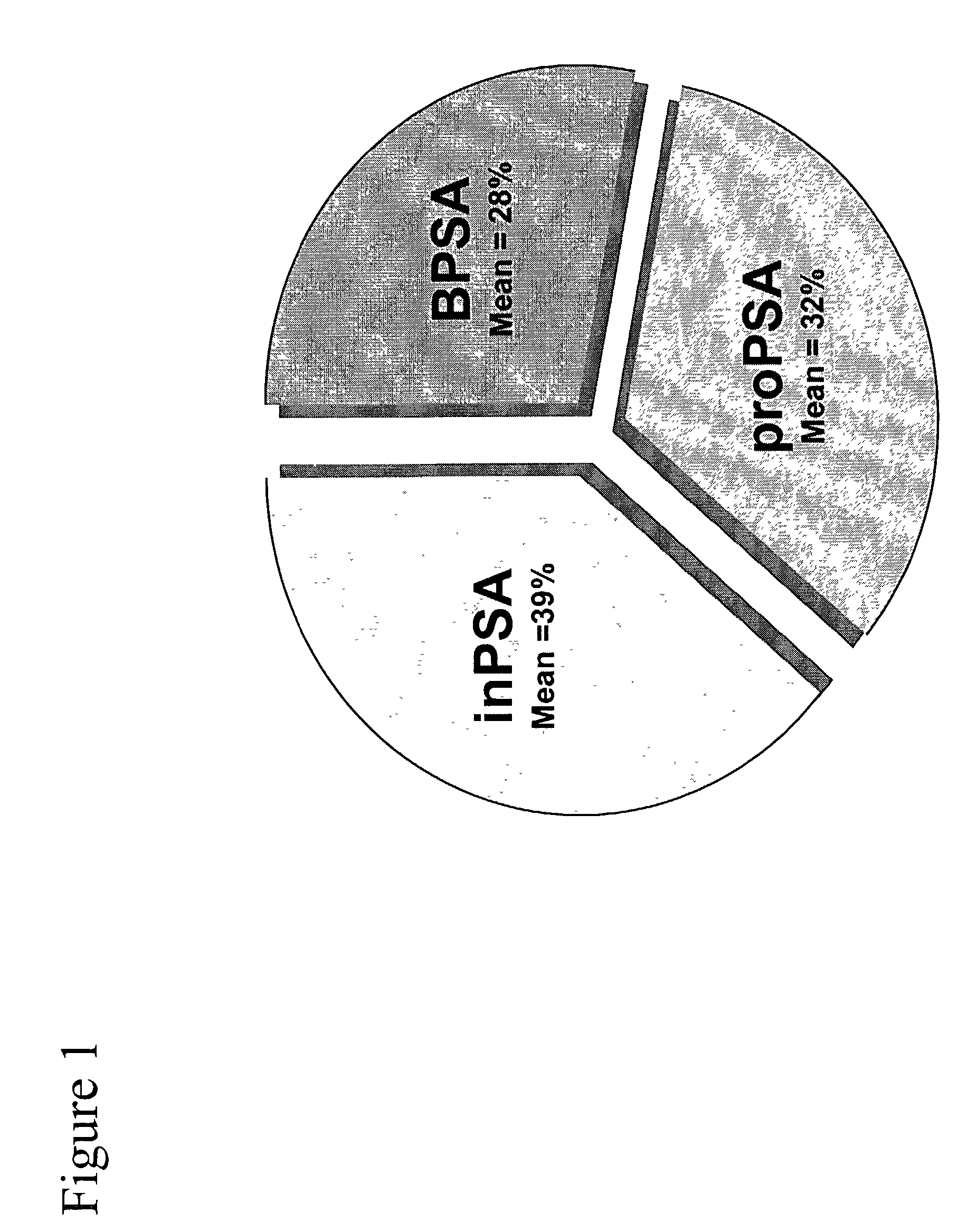
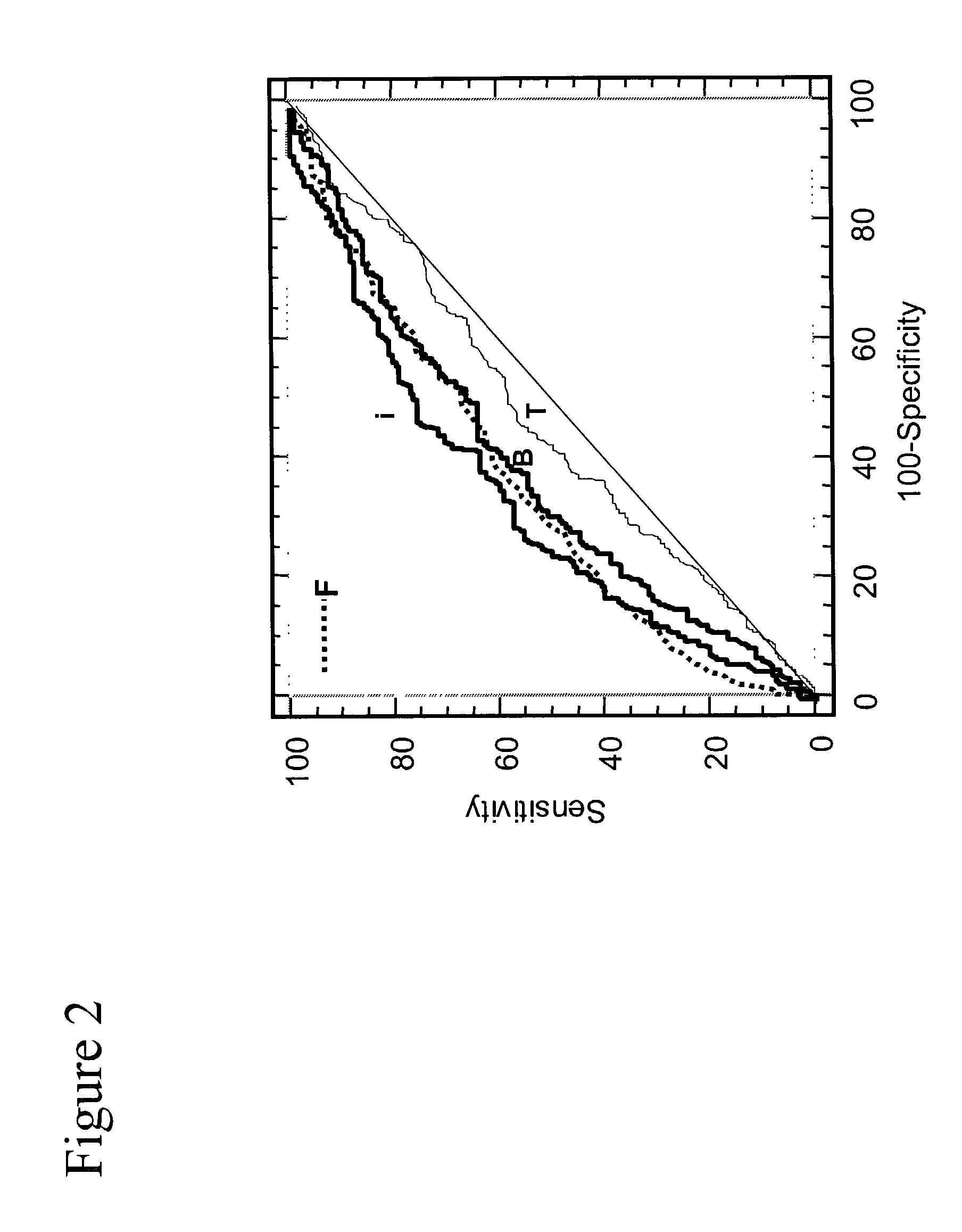
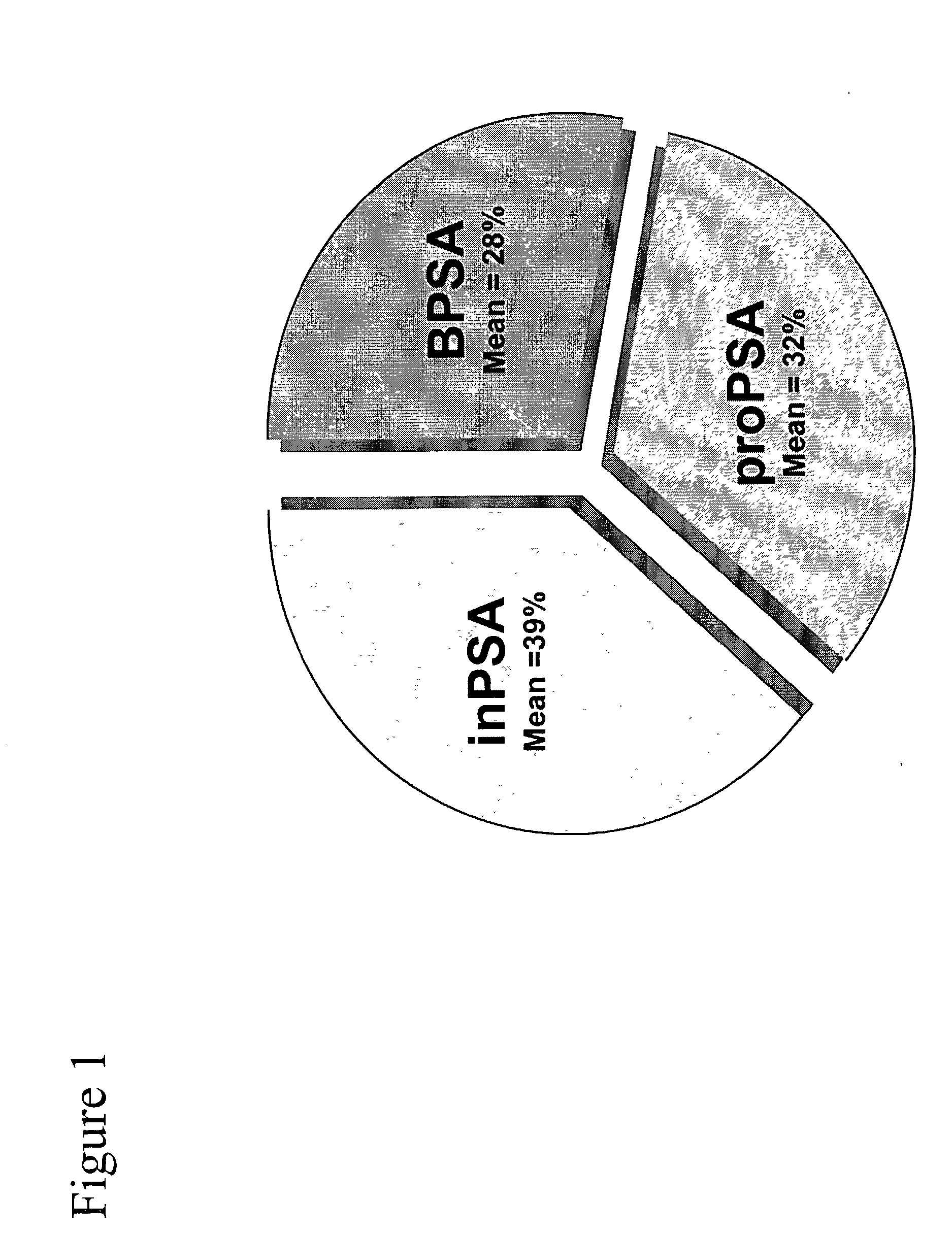
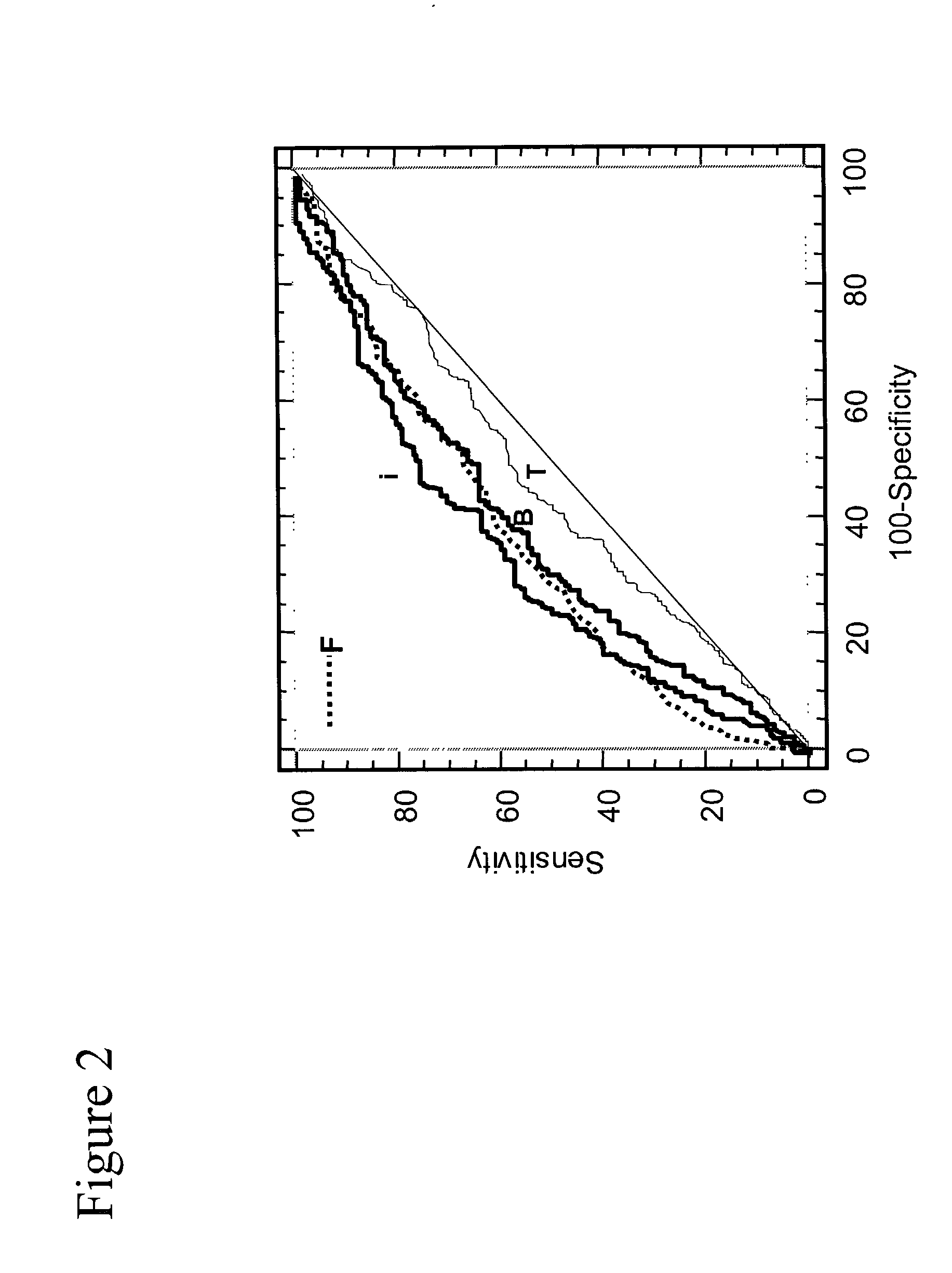
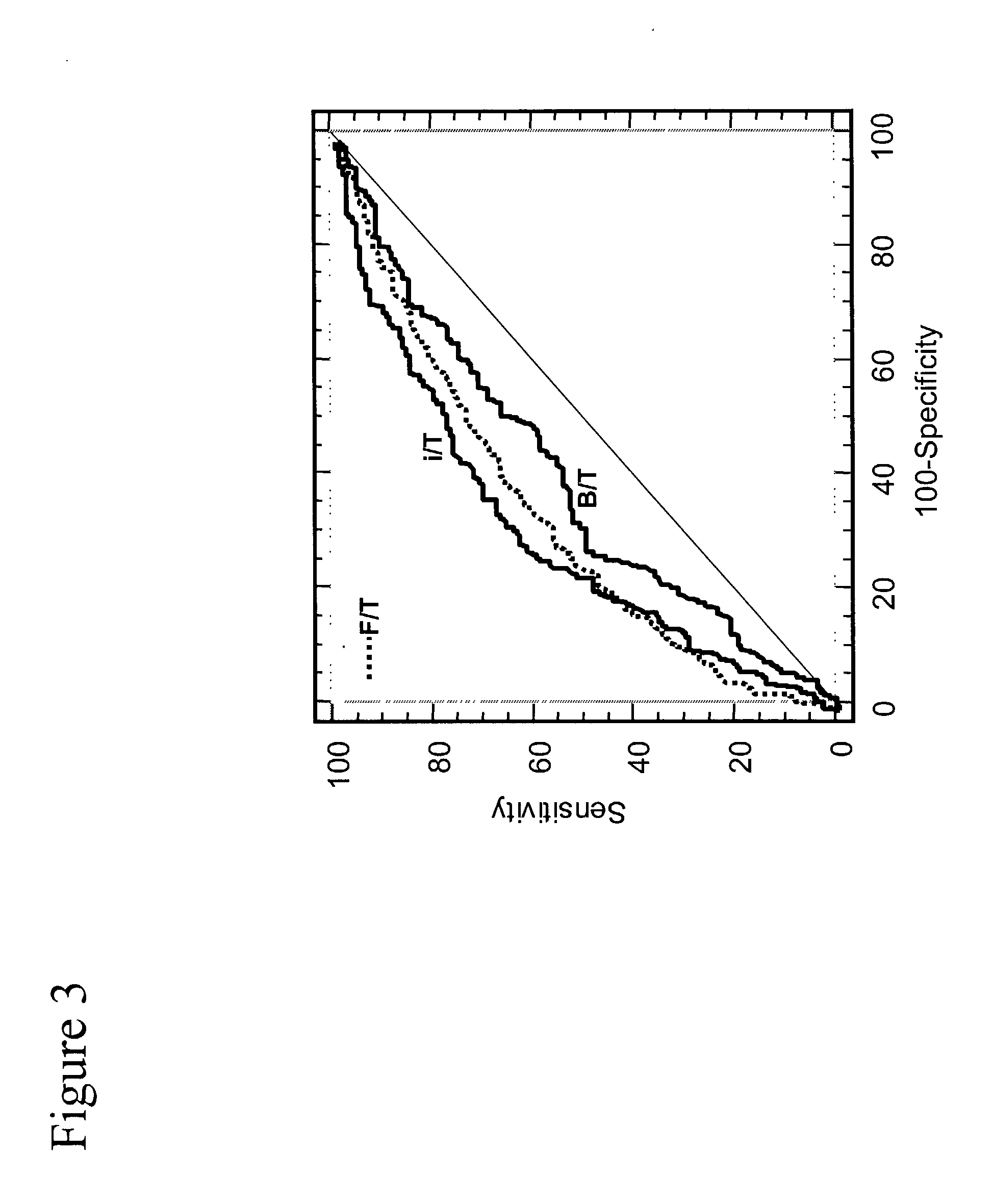
Assays for detecting and determining the presence of prostate cancer is provided. The assays are capable of detecting prostate cancer in the population of men with a significantly higher ratio of free PSA to total PSA. The assays are also capable of detecting prostate cancer in the population of men with a low amount of total PSA, i.e., in the range of 2 to 4 ng / ml. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, the assay includes the steps of (a) determining the amount of total PSA contained in a biological sample from the patient, (b) determining the amount of free PSA in the sample; and calculating the ratio of the free PSA to the total PSA, (c) determining the amount of pPSA in the sample, (d) determining the amount of BPSA in the sample, (e) determining the amount of inPSA in the sample, and (f) correlating the amount of inPSA contained in the sample to the presence of prostate cancer in the patient by comparing the amount of inPSA to a predetermined value established with control samples of known cancer and benign disease diagnosis, based on both the level of total PSA and the % free PSA.
Owner:HYBRITECH
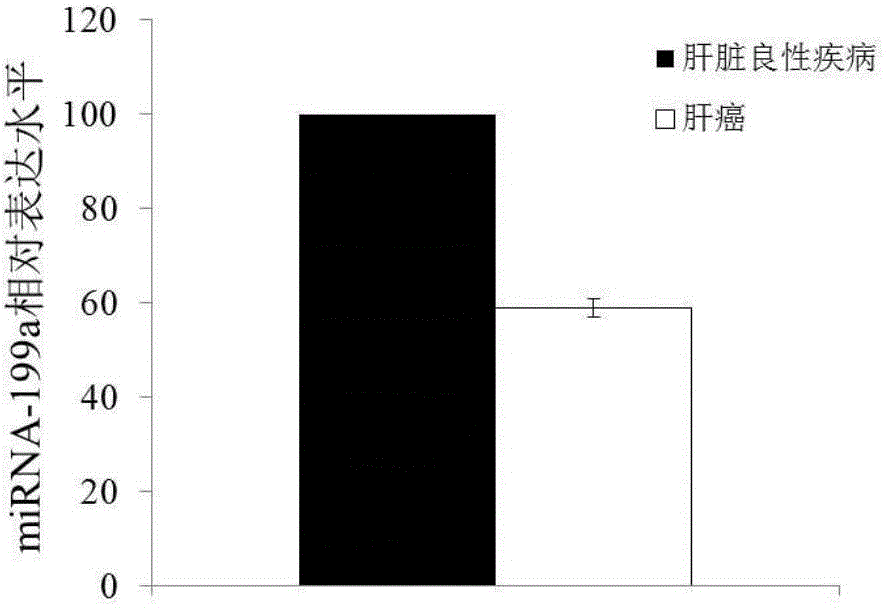
Application of miRNA-199a in preparation of diagnostic kit
InactiveCN104152567AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMirna microarrayWilms' tumor
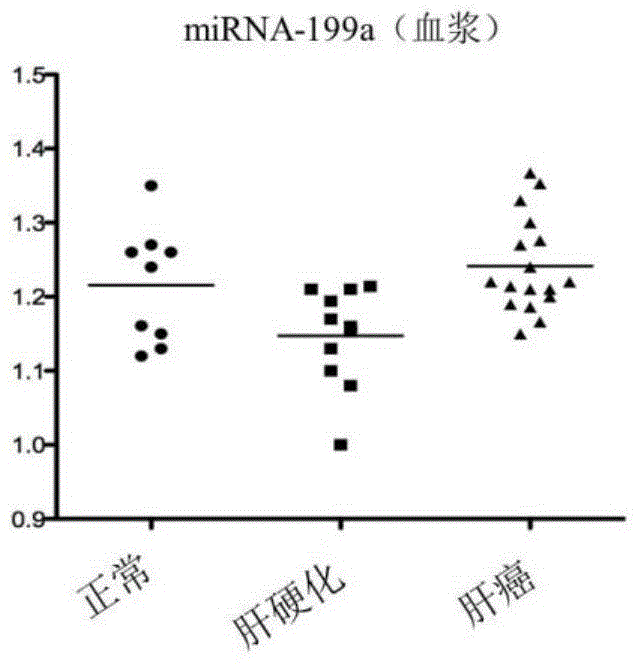
The invention discloses a blood miRNA marker related to human liver cancer and an application. The marker is miRNA-199a from exosome. According to the invention, tumor-induced exosome in peripheral blood of liver cancer patient and liver benign disease patient can be separated and purified, miRNA-199a for expressing difference can be analyzed and screened by a miRNA chip, and the above conclusion is verified through QPCR. The marker and its detection reagent can be used for preparing a diagnostic kit and used for early diagnosis of liver cancer.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Composition for improving premature ovarian failure, preparation method therefor and application of composition
PendingCN113244272AImprove premature agingReduce inflammationCulture processUnknown materialsDiseasePhysiology
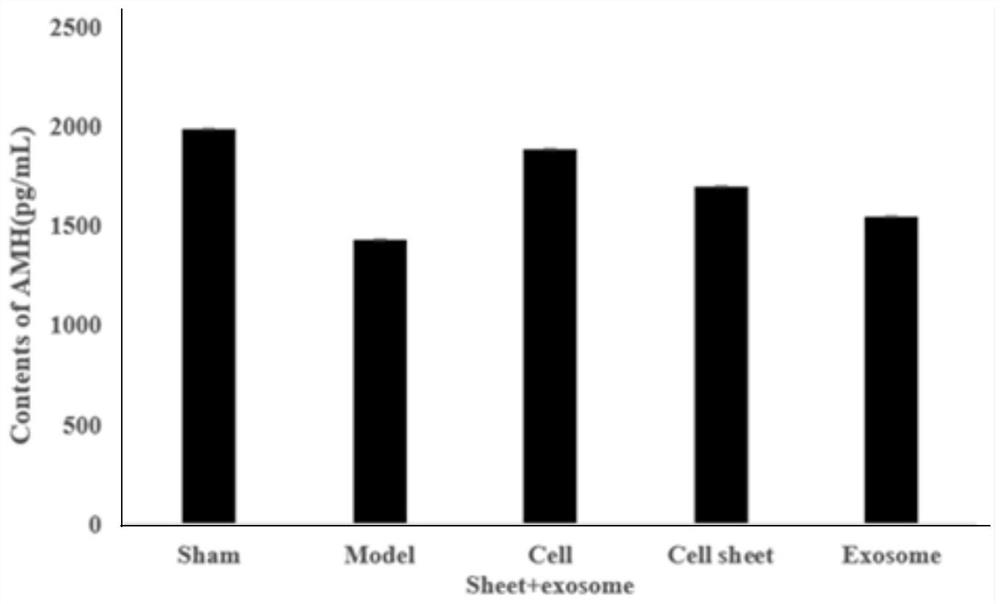
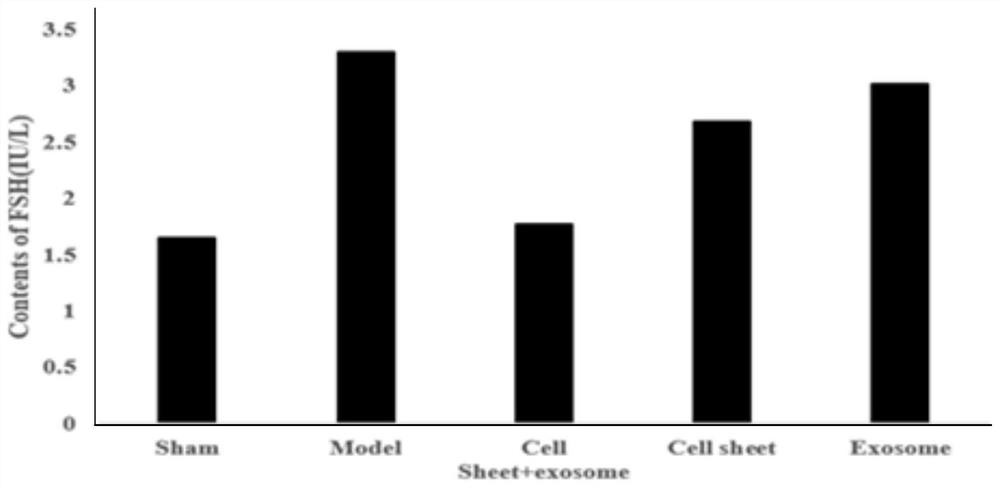
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicines and particularly relates to a composition for improving premature ovarian failure, a preparation method therefor and application of the composition. According to the composition for improving the premature ovarian failure, provided by the invention, an in-vitro-constructed human uterine endometrium stem-cell cell membrane and a mesenchymal stem cell exosome are used in a compounded manner, thus, the development of ovarian follicles can be promoted, ovaries can be promoted to secrete an anti-Mullerian hormone, an ovarian follicle generator promoting level can be regulated, the apoptosis of ovarian cells can be inhibited, the adverse reserve function disease of the ovaries can be improved, the effect of improving primary or secondary premature ovarian failure is good, and thus, a new way of think is provided for clinically treating ovarian insufficiency and polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Owner:陕西中鸿科瑞再生医学研究院有限公司
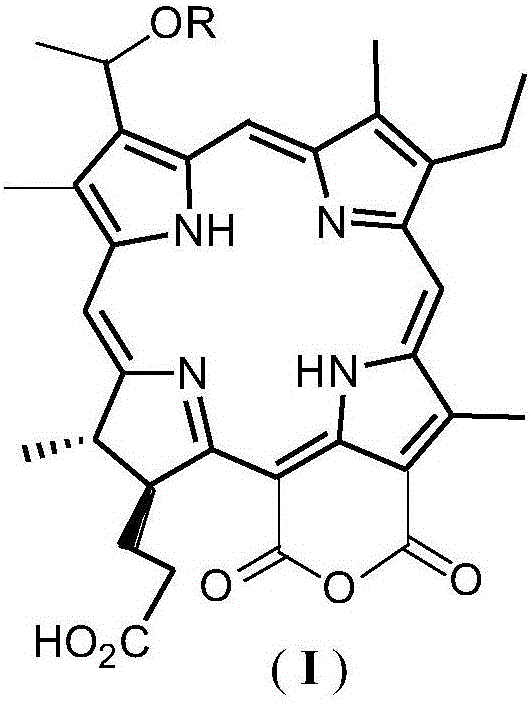
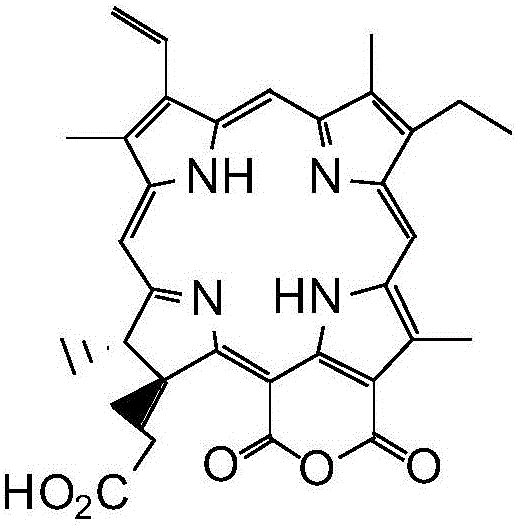
Purpurin-18 ether derivative, and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN106083872AExcellent PDT killing effectSenses disorderOrganic chemistryChemical structureSenile macular degeneration
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and concretely relates to a novel dihydroporphine photosensitizer - purpurin-18 ether derivative, a preparation method thereof, and a use of the purpurin-18 ether derivative in the preparation of antitumor medicines. The chemical structure of the purpurin-18 ether derivative is represented by general formula (I) shown in the description. The purpurin-18 ether derivative has the advantages of high efficiency and low toxicity, and can be used for preparing new photodynamic therapy medicines of cancers, photodynamic therapy medicines of benign diseases, such as senile macula lutea denaturation and nevus flammeus, and photodynamic therapy medicines of condyloma acuminatum.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Antisense polynucleotides to induce exon skipping and methods of treating dystrophies
ActiveUS9499817B2Inhibit progressImprove muscle functionSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDiseaseNucleotide
Antisense polynucleotides and their use in pharmaceutical compositions to induce exon skipping in targeted exons of the gamma sarcoglycan gene are provided, along with methods of preventing or treating dystrophic diseases such as Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. One aspect the disclosure provides an isolated antisense polynucleotide wherein the polynucleotide specifically hybridizes to an exon target region of a gamma sarcoglycan RNA, wherein the exon is selected from the group consisting of exon 4 (SEQ ID NO:1), exon 5 (SEQ ID NO: 2), exon 6 (SEQ ID NO: 3), exon 7 (SEQ ID NO: 4) and a combination thereof. In some embodiments, the antisense polynucleotide cannot form an RNase H substrate, and in further embodiments the antisense polynucleotide comprises a modified polynucleotide backbone.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Metabolomics for diagnosing pancreatic cancer
The present disclosure is drawn to methods of diagnosing and classifying pancreatic cancer by examining the expression of particular metabolites that distinguish this disease state from benign disease and periampullary adenocarcinoma.
Owner:UTI LLP
Non-conventional Cellular Based Immunotherapy
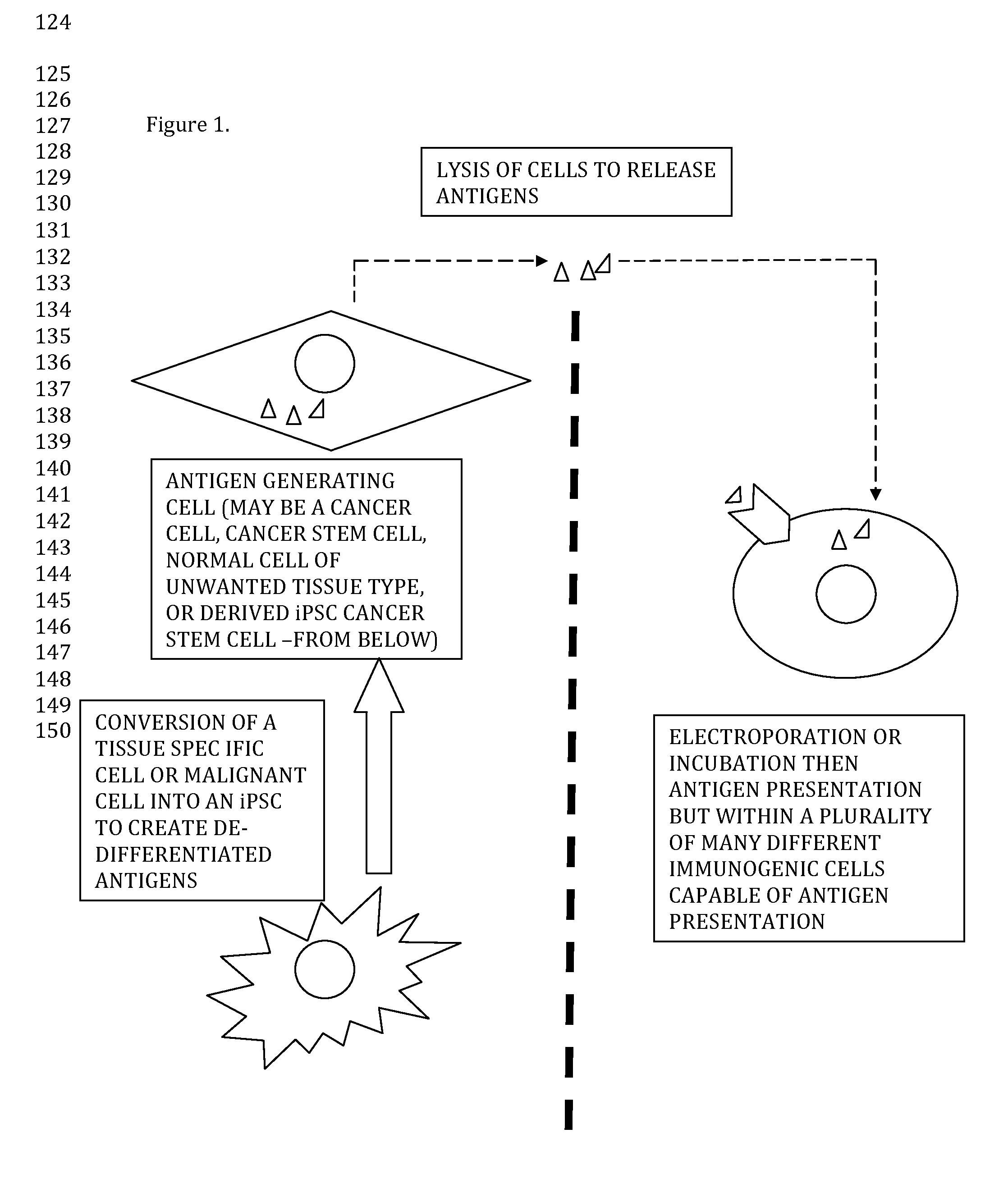
The proposed patent is a method of immunotherapy wherein unique and novel sources of antigen generating organisms / viruses / cells are incubated or electroporated into further novel immunogenic cells. This method may be used for cancer therapy or therapy of benign disease. This method may also be used for immunization from infectious organisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses or parasites. An aliquot of cells or materials obtained from the antigen generating component or electroporated immunogenic cells may be preserved long-term (i.e. cryopreservation or lyophilization or desiccation) for the purpose of forming a library or archive for future therapy or drug development / research.Most importantly non-obviousness of this patent is clearly elucidated in the proposed method of immunotherapy whereby cancer stem cells (either directly isolated in culture or created by an induced process like iPSCs) are lysed for their protein antigens and electroporated or incubated with novel immunogenic cells (not dendritic cells) such as SVF and given back to the same patient in an autologous and personalized fashion. (In this way both MHC I and MHC II pathways may be utilized and a plurality of non-dendritic cells with antigen presenting capabilities are advantageously used in a plural immune like fashion raising immunogenicity through multiple novel and unique epitopes.
Owner:WU ALLAN YANG
Plasma-depleted, non-red blood cell-depleted cord blood compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS20080008693A1Better clinical outcomeMaximize recoveryBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCord blood stem cell
The umbilical cord blood (UCB) compositions of the present invention possess the unique features of having plasma that is substantially depleted from the UCB unit and red blood cells (RBC) that are not depleted from the UCB unit. Such UCB units can be prepared by a process that combines plasma depletion with cryopreservation, selection, thawing, and / or transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells to provide superior clinical outcome by maximizing post-processing cell recovery and post-thaw infusion cell dose. Methods for treating a wide variety of malignant diseases and benign diseases associated with the hematopoietic system by administering the UCB compositions of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:STEMCYTE
Bionic heating traditional Chinese medicine breast pad and application thereof
InactiveCN106075288AConvenient for free activitiesImprove protectionHydroxy compound active ingredientsMedical devicesSemenMammary gland structure
The invention discloses a bionic heating traditional Chinese medicine breast pad and application thereof. The breast pad comprises a heating breast pad body and traditional Chinese medicine unguent, the traditional Chinese medicine unguent is prepared from 10-15 parts of medicine raw material, 10-15 parts of rhizoma cyperi, 10-15 parts of radix curcuma zedoaria, 15-20 parts of prunella spike, 60-100 parts of semen raphani, 60-100 parts of semen brassicae, 10-15 parts of radix angelicae and 5-10 parts of borneol. The unguent formed by combining the eight kinds of precious traditional Chinese medicine is prepared into the heating breast pad which is used for preventing and treating woman breast benign diseases and improving clinical symptoms. An improved self-heating material can promote effective components of the medicine to permeate into breasts through pores of the human skin to dredge blood vessels of the breasts and meridian vessels of mammary gland tubes, and the effects of soothing the liver, regulating vital energy, relieve swelling and pain and softening node and lumps are achieved by regulating mammary gland microcirculation.
Owner:王志宇
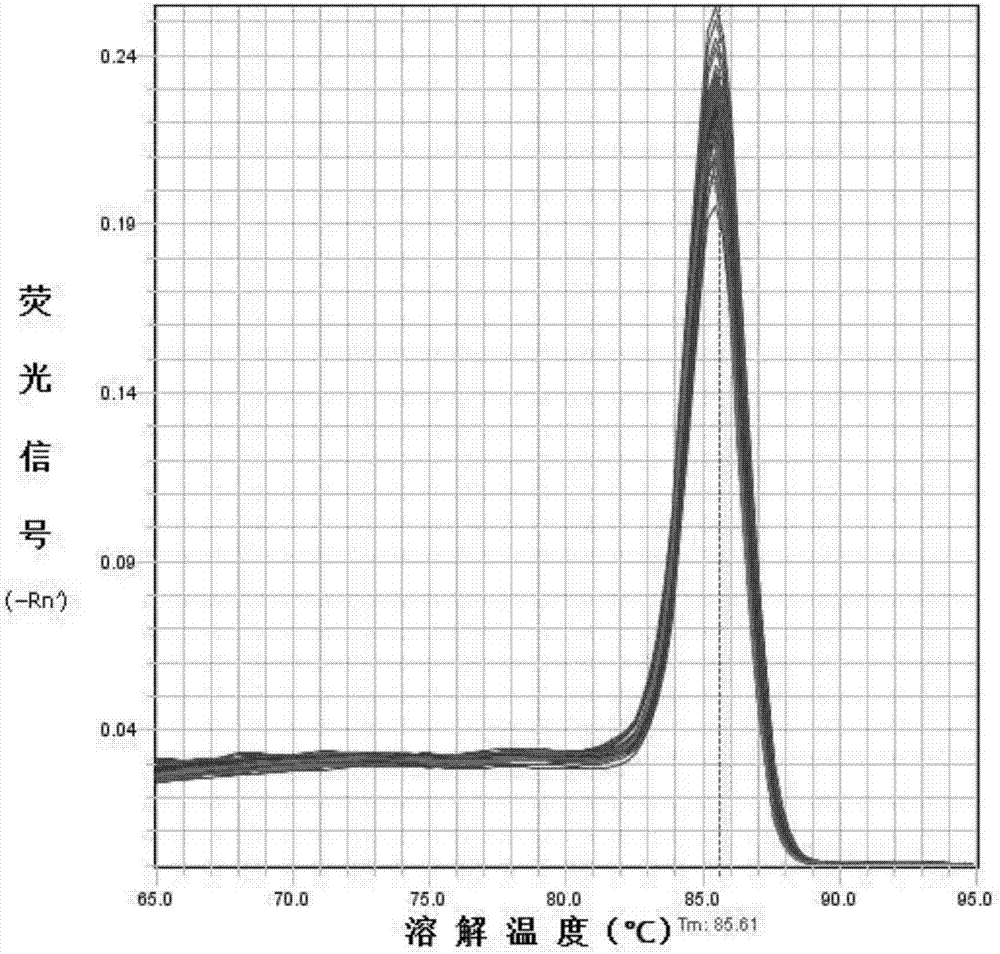
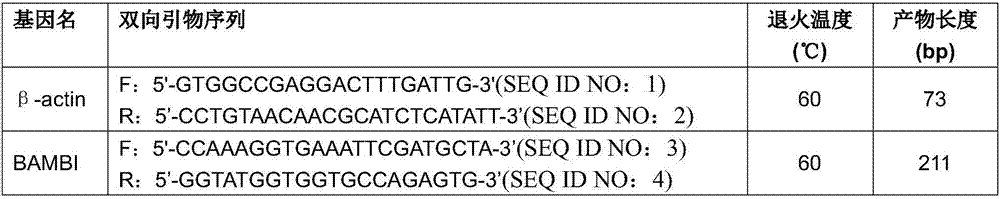
Application of BAMBI as nasopharyngeal carcinoma maker
ActiveCN107267642AHigh expressionEasy to obtainMicrobiological testing/measurementChronic nasopharyngitisStatistical analysis
The invention discloses an application of BAMBI as a nasopharyngeal carcinoma maker. Through experiment researches by an applicant and a whole team for three years, researches on tissues and serums of 38 nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients, 12 chronic nasopharyngitis patients and 49 healthy volunteers are carried out, the researches show that the nasopharyngeal tissue BAMBI expression amount of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients is obviously increased, the expression amount of nasopharyngitis (nasopharyngitis is common benign disease) is relatively low, wherein p equals 0.0038, and the difference between nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngitis is obvious. The serum BAMBI of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients is obviously increased, through statistical analysis, t equals 2.639, and p equals 0.012. No matter in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissue or nasopharyngeal carcinoma serum, BAMBI presents up-regulated expression, so that the detection of BAMBI can be taken as a nasopharyngeal carcinoma molecular screening index.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE HOSPITAL
Plasma-depleted, non-red blood cell-depleted umbilical cord blood compositions and methods of use
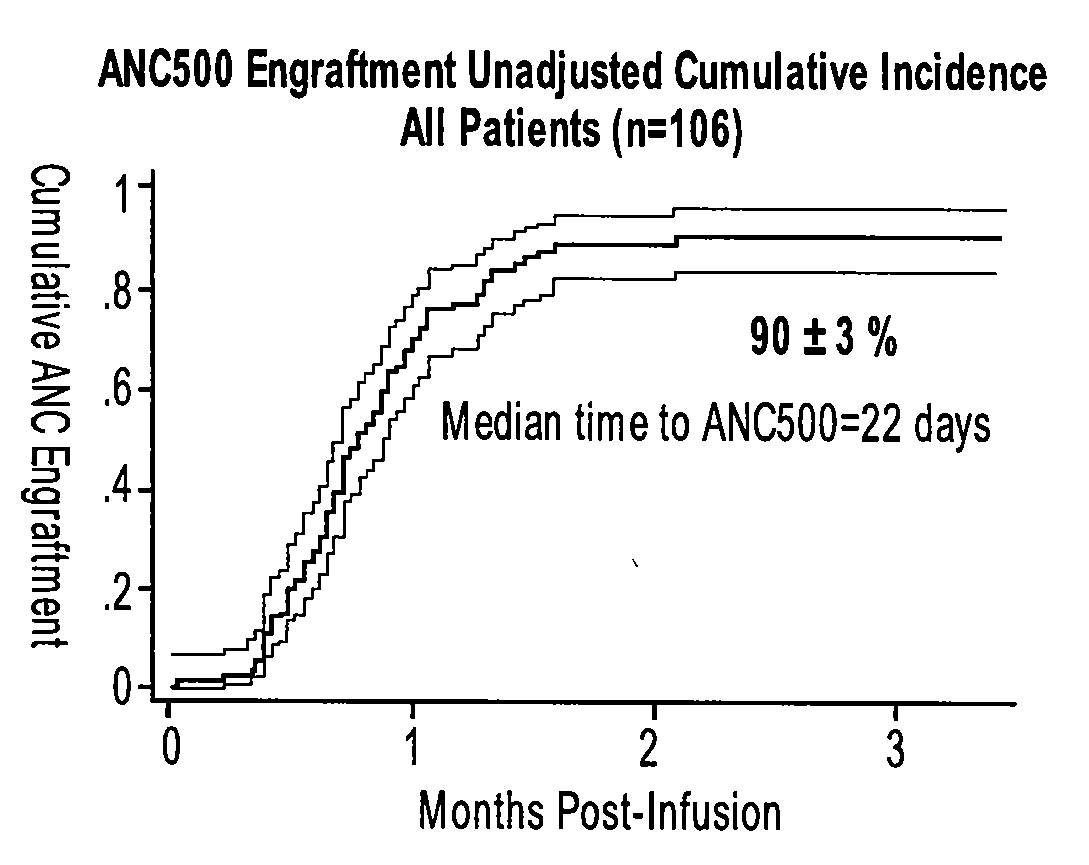
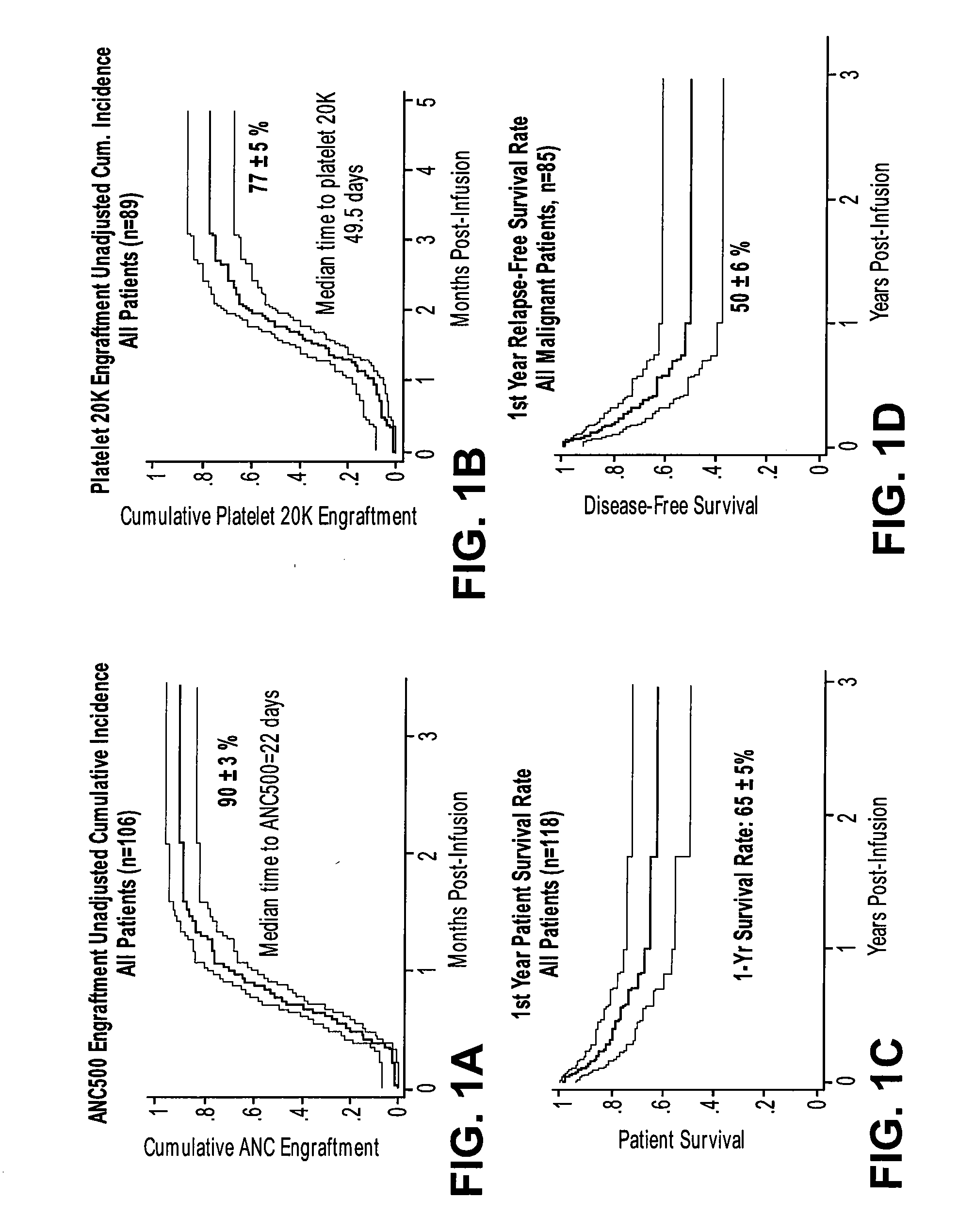
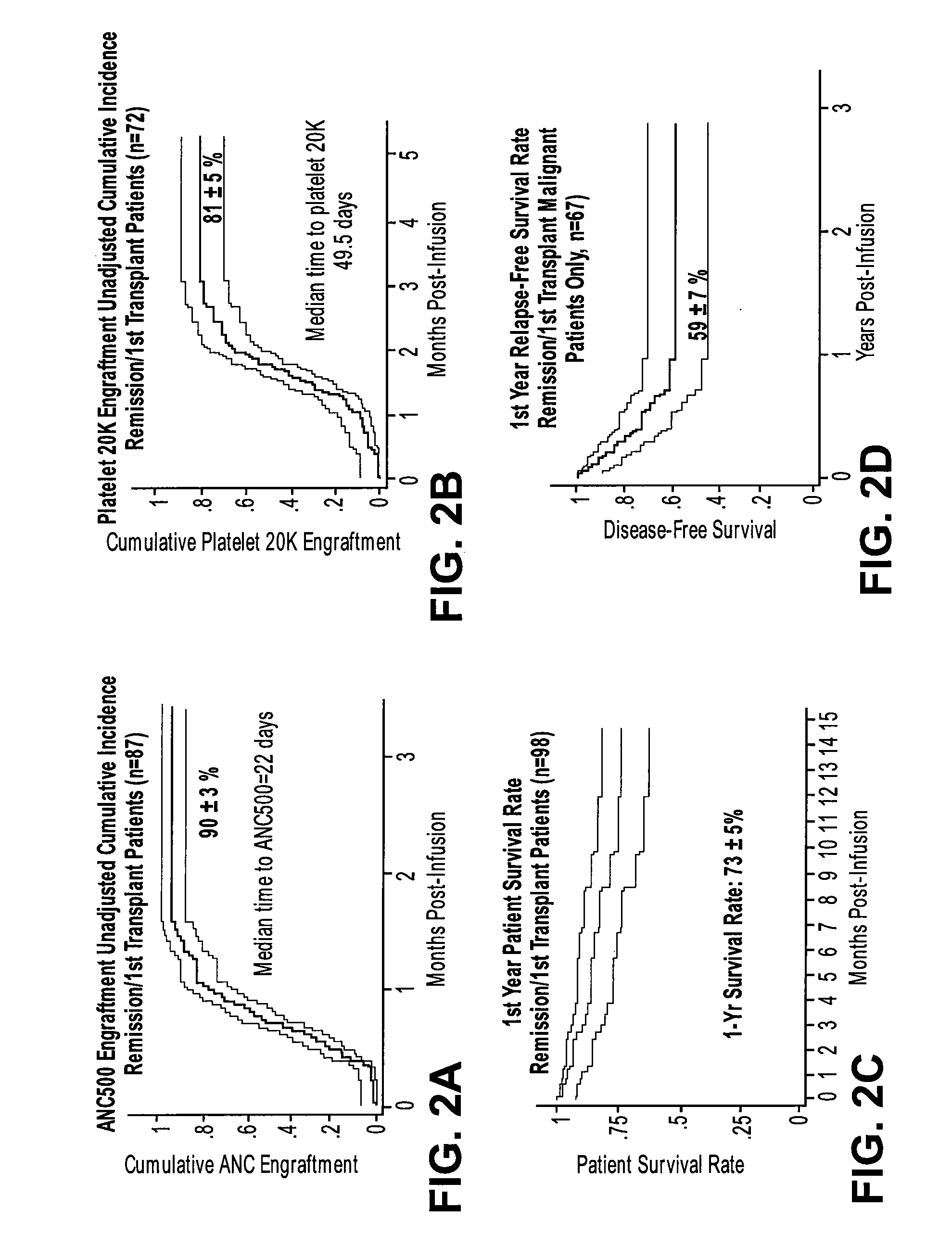
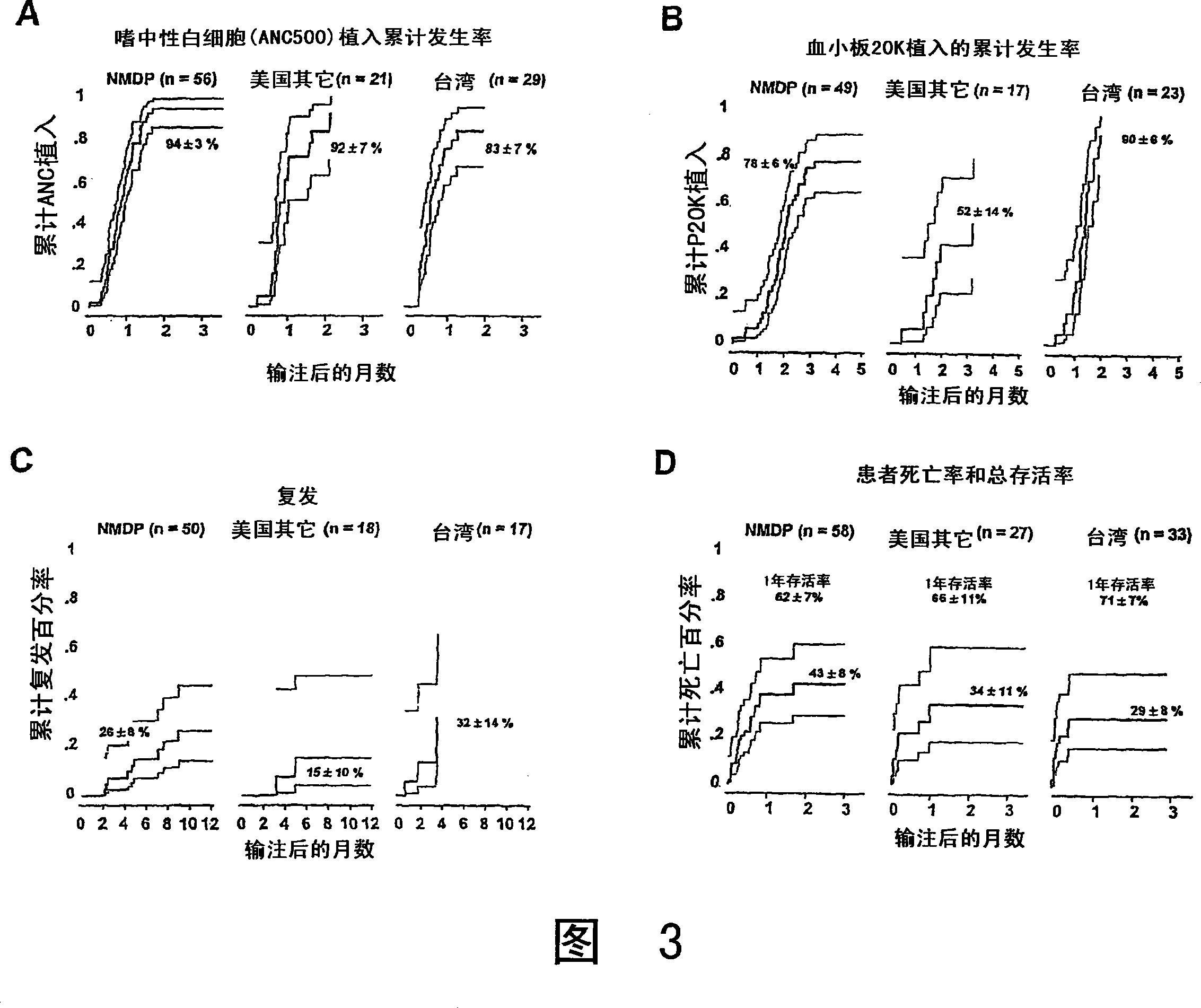
ActiveCN101252834ASignificant clinical effectElevated cumulative incidenceDead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCell dose
The umbilical cord blood (UCB) compositions of the present invention possess the unique features of having plasma that is substantially depleted from the UCB unit and red blood cells (RBC) that are not depleted from the UCB unit. Such UCB units can be prepared by a process that combines plasma depletion with cryopreservation, selection, thawing, and / or transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells to provide superior clinical outcome by maximizing post-processing cell recovery and post-thaw infusion cell dose. Methods for treating a wide variety of malignant diseases and benign diseases associated with the hematopoietic system by administering the UCB compositions of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:STEMCYTE
Method for detecting a solid tumor cancer
ActiveUS10451626B2Improve abilitiesReduce riskTherapiesMicrobiological testing/measurementTumour volumeBiologic marker
Owner:PHADIA AB
Sufficiently diverse amphiphilic MHC II binding polypeptide, immunocarrier microsphere and preparation method and application thereof
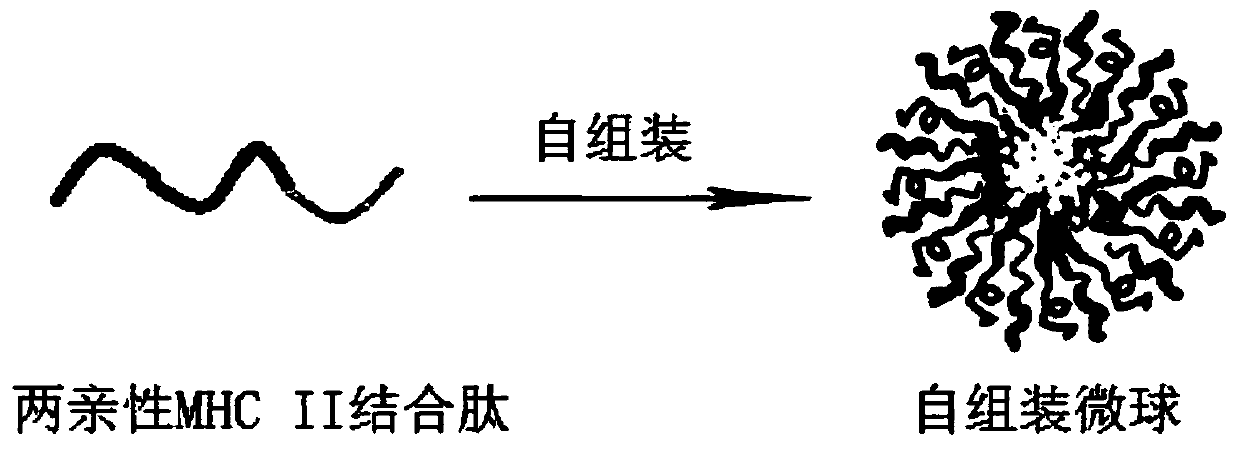
ActiveCN109758575APrevent competitive inhibitionHigh titer antibodyMammal material medical ingredientsPeptidesAntigenMicrosphere
The invention relates to a sufficiently diverse amphiphilic MHC II binding polypeptide, an immunocarrier microsphere and a preparation method and application thereof. The sequence structure of the amphipathic MHC II binding polypeptide is fatty acyl-beta-pleated sheet peptide-C-MHC II binding polypeptide-hydrophilic beta-pleated sheet peptide-maleimide, and an amphipathic MHC II binding polypeptide forms the immunocarrier microsphere by self-assembly. Coupling groups are located on the surface of the microsphere. The microsphere is particularly suitable for the preparation of antibody vaccinesfor the treatment of benign diseases and the preparation of antibody vaccines for the treatment of tumors. The antigen can be coupled to the coupling groups on the surface of the immunocarrier microsphere. The antibody vaccines can also be used in combination with FcR-CART cells or NK cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEIQIU BIOTECH
Method for detecting a solid tumor cancer
ActiveUS20170108501A1Improve abilitiesReduce riskTherapiesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseVolume Doubling Time
A method for indicating a presence or non-presence of a predefined solid tumor cancer in an individual, comprising the steps of: A. Providing at least one biological sample originating from said individual at a first point in time; B. Providing at least one biological sample originating from said individual at a second point in time; C. In said at least two biological samples, measuring a presence or concentration of at least one biomarker related to said predefined solid tumor cancer; D. Combining data regarding the presence or concentration of the at least one biomarker to form a kinetic composite value that reflects the change of biomarker presence or concentration; E. Correlating the kinetic composite value to the presence or non-presence of said predefined solid tumor cancer in said individual by comparing the kinetic composite value to a pre-determined cut-off value established with control samples of known predefined solid tumor cancer and benign disease diagnosis; wherein the time period between the first point in time and the second point in time is in the range from 0.5% to 25%, or more preferably in the range from 0.1% to 15%,of a typical tumor volume doubling time of said predefined solid tumor cancer; and the at least one biomarker determined is the same biomarker in each of the biological samples.
Owner:PHADIA AB
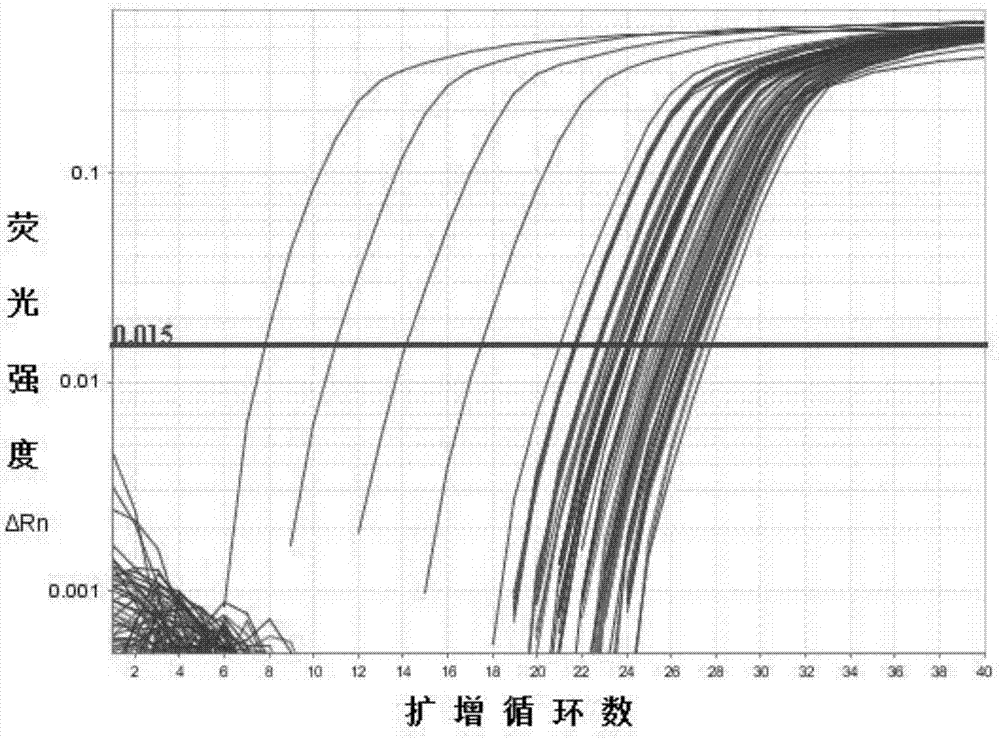
Artificial intelligence blood smear cell labeling system and method
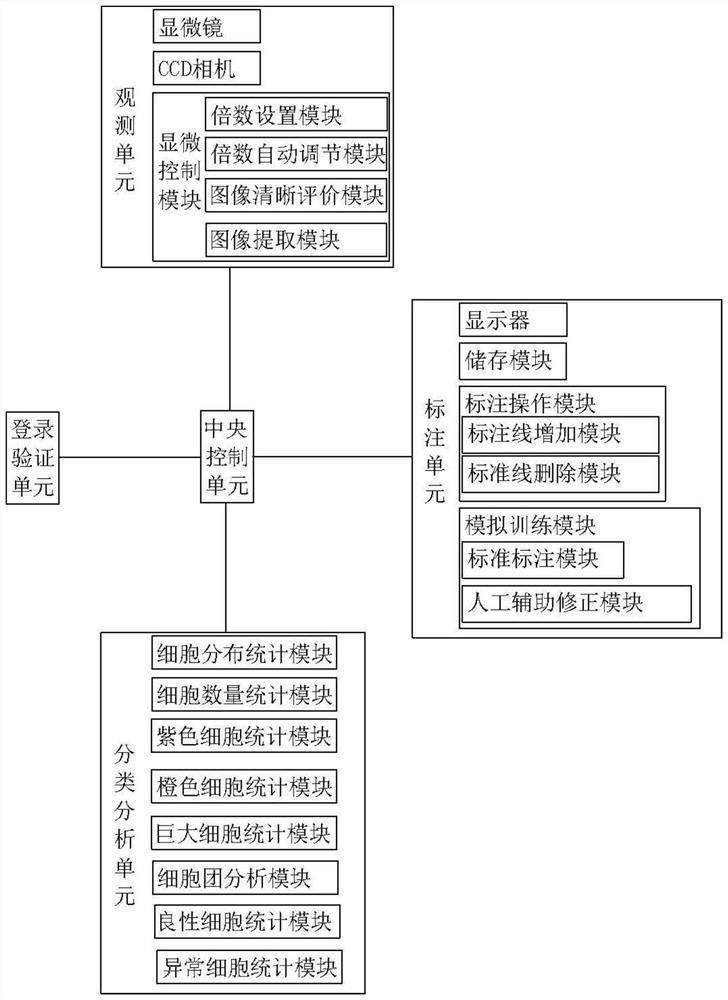
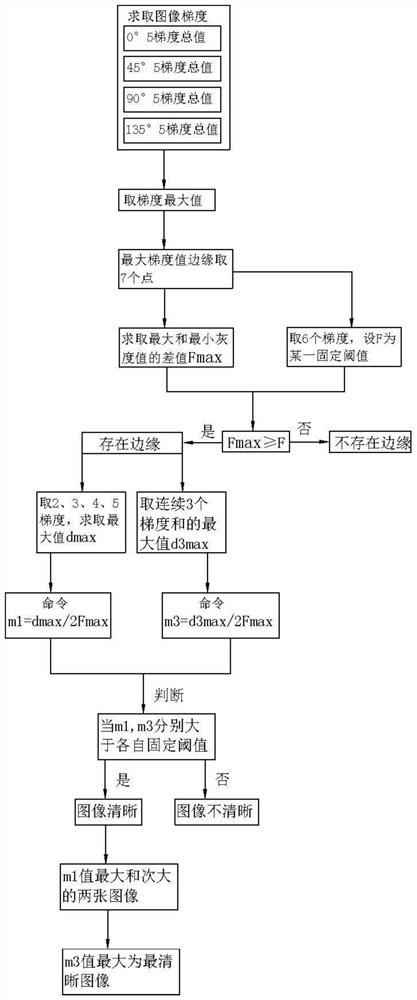
PendingCN113241154AImprove performanceTargetedImage enhancementImage analysisAbnormal cellCcd camera
The invention relates to the technical field of medical auxiliary diagnosis, and discloses an artificial intelligence blood smear cell labeling system and method. The artificial intelligence blood smear cell labeling system comprises an observation unit, a labeling unit, an analysis and classification unit and a central control unit; wherein the observation unit comprises a microscope, a CCD camera and a microscopic control module; the labeling unit comprises a display module and a labeling operation module, and the labeling operation module comprises a labeling line adding module and a standard line deleting module; and the analysis and classification unit comprises a cell distribution statistical template, a cell quantity statistical module, a purple cell statistical module, an orange cell statistical module, a huge cell statistical module, a cell cluster analysis module, a benign cell statistical module and an abnormal cell statistical module. According to the method, the multiple of the microscope can be automatically adjusted, the clearest image in the same visual field image is found around the set multiple and cells in the image are marked, wherein the benign cells enter a benign disease classification system, and abnormal cells enter a pathology classification system.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method of Diagnosing Pancreatic Cancer with the Use of N-Binding Type Sugar Chains
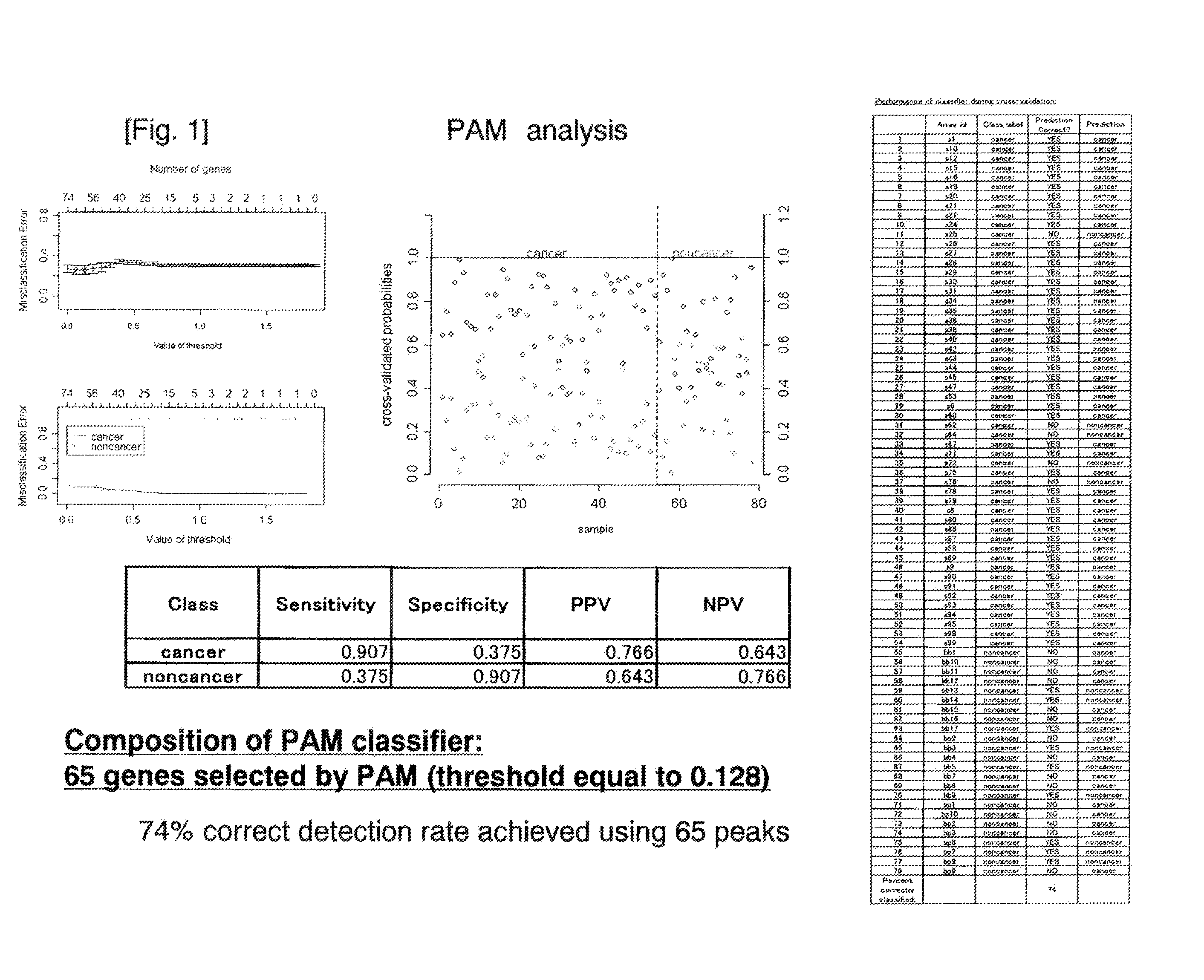
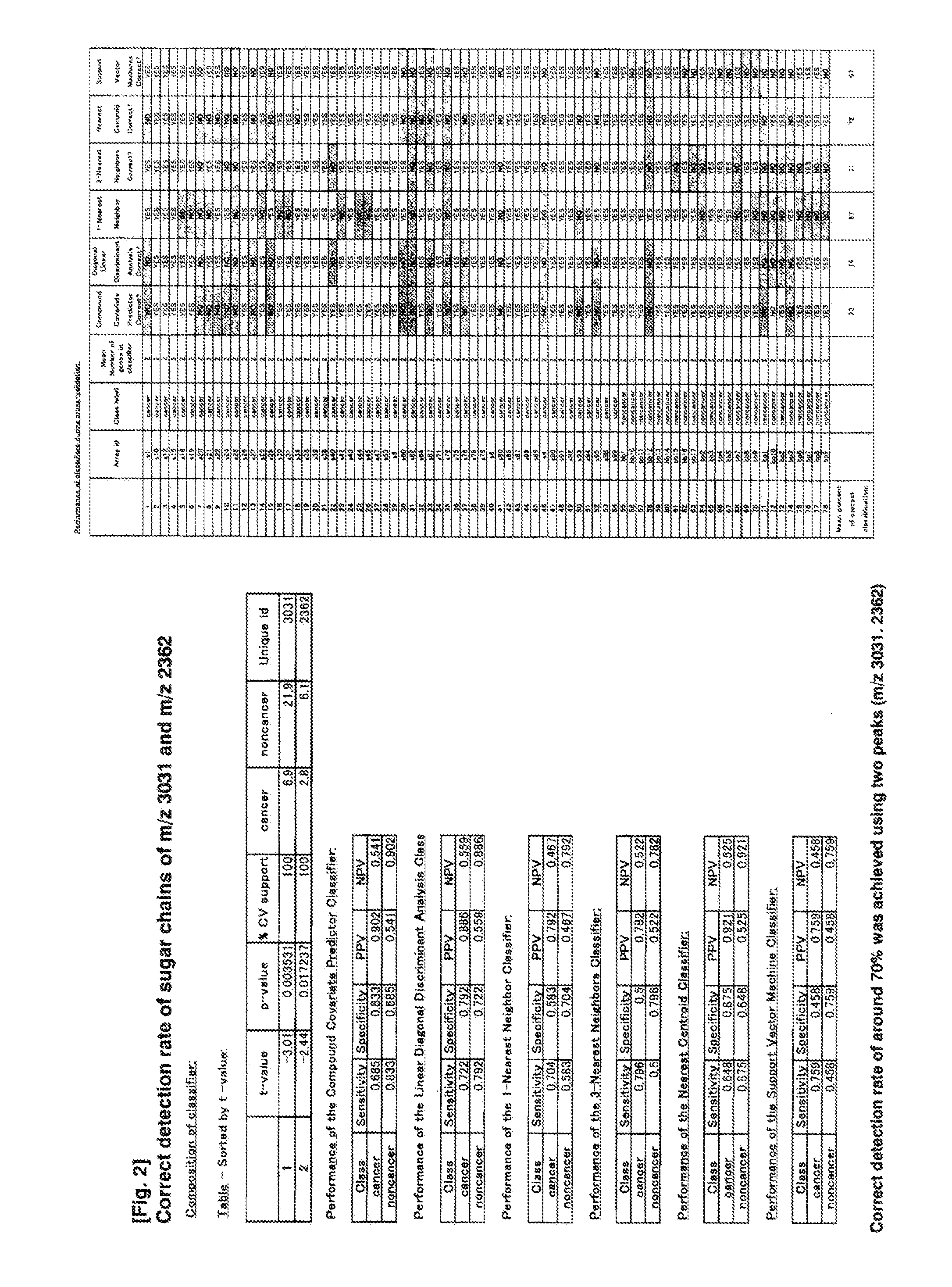
InactiveUS20110065141A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention is to provide a novel marker for diagnosing pancreatic cancer, a method for determining if a subject has pancreatic cancer utilizing the marker, etc. The present inventors collected blood from patients of 78 cases in total including patients of 24 cases with pancreaticobiliary-duct benign disorder (16 gallstone cases and 8 pancreatitis cases) and patients of 54 cases with pancreatic cancer, and mass spectrometry was performed on N-linked sugar chains in plasma. From the 74 mass-spectrometric peaks detected, 65 sugar chains were extracted based on the results of PAM analysis. These extracted sugar chains were then used to predict pancreatic cancer or pancreaticobiliary-duct benign disorder, to correctly diagnose 74% cases. Further, a T-test was performed between the two groups, the group of pancreaticobiliary-duct benign disorder and the group of pancreatic cancer, which identified two sugar chains, the sugar chain of m / z 3031 and the sugar chain of m / z 2362, as sugar chains demonstrating significant difference (p<0.05) and exhibiting 2-fold or greater difference in expression levels between the two groups. The rate of correct detection when using these sugar chains was calculated with six classifiers, all of which gave the result of about 70% correct detection.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Method of analyzing non-complexed forms of prostate specific antigen in a sample to improve prostate cancer detection
Assays for detecting and determining the presence of prostate cancer is provided. The assays are capable of detecting prostate cancer in the population of men with a significantly higher ratio of free PSA to total PSA. The assays are also capable of detecting prostate cancer in the population of men with a low amount of total PSA, i.e., in the range of 2 to 4 ng / ml. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, the assay includes the steps of (a) determining the amount of total PSA contained in a biological sample from the patient, (b) determining the amount of free PSA in the sample; and calculating the ratio of the free PSA to the total PSA, (c) determining the amount of pPSA in the sample, (d) determining the amount of BPSA in the sample, (e) determining the amount of inPSA in the sample, and (f) correlating the amount of inPSA contained in the sample to the presence of prostate cancer in the patient by comparing the amount of inPSA to a predetermined value established with control samples of known cancer and benign disease diagnosis, based on both the level of total PSA and the % free PSA.
Owner:HYBRITECH
Product for screening and evaluating benign lung diseases based on saliva specific glycoprotein sugar chain structure and application
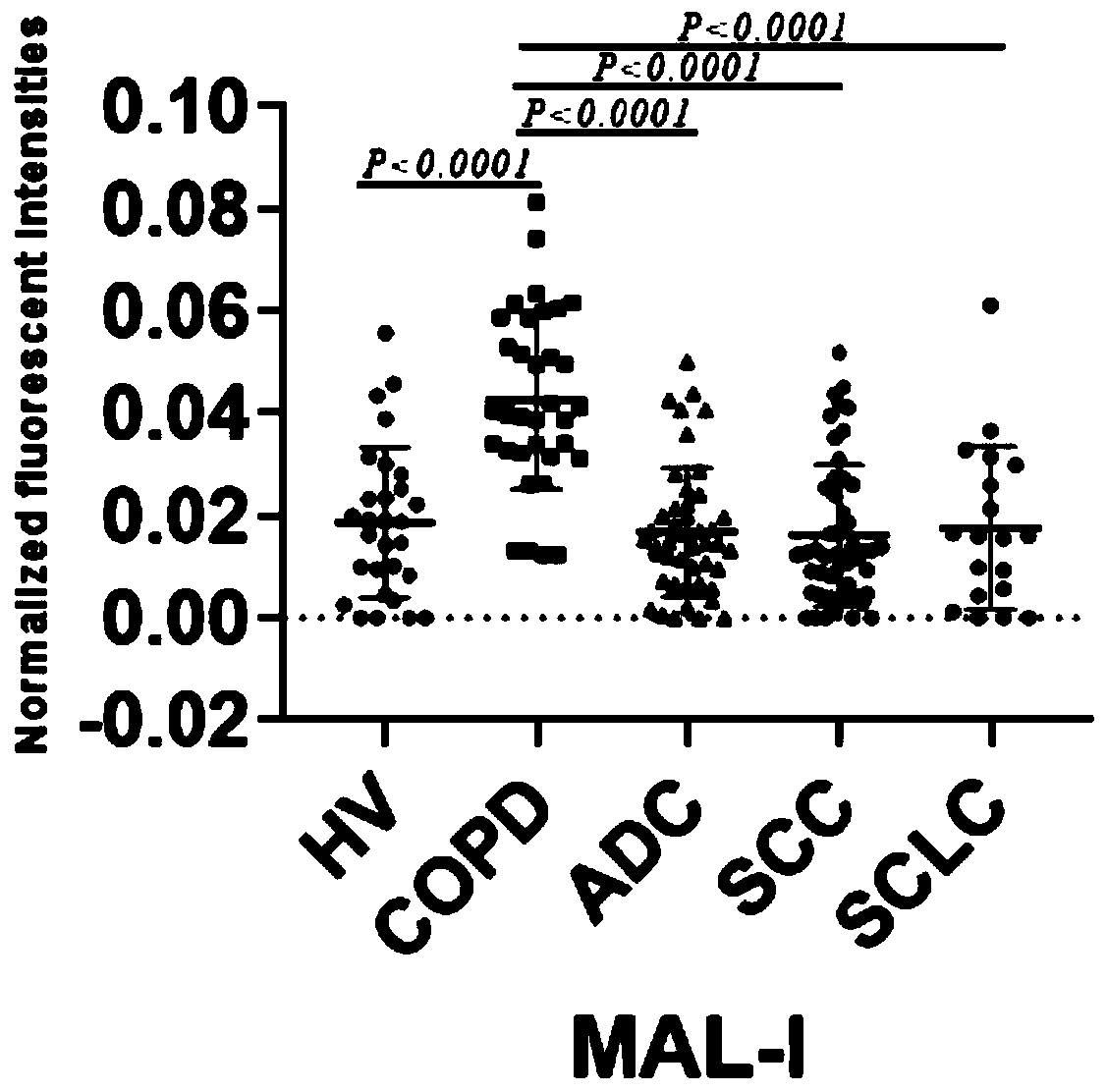
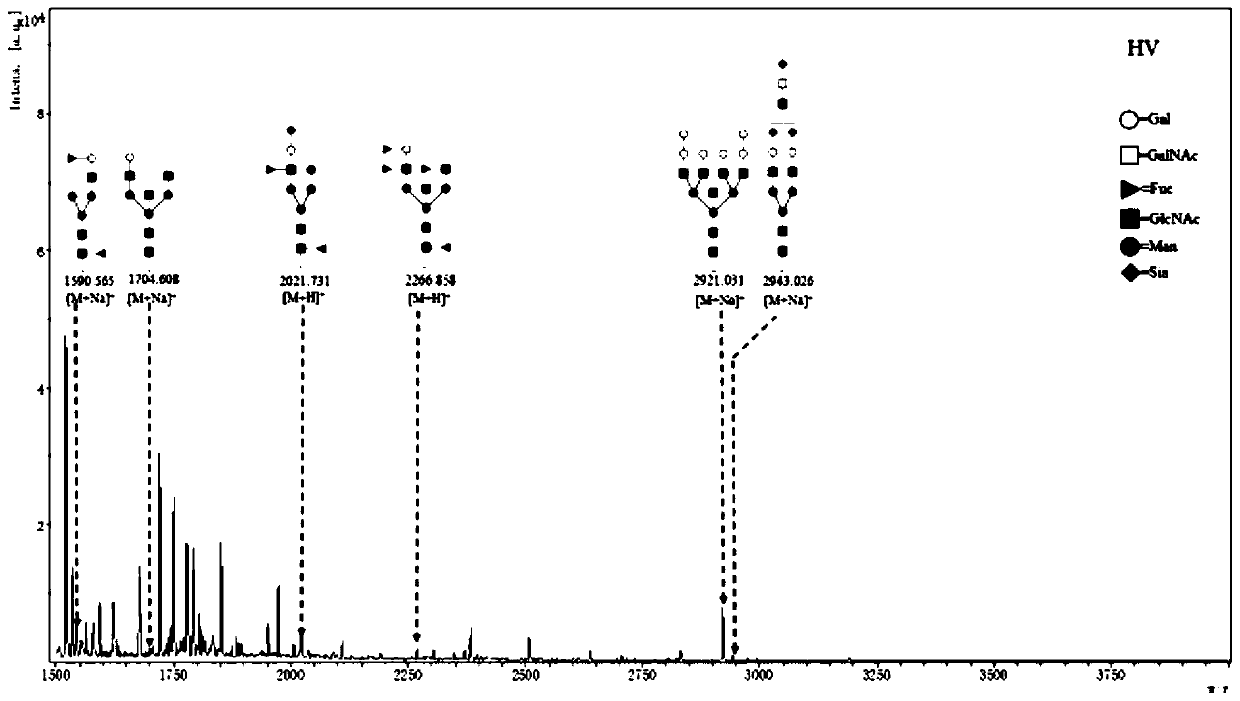
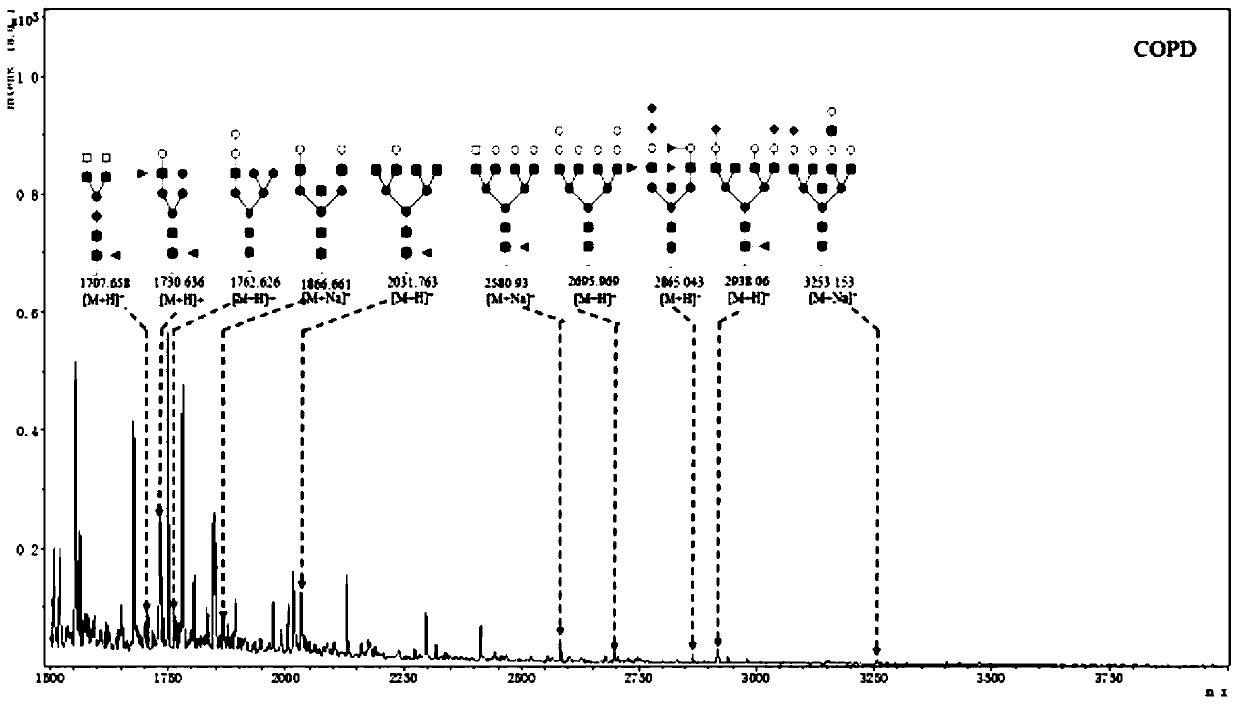
PendingCN111366633ARapid identificationAccurate identificationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiseaseCOPD
The invention discloses a lung benign disease (COPD) related screening and evaluation product based on a saliva specific glycoprotein sugar chain structure and an application. Products for lung benigndisease screening, early diagnosis, risk assessment, drug screening and / or curative effect assessment are provided for saliva samples. According to the product, change of expression levels of specific glycoprotein sugar chain structures (4GlcNAc, Sia [alpha] 2-3Gal, Gal [beta] 1-3GlcNAc, Sia [alpha] 2-3) in a saliva sample is detected, and whether 10 specific N-sugar chains are contained is detected, correspondingly, lectin playing a role in specific binding recognition is MAL-I and can be independently used as a reagent for recognizing a saliva specific glycoprotein sugar chain structure tobe used for preparing related medical products.
Owner:深圳格道糖生物技术有限公司
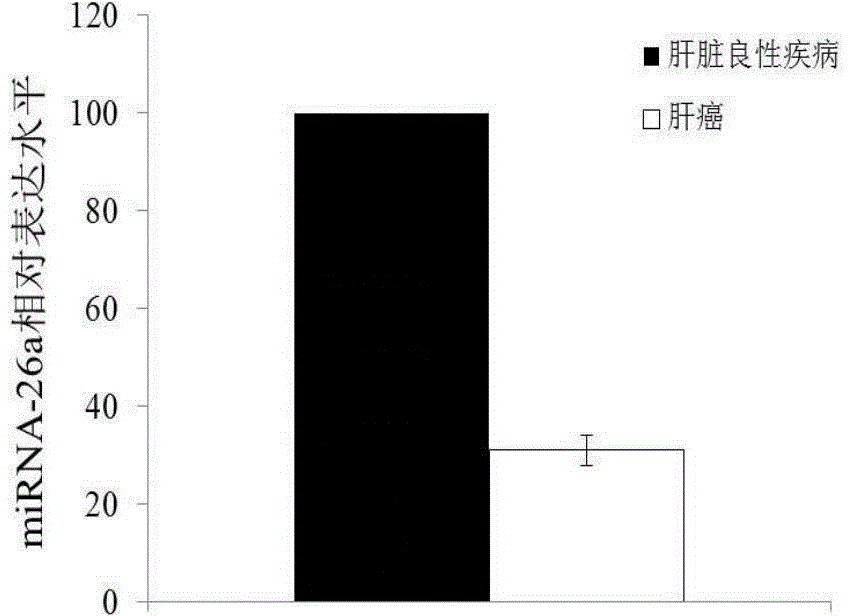
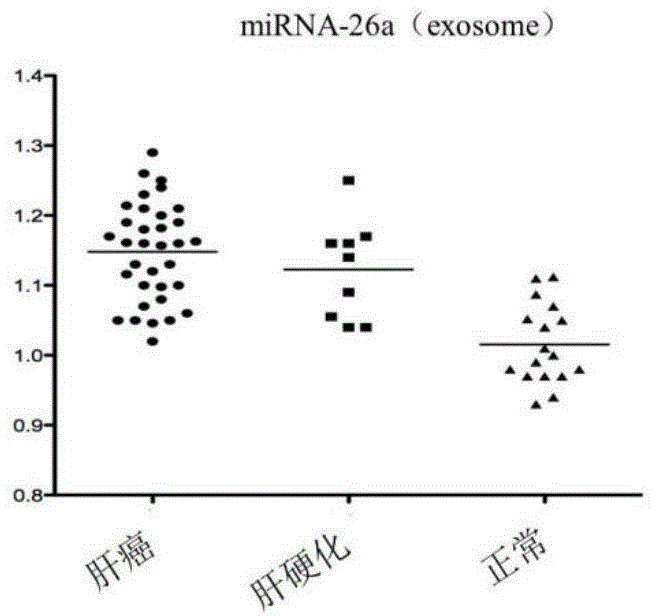
Application of miRNA-26a
InactiveCN104152566AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMirna microarray
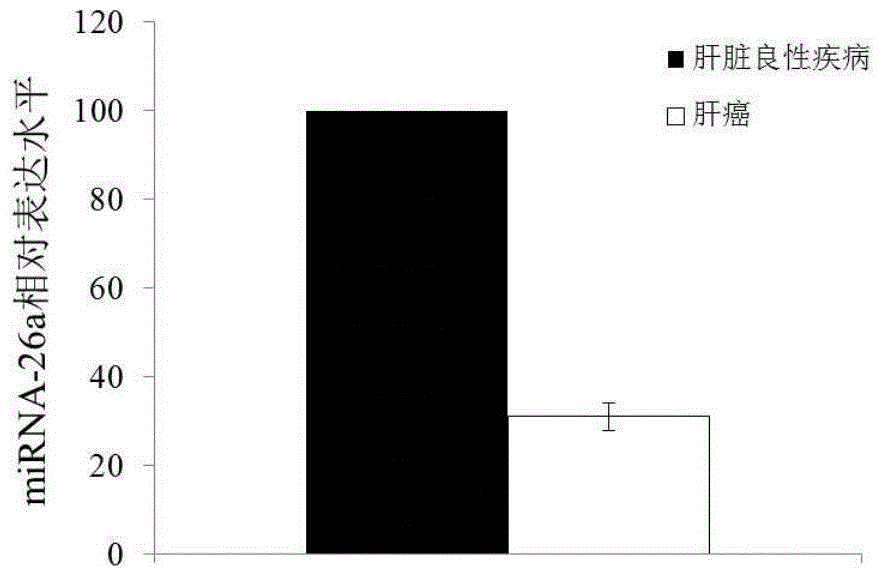
The invention discloses a blood miRNA marker related to human liver cancer and an application. The marker is miRNA-26a from exosome. According to the invention, tumor-induced exosome in peripheral blood of liver cancer patient and liver benign disease patient can be separated and purified, miRNA-199a for expressing difference in the liver cancer patient and liver benign disease patient can be analyzed and screened by a miRNA chip, and the liver cancer can be determined for the subjects by detecting miRNA-26a. The marker and its detection reagent can be used for preparing a diagnostic kit and used for early diagnosis of liver cancer.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Human homeobox gene ventx and macrophage terminal differentiation and activation, compositions and methods thereof
The invention relates to a unique formulated pharmaceutical composition and a novel treatment method of intratumoral injection. The pharmaceutical composition of the invention is the saturated ionic solution of sodium ions and calcium ions (the “medicinal ion bomb”). The invention of intratumoral injection with the “medicinal ion bomb” can be used as the first-line treatment in treating cancer and tumor in nine human organs (carcinoma and tumor of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, breast, prostate, thyroid, lung, liver, genital organ, brain and pancreas) and certain other benign diseases (skin and subcutaneous neoplasm, breast fibrocystic change, benign prostatic hyperplasia and thyroid nodules).
Owner:LIU DAVID LEXIN
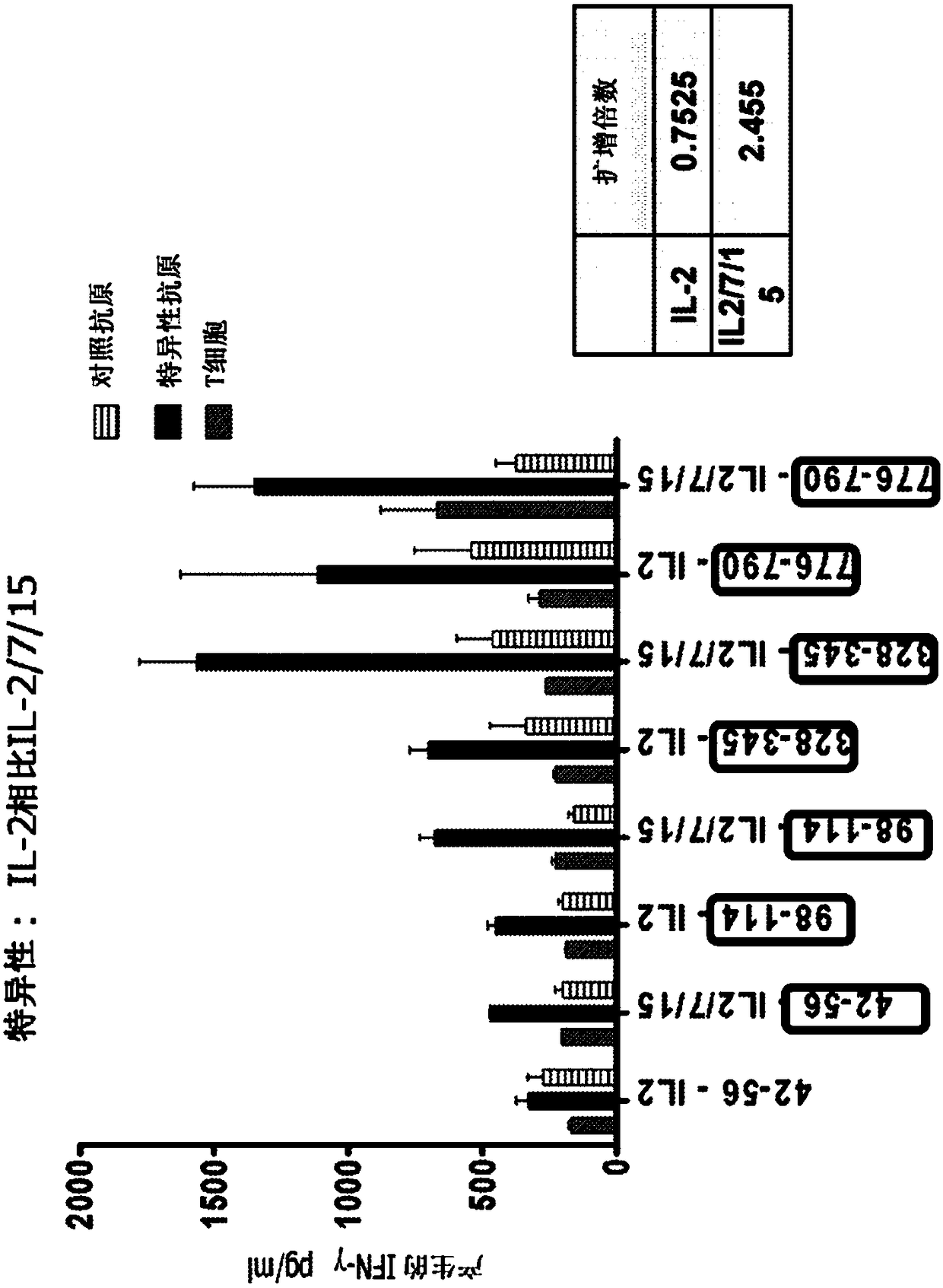
In vitro artificial lymph node for sensitization and expansion of t cells for therapy and epitope mapping
InactiveCN108289910AMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCulture expansionInvasive breast carcinoma
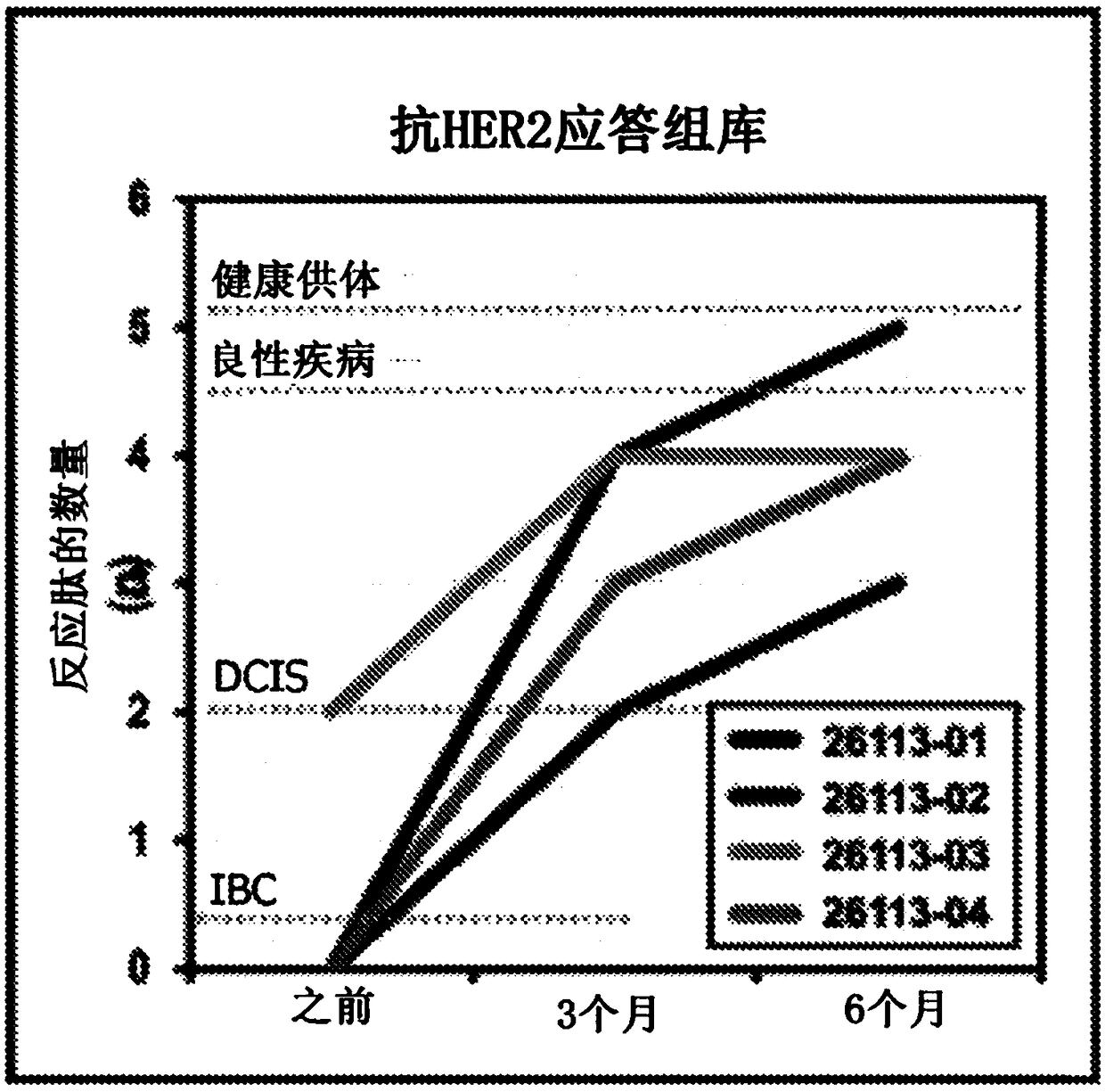
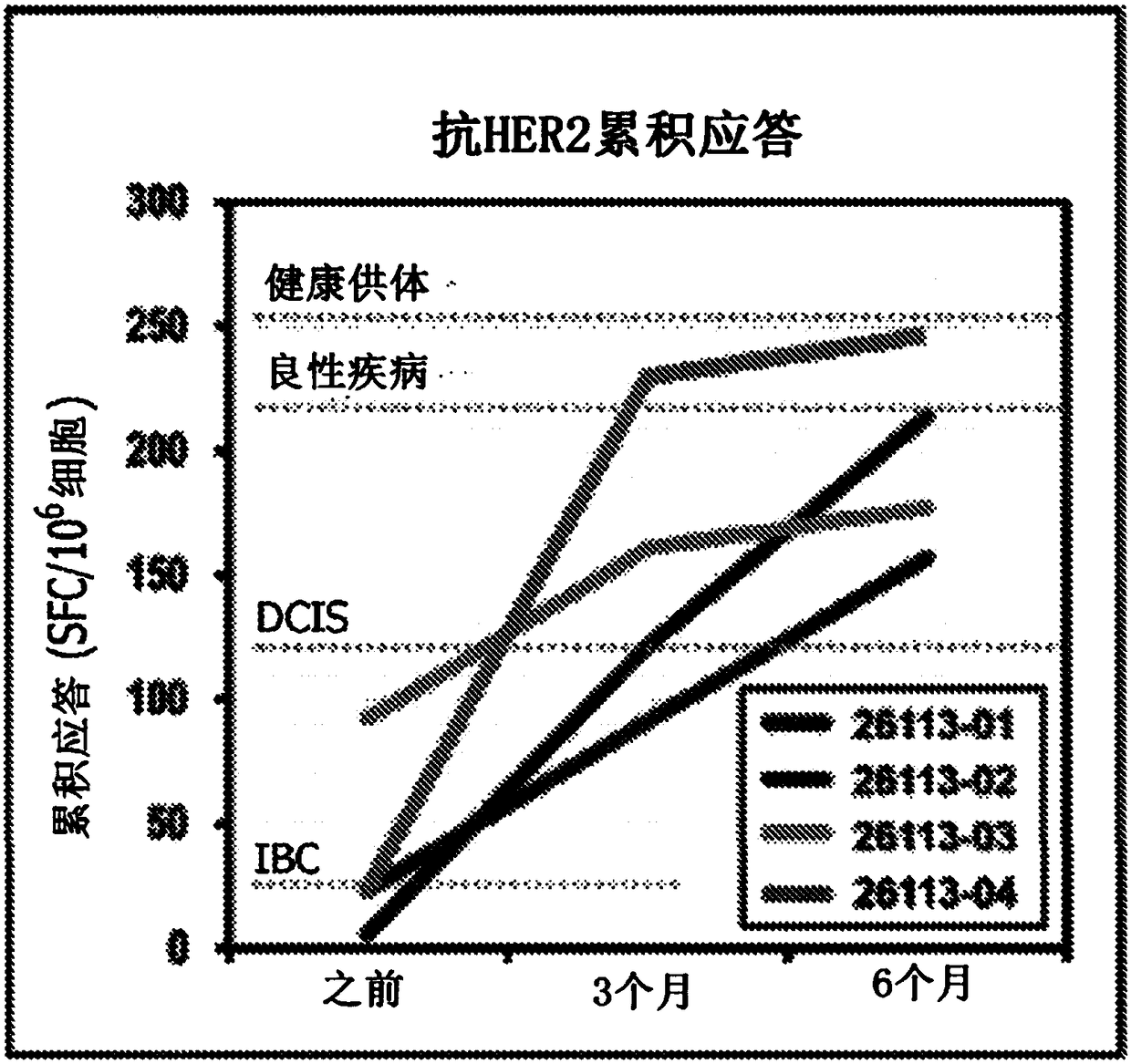
HER2+ invasive breast cancer (IBC) patients with residual disease following neoadjuvant chemotherapy have an anti-HER2 Type 1 T helper (Th1) cell immune deficit and a significant risk of recurrent disease. It has been shown that anti-HER2 CD4+ T-cell responses incrementally decrease along the breast cancer continuum - a robust response in healthy donors and patients with benign disease, a depressed response in patients with HER2+ ductal carcinoma in situ, and a nearly absent response in patients with HER2+ IBC. This invention relates to a method of creating a microenvironment for culture expansion of T cells. The expanded T cells can be used for a variety of therapeutic and research purposes.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Application of bambi as a marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
ActiveCN107267642BHigh expressionEasy to obtainMicrobiological testing/measurementChronic nasopharyngitisStatistical analysis
The invention discloses an application of BAMBI as a nasopharyngeal carcinoma maker. Through experiment researches by an applicant and a whole team for three years, researches on tissues and serums of 38 nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients, 12 chronic nasopharyngitis patients and 49 healthy volunteers are carried out, the researches show that the nasopharyngeal tissue BAMBI expression amount of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients is obviously increased, the expression amount of nasopharyngitis (nasopharyngitis is common benign disease) is relatively low, wherein p equals 0.0038, and the difference between nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngitis is obvious. The serum BAMBI of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients is obviously increased, through statistical analysis, t equals 2.639, and p equals 0.012. No matter in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissue or nasopharyngeal carcinoma serum, BAMBI presents up-regulated expression, so that the detection of BAMBI can be taken as a nasopharyngeal carcinoma molecular screening index.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE HOSPITAL
Application of PEFL-1 detection reagent in preparation of lung cancer screening kit
PendingCN113917147AEfficient screeningReduce harmBiological material analysisDiseaseElongation factor
The invention relates to the field of in-vitro diagnostic reagents, in particular to application of a similar alpha assumed elongation factor 1 Putativeelongation factor 1-alpha-like 3, (PEFL-1) in preparation of a lung cancer screening kit. The invention finds that the PEFL-1 protein level in the plasma exosome of a lung cancer patient is obviously higher than that of a lung benign disease patient for the first time. The reagent for detecting the PEFL-1 protein is used for preparing the lung cancer screening kit, and effective screening of lung cancer can be achieved.
Owner:核工业四一六医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com