Contactor power saver detecting circuit
A technology for detecting circuits and contactors, applied in circuits, relays, electrical connection tests, etc., can solve problems such as the inconsistency of AC input and DC input operating voltages, and achieve the effect of reducing production and inventory pressure and making circuits simple and easy to use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
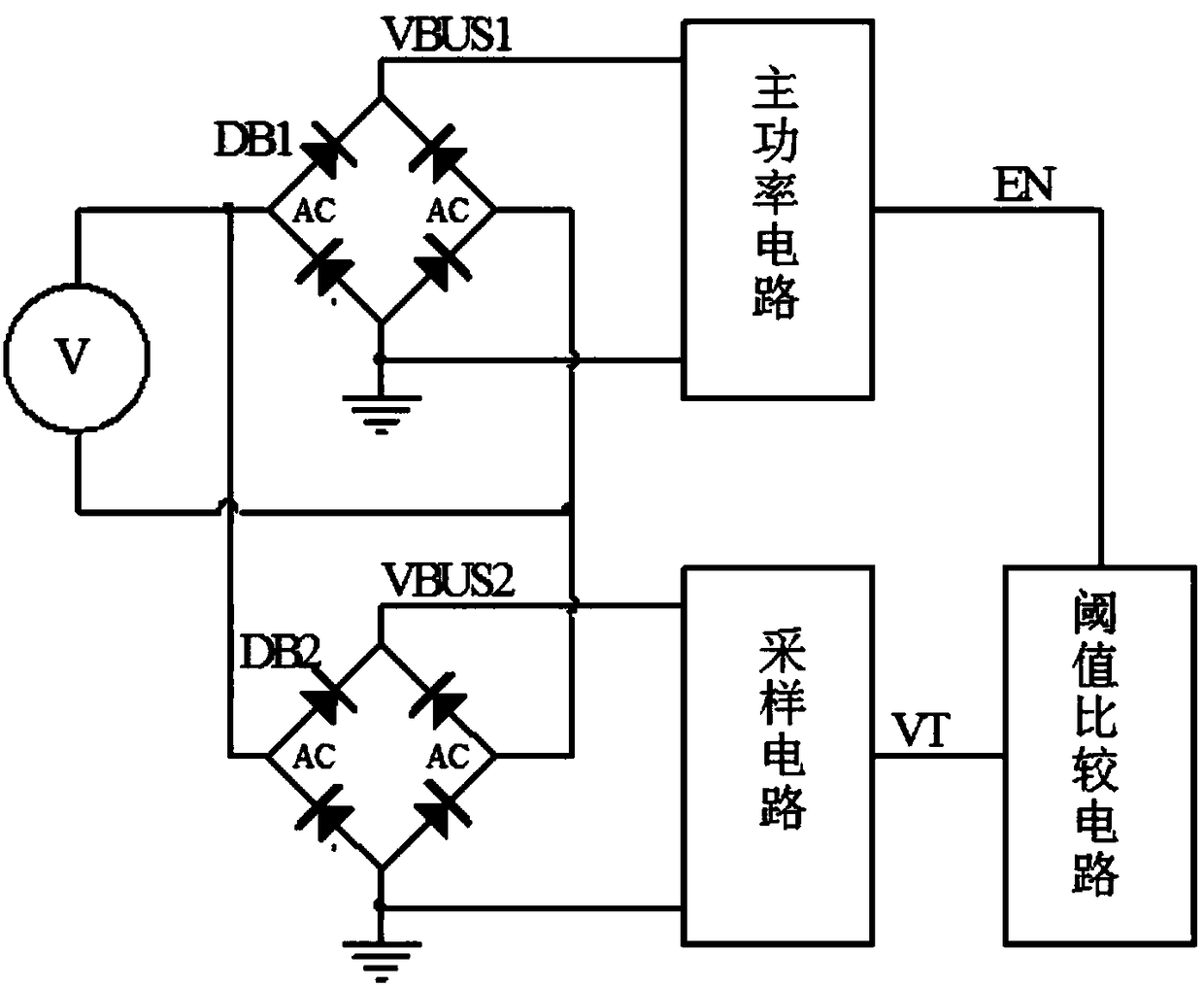
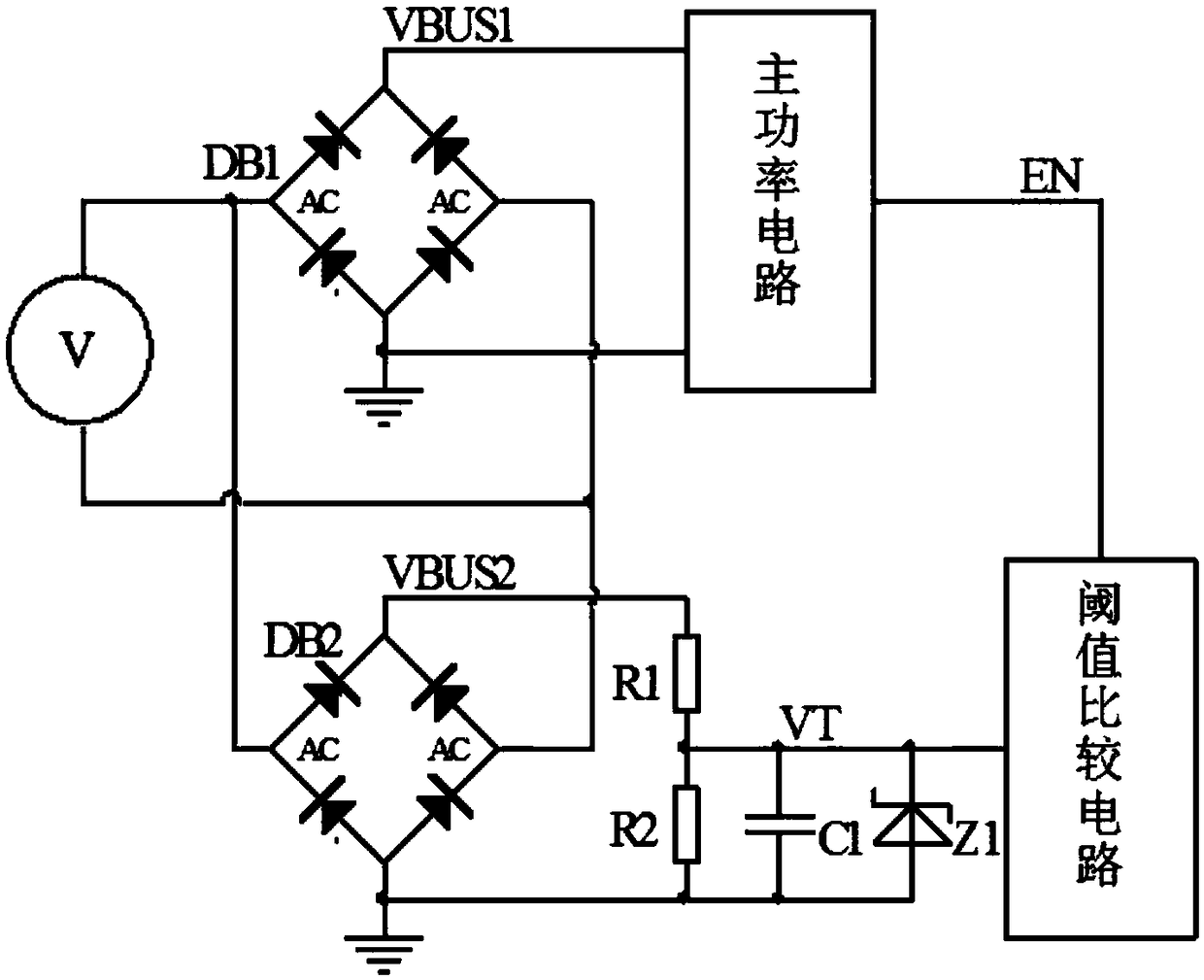
[0051] figure 2 It is a principle diagram of the first embodiment of the present invention, and a general contactor power saver includes a rectifier bridge DB1 and a main power circuit for controlling the current of the contactor coil. This embodiment also includes a rectifier bridge DB2, a resistor R1, a resistor R2, a capacitor C1 and a threshold comparison circuit. The AC input terminals of the rectifier bridge DB1 and the rectifier bridge DB2 are connected in parallel to the input voltage, the positive output terminal VBUS1 of the rectifier bridge DB1 is connected to the main power circuit, and the negative output terminal of the rectifier bridge DB1 is connected to the ground. The positive output terminal VBUS2 of the rectifier bridge DB2 is connected to one end of the resistor R1, the other end of the resistor R1 is connected to one end of the resistor R2, and the connection point of the resistor R1 and the resistor R2 is used as the output terminal to be connected to t...
no. 2 example
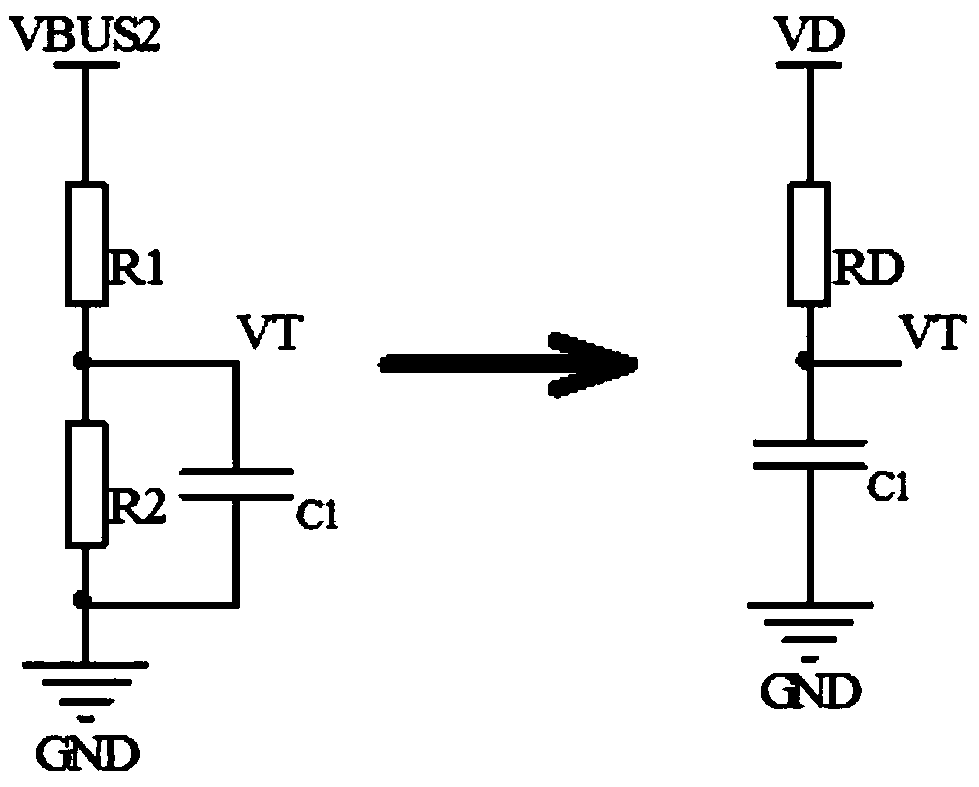
[0077] Figure 5 It is the schematic diagram of the second embodiment of the present invention. The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the sampling circuit is composed of an inductor L1, a resistor R3 and a resistor R4, and the inductor L1, the resistor R3 and the resistor R4 are connected in series. The terminal forms the input terminal of the sampling circuit, and the connection point of the resistor R3 and the resistor R4 is the output terminal of the sampling circuit. This embodiment also further includes a Zener diode Z1, which is connected in parallel to both ends of the resistor R4, wherein the cathode of the Zener diode Z1 is connected to the connection point of the resistors R3 and R4, and the anode of the Zener diode Z1 is grounded.
[0078] The basic principle of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment, and the transfer function of the sampling circuit composed of the inductor L1, the resistor R3 and t...
no. 3 example
[0086] Figure 6 It is the schematic diagram of the third embodiment of the present invention. The difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that the rectifier bridge DB2 is replaced by a diode D1 and a diode D2, and the diode D1 and the diode D2 are grounded with the two diodes of the rectifier bridge DB1. form a full wave rectifier circuit. The connection relationship is: the anode of the diode D1 is connected to one end of the AC input AC of the rectifier bridge DB1, and the anode of the diode D2 is connected to the other end of the AC input AC of the rectifier bridge DB1. The cathode of diode D1 and the cathode of diode D2 are connected to one end of resistor R1, and the other end of resistor R1 is connected to one end of resistor R2. It is connected to the negative output terminal of the rectifier bridge DB2 and then grounded, the capacitor C1 is connected in parallel to both ends of the resistor R2, and the threshold comparison circuit is conne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com