Preparation method of null type HMW-GS (High Molecular Weight Glutenin Subunits) wheat
An HMW-GS, wheat technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, plant genetic improvement, application, etc., can solve the poor stability of quality indicators, reduce the quality indicators of wheat flour and gluten processing, and cannot find hexaploid wheat, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
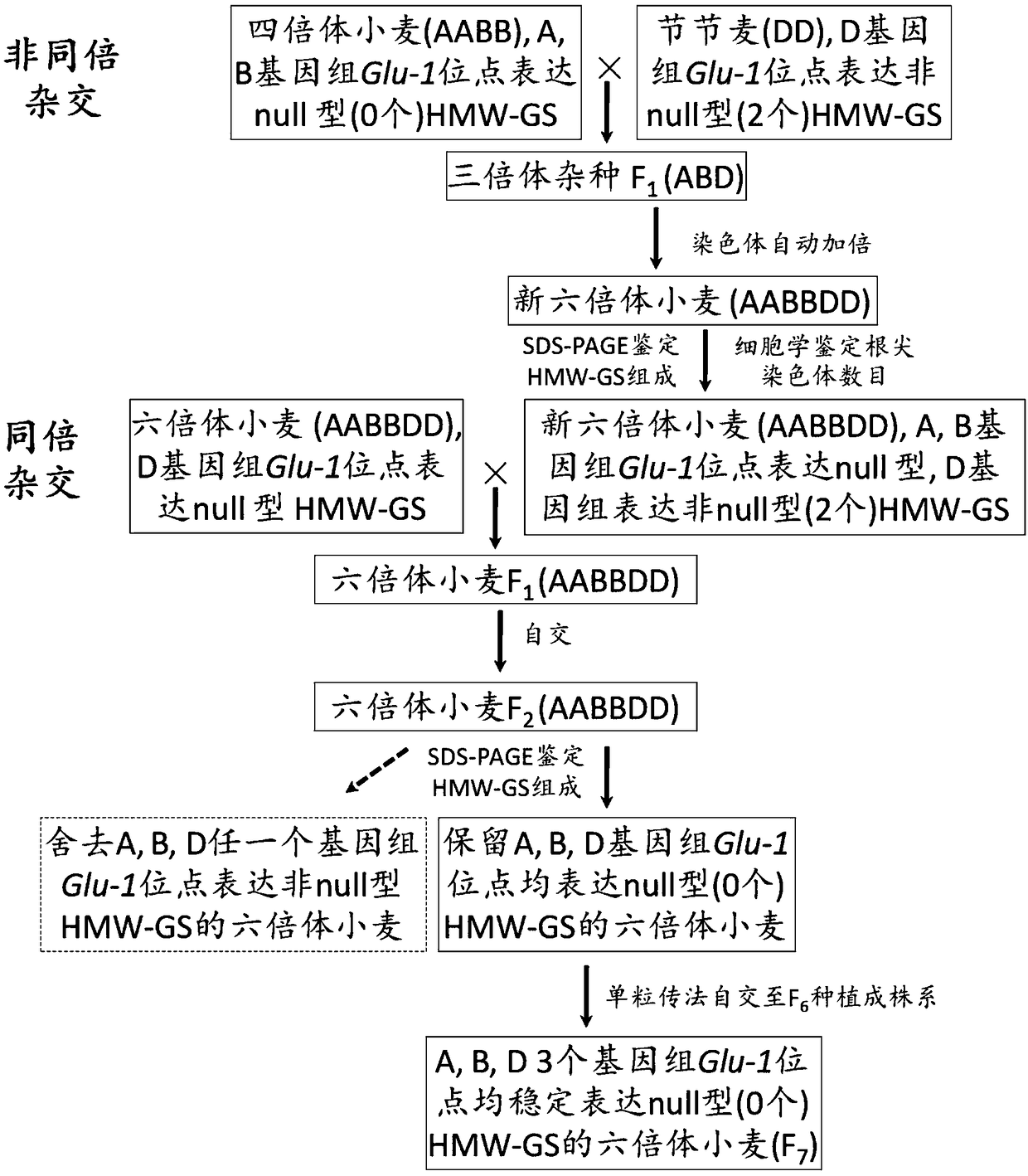
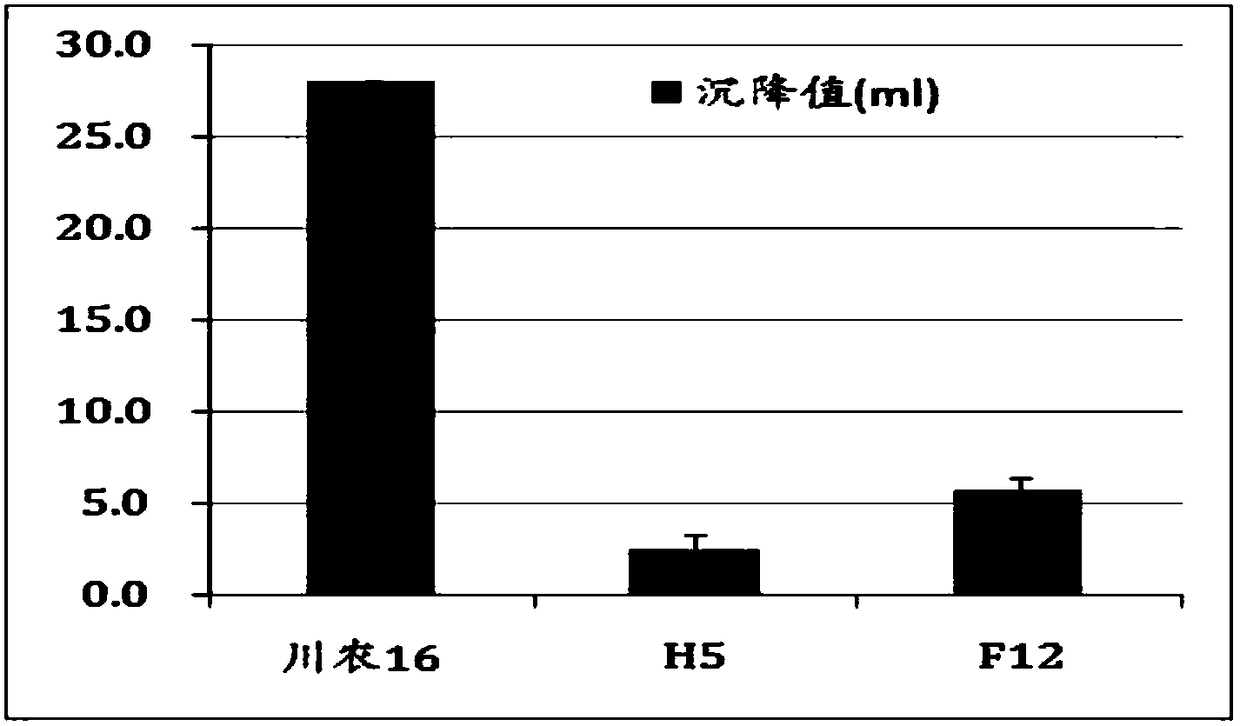
[0034] In the present invention, by creating a new hexaploid wheat approach, the null type HMW-GS of the A and B genome Glu-1 sites and the D genome Glu-1 site of the tetraploid wheat (cultivated emmer) express the non-null type HMW-GS GS was aggregated, and finally a new hexaploid wheat expressing two HMW-GSs was obtained. The new hexaploid wheat was homoploidy hybridized with the hexaploid wheat expressing null-type HMW-GS at the Glu-1 site of the D genome to polymerize the null-type HMW-GS at the Glu-1 site of the D genome, and in F 2 The Glu-1 loci of the three genomes in the seeds were screened to express a single seed o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com