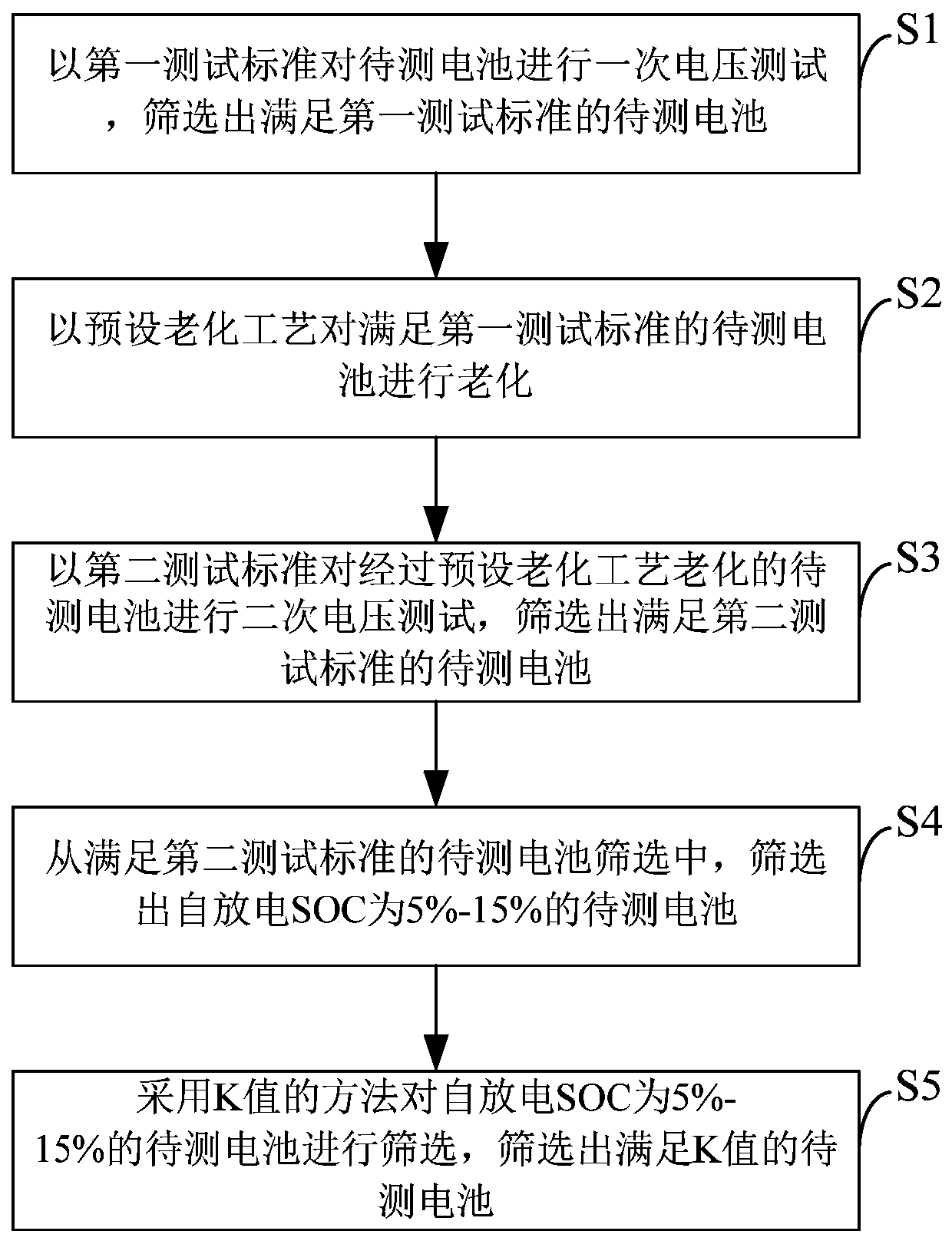
A screening method for lithium-ion battery self-discharge
A technology of lithium-ion battery and screening method, applied in the field of self-discharge screening of lithium-ion batteries, can solve the problems of low selection accuracy of defective cells, failure to select self-discharge, long self-discharge selection cycle, etc., so as to reduce customer complaints Risks, shortened lead times, and the effect of shortened screening cycles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Take the C1865135E-12Ah lithium iron phosphate square cell as an example.
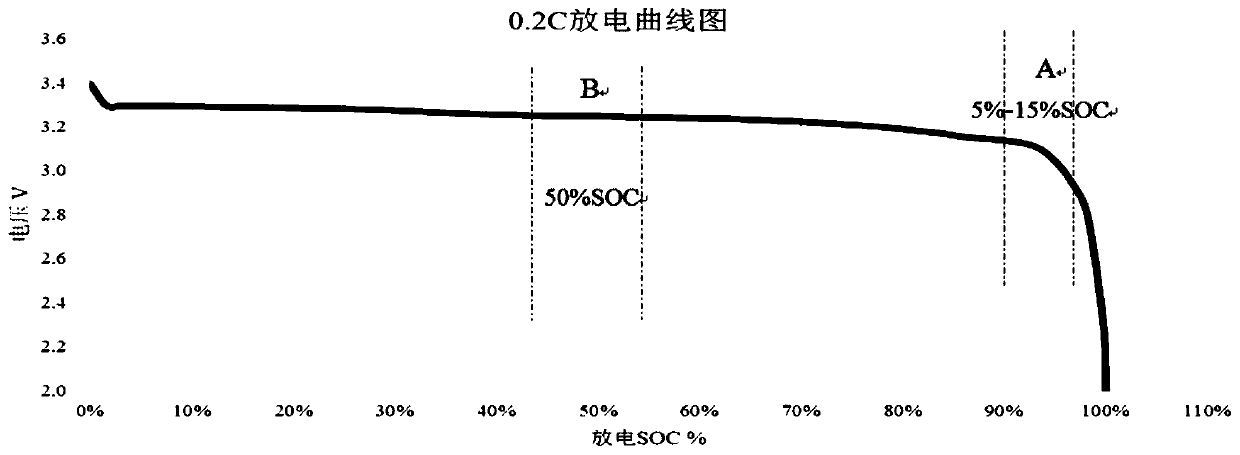
[0069] The existing self-discharge screening SOC standard is 50%, and the self-discharge SOC standard adopted in the present invention is 5%-15%. When using the self-discharge screening SOC standard is 50%, such as figure 2 As shown in the B curve,
[0070] Poor self-discharge screening is based on voltage drop screening, that is, the voltage drop △V will increase with the increase of the capacity C consumed by self-discharge. However, due to the relatively flat discharge platform of lithium iron phosphate batteries, the change in △V with the increase of C is not large at the stage when the remaining SOC is 15%-90%, and it is not easy to select bad batteries; At the stage of 5%-15%, the change of △V is relatively obvious with the increase of C, such as Figure 1 As shown in the middle A curve; but in the area of SOC<5%, the change of △V is too obvious, and it is easy to misjudge the good b...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Take the C1865135E-12Ah lithium iron phosphate square cell as an example.
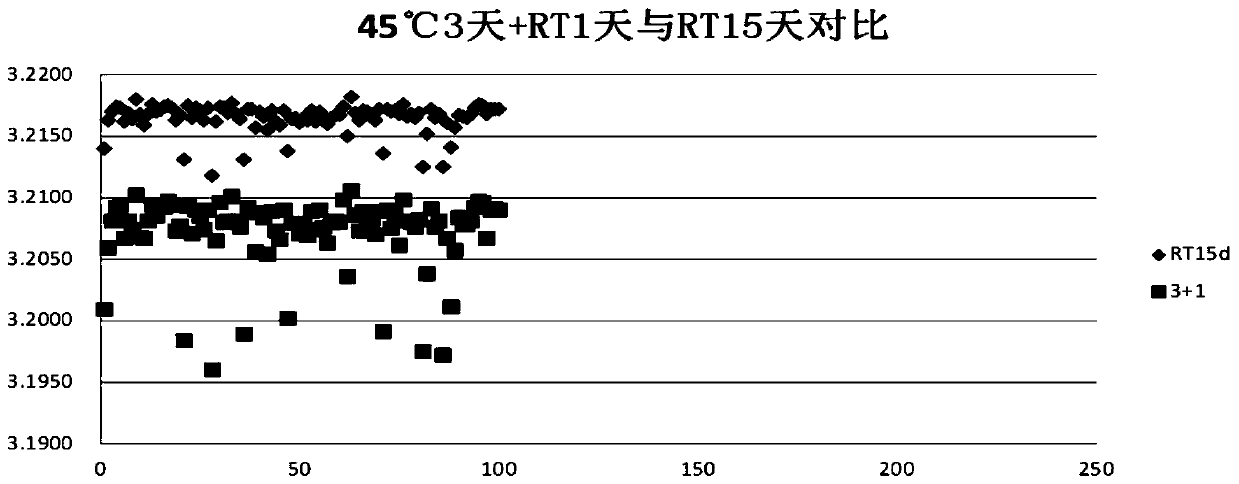
[0074] The present invention is as follows: after the primary capacity division of the battery to be tested is completed, the value of the first open circuit voltage V1 of the test OCV1 (namely the first open circuit voltage V1) is: 3.180V-3.230V. The preset aging process is: stand at a high temperature of 45°C±3°C for 3 days, and at the same time stand at a normal temperature of 25°C±3°C for 1 day (24h), test OCV2 (that is, the second open circuit voltage V2), the second open circuit voltage The value of V2 is: 3.180V-3.230V.
[0075] The existing scheme is: stand at room temperature for 15 days.
[0076] After comparing the two batteries, the test results are as follows: image 3 shown.
[0077] Depend on image 3 It can be seen from the figure that the second open circuit voltage OCV2 after standing for 3 days at 45°C±3°C and 1 day at room temperature 25°C±3°C has little correlation with ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Take the C1865135E-12Ah lithium iron phosphate square cell as an example.
[0081] The present invention adopts the K method to screen the self-discharge of the battery to be tested. Wherein, the value of K is: 0-5mV / d (millivolts / day). The existing scheme is to use the △V method to screen. The two are compared and tested, and the test results are as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0082] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen from the figure that from the point of view of the concentration of voltage distribution, the concentration of constant voltage charging voltage is higher than that of constant current charging. It shows that the pass-through rate of self-discharge screened by the K value method is much higher than that screened by the △V method. That is, using K value to screen self-discharge can improve the accuracy of defective product selection.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com