Inductive temperature sensing
An inductive, temperature-sensing technology, used in thermometers, temperature measurement in household appliances, thermometer applications, etc., can solve problems such as sensor operating temperature contamination errors, increased cost and thermal insulation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
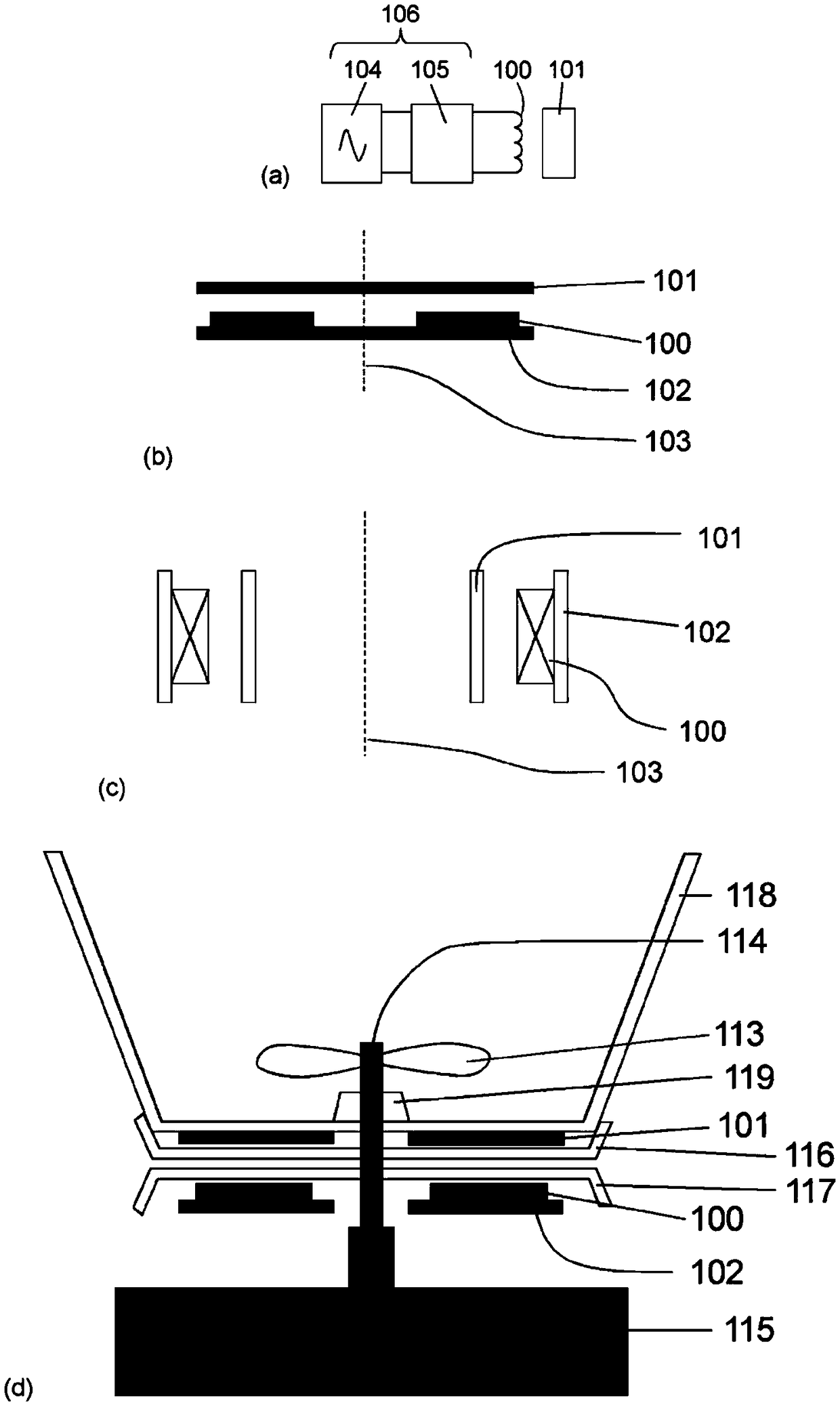
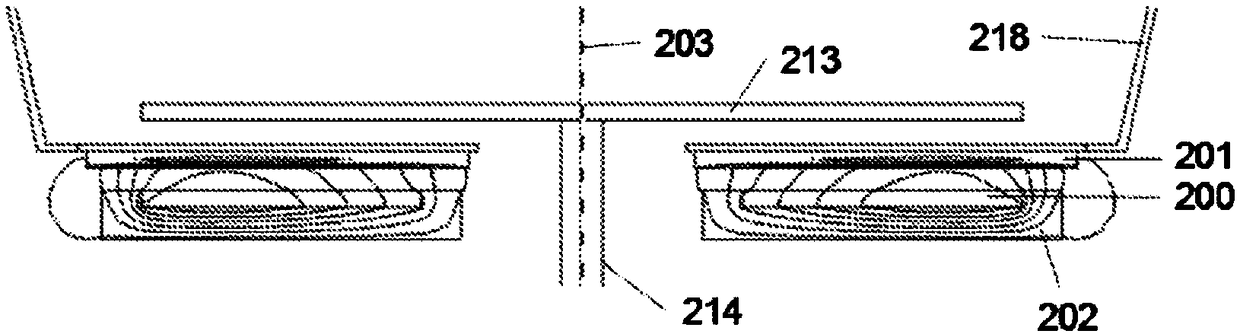
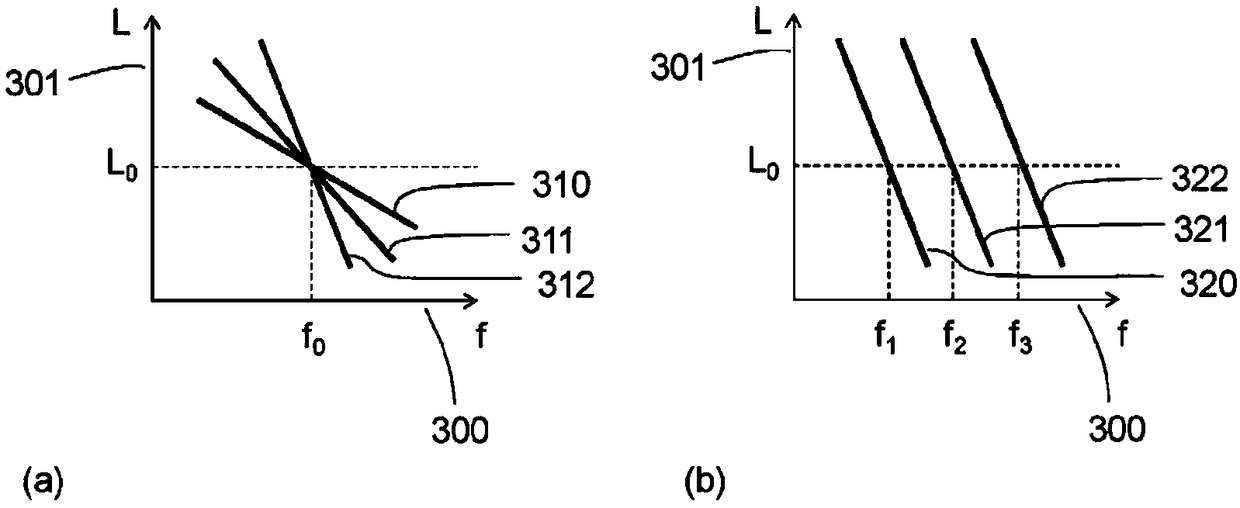
[0030] figure 1 (a) shows the elements of the inductive temperature sensing system. The coil arrangement (100) is energized by an AC signal from an excitation circuit (104). The apparent impedance of the coil construction is measured or inferred by a measurement circuit (105). Note that the excitation and measurement functions may be integrated into a single circuit, such as a microprocessor, and together form the "impedance measurement circuit" (106). The apparent impedance of the coil construction is affected by the nature and temperature of the target (101). Targets that are conductive and magnetically sensitive, ie have a non-zero magnetic susceptibility, are also said to be permeable. The frequency at which the apparent inductance of the coil construction (100) is equal to the inductance of the coil construction (100) in the absence of the target (101) is measured. In this application we call this frequency the cross-over frequency (cross-over frequency). As describe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com