Plant-derived insecticide for organic vegetables and preparation method thereof
A technology of botanical pesticides and organic vegetables, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, pesticides, plant growth regulators, etc. High extraction efficiency, good insecticidal and bactericidal effect, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
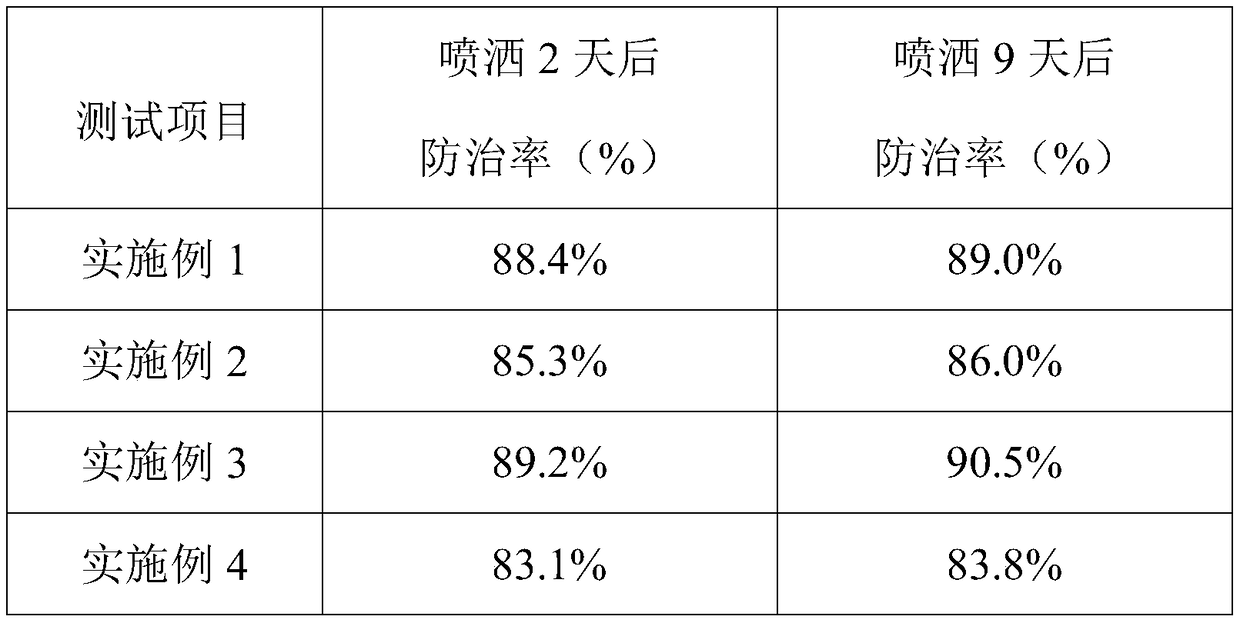
Embodiment 1
[0020] A botanical insecticide for organic vegetables, its raw materials include by weight: 30 parts of betel nut skin, 20 parts of cassava root, 10 parts of radish leaves, 8 parts of eggplant skin, 8 parts of tallow leaves, 6 parts of neem skin, Ailanthus sinensis 6 parts of leaves, 4 parts of croton leaves, 1 part of fatty acid glyceride, 0.1 part of ascorbic acid.
[0021] The preparation method of the above-mentioned botanical insecticide for organic vegetables comprises the following steps:
[0022] S1. Wash, dry and pulverize fresh betel nut skins, cassava roots, radish leaves, eggplant skins, tallow leaves, neem skins, Ailanthus leaves, and croton leaves, and mix them uniformly to prepare a mixture;
[0023] S2. Add the mixed material into a 50% acetone solution with a mass fraction of 3 times the weight, heat to 50° C. and stir for 2 hours, then filter and take the filtrate to obtain the prefabricated material A;
[0024] S3. Add the filter residue in S2 to a 75% etha...
Embodiment 2
[0027] A botanical insecticide for organic vegetables, its raw materials include by weight: 40 parts of betel nut skin, 30 parts of cassava root, 20 parts of radish leaves, 16 parts of eggplant skin, 16 parts of tallow tree leaves, 12 parts of neem skin, Ailanthus sinensis 12 parts of leaves, 10 parts of croton leaves, 3 parts of fatty acid glycerides, 0.5 parts of ascorbic acid.
[0028] The preparation method of the above-mentioned botanical insecticide for organic vegetables comprises the following steps:
[0029] S1. Wash, dry and pulverize fresh betel nut skins, cassava roots, radish leaves, eggplant skins, tallow leaves, neem skins, Ailanthus leaves, and croton leaves, and mix them uniformly to prepare a mixture;
[0030] S2. Add the mixed material into a 60% acetone solution with a mass fraction of 5 times the weight, heat to 60° C. and stir for 4 hours, then filter the filtrate to obtain the prefabricated material A;
[0031] S3. Add the filter residue in S2 to 80% et...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A botanical insecticide for organic vegetables, its raw materials include by weight: 35 parts of betel nut skin, 25 parts of cassava root, 15 parts of radish leaves, 12 parts of eggplant skin, 12 parts of tallow tree leaves, 9 parts of neem skin, Ailanthus sinensis 9 parts of leaves, 7 parts of croton leaves, 2 parts of fatty acid glycerides, 0.3 parts of ascorbic acid.
[0035] The preparation method of the above-mentioned botanical insecticide for organic vegetables comprises the following steps:
[0036] S1. Wash, dry and pulverize fresh betel nut skins, cassava roots, radish leaves, eggplant skins, tallow leaves, neem skins, Ailanthus leaves, and croton leaves, and mix them uniformly to prepare a mixture;
[0037] S2. Add the mixed material into a 55% acetone solution with a mass fraction of 4 times the weight, heat to 55° C. and stir for 3 hours, then filter the filtrate to obtain the prefabricated material A;
[0038] S3. Add the filter residue in S2 to a 77% eth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com