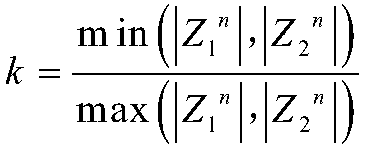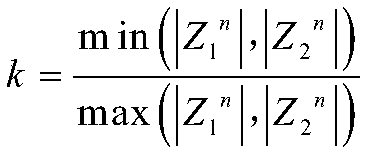Method for identifying grounding electrode line fault of high-voltage direct current power transmission system
A power transmission system, high-voltage direct current technology, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, measuring resistance/reactance/impedance, etc., can solve the problems of difficult project implementation, high hardware requirements, overload rupture of ground electrode lead 1, etc. Fast and effective processing, high detection sensitivity, and easy on-site implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0036]A specific embodiment of the present invention is a method for identifying a fault in a ground electrode line of a high-voltage direct current transmission system, the steps of which are as follows:
[0037] A. Data collection
[0038] The electrical measuring device of the grounding electrode system is installed on the neutral busbar of the converter station of the HVDC power transmission system. A current signal I 1 (t) and the second current signal I of the second ground electrode line 2 (t), and the collected voltage signal U(t), the first current signal I 1 (t) and the second current signal I 2 (t) sent to the relay protection device of the system, where t represents the sampling time;
[0039] B. Data processing
[0040] The relay protection device of the system performs the following processing on the data sent by the electrical measuring device:
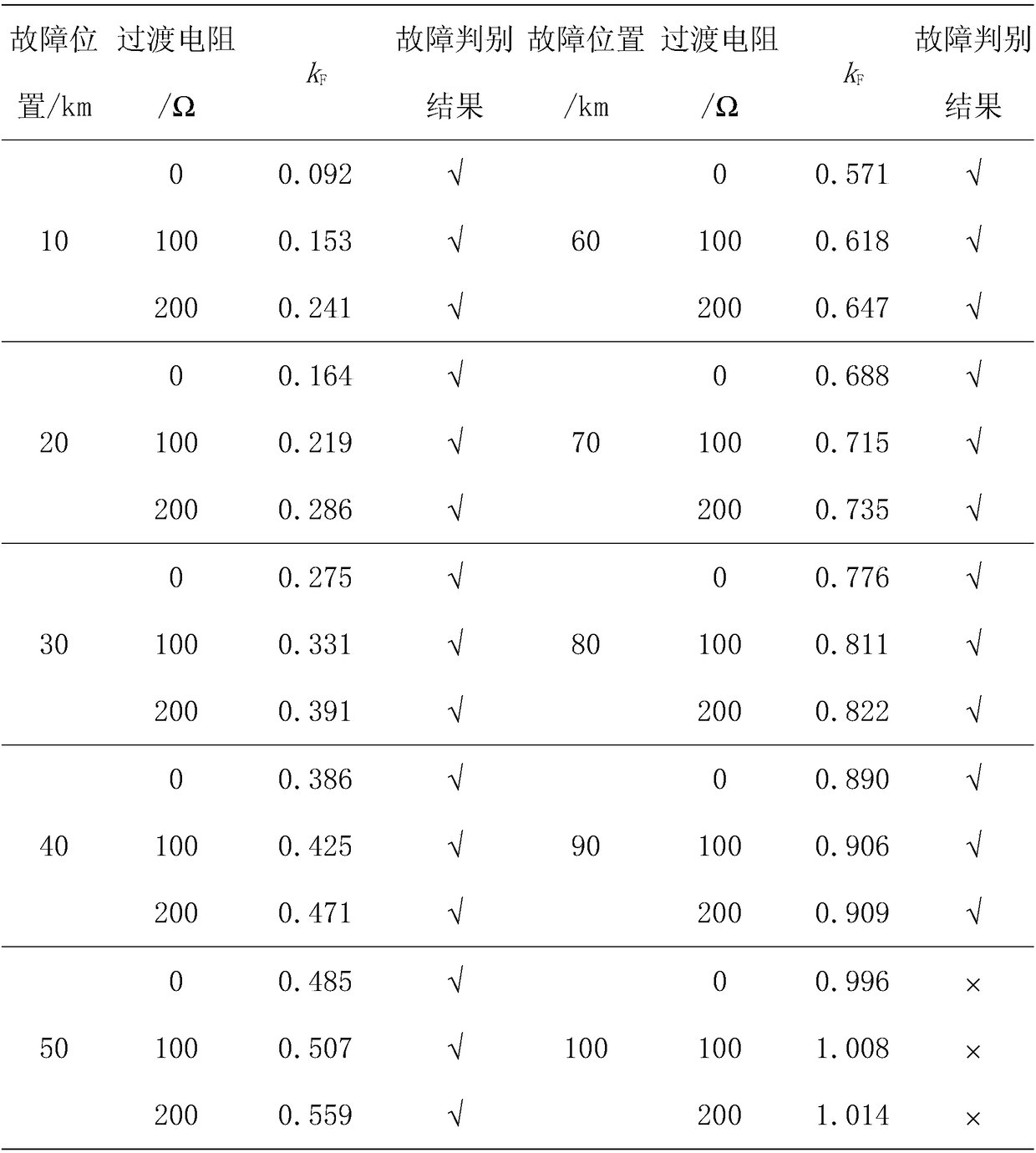
[0041] Using the full-wave Fourier algorithm to extract the voltage signal U(t) and the first current signal I ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com