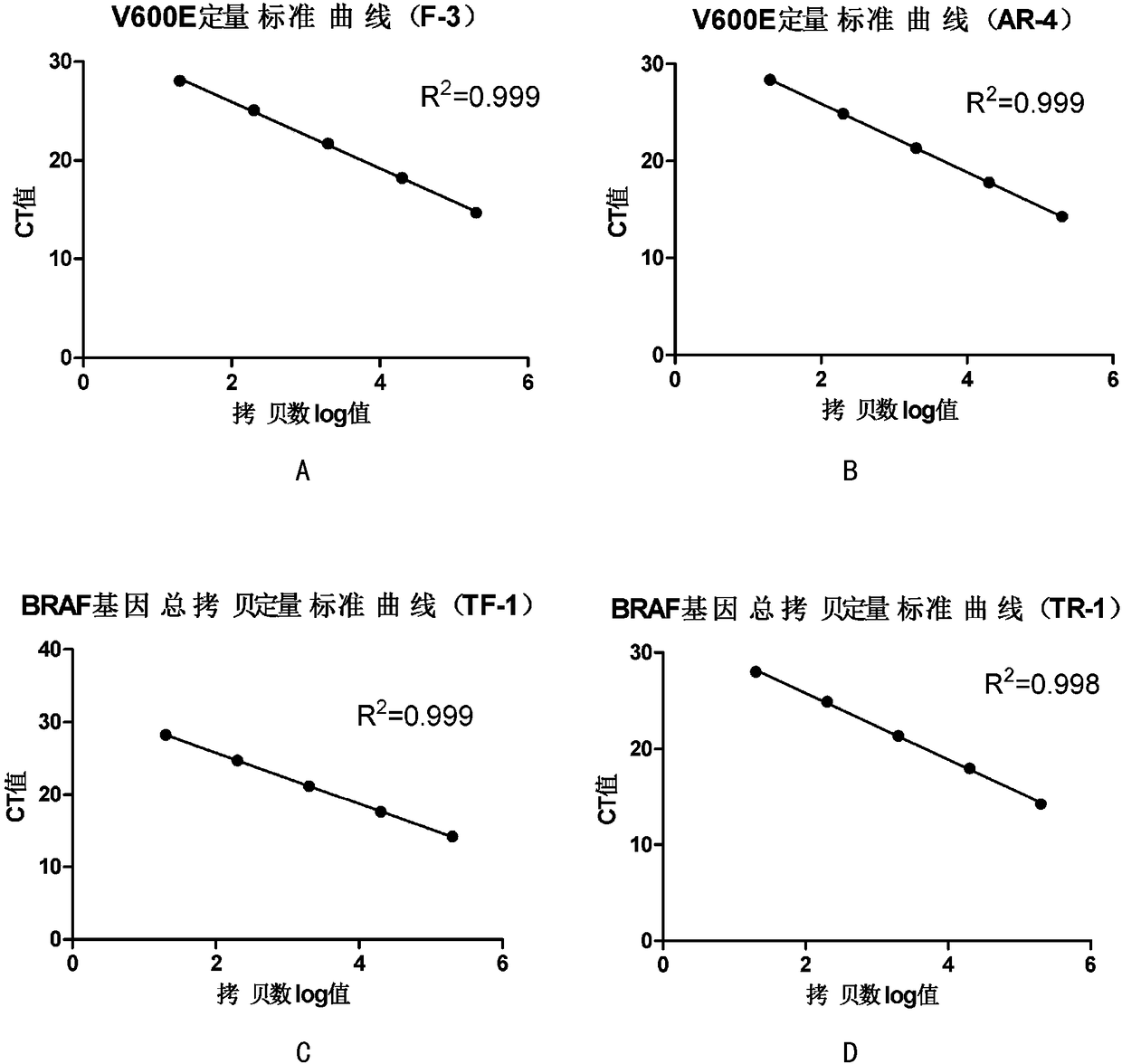
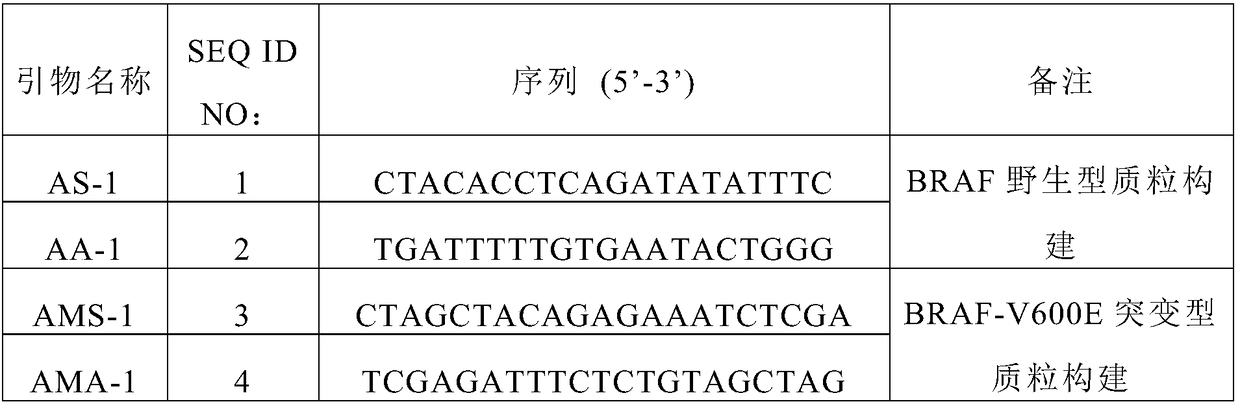
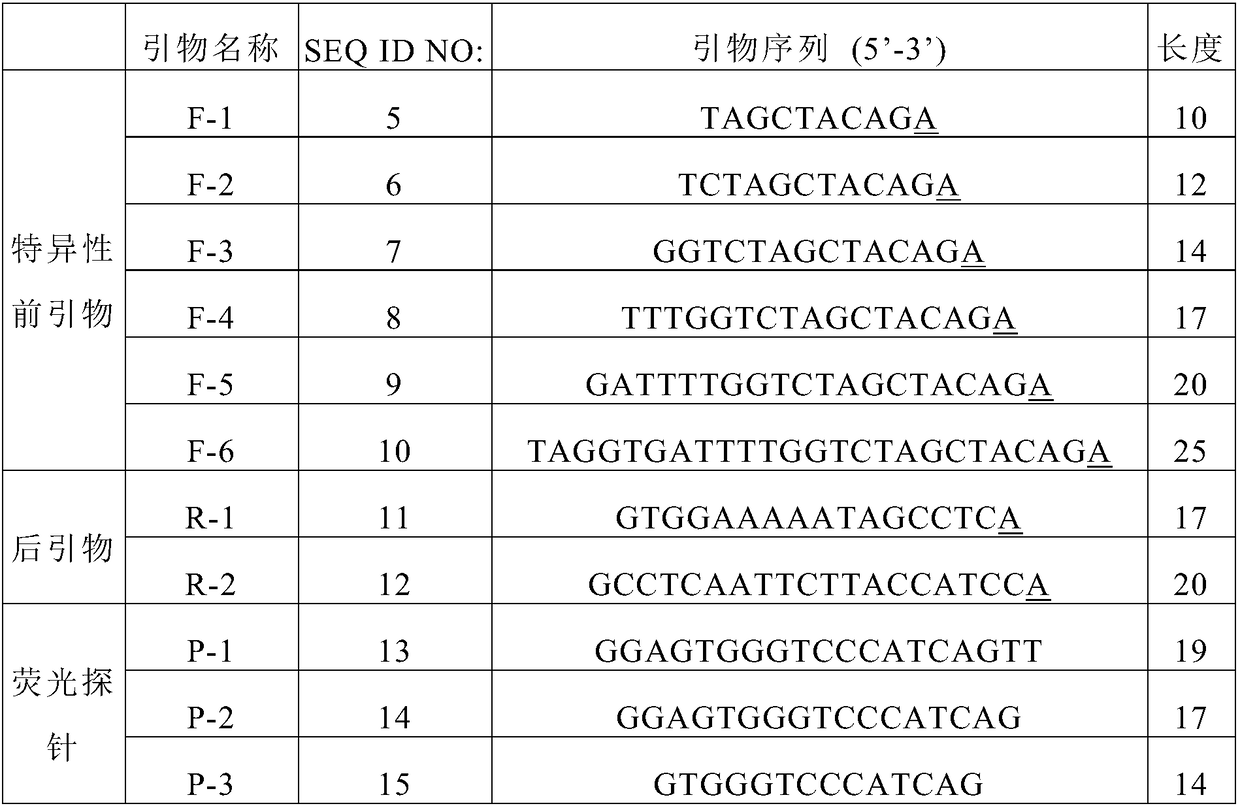
Method for improving diagnosis efficiency of BRAF gene V600E mutation
A gene and mutation site technology, applied in the field of improving the diagnostic efficiency of the BRAF gene V600E mutation, can solve the problems of difficult and effective detection, PCR cannot be extended, and the proportion of tumor mutations cannot be given
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Embodiment 1, the selection of primer
[0076] The present inventor designs the mutation site to be detected on the front primer or the back primer, and the primer (containing a base complementary to the mutation site) comprising the detection site is a specific primer, and its 3' terminal base is compatible with the mutation site. The V600E site mutant is completely complementary, which is the key to distinguish the mutant from the wild-type gene. In this example, the ability of specific primers of different lengths to distinguish mutant genes from wild genes was investigated.
[0077]The V600E site is a total of 20 copies of the mutant plasmid pMUT-V600E, which is incorporated into 2.0×10 4 In the corresponding copy of the wild-type plasmid pWT-V600E, real-time fluorescent PCR detection was performed to calculate the difference between the two Ct values, ΔCt=Ct wild type-Ct mutant type.
[0078] The specific primers of different lengths used in this example, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Embodiment 2, the effect of competitive Block oligonucleotide
[0095] Considering that tissue and blood samples contain a large amount of wild-type DNA in addition to mutant DNA, in order to further improve the specificity of detection, the inventors conducted analysis, comparison and combination experiments to verify the characteristics of the BRAF gene V600E mutation site and adjacent sequences. , to find a suitable competitive Block oligonucleotide. Block oligonucleotides are completely complementary to wild-type genes and partially complementary to mutant genes. In the presence of wild-type genes, Block oligonucleotides can block wild-type genes and prevent wild-type genes from being amplified. false positive.
[0096] A total of 20 copies of the V600E site as a mutant plasmid (pMUT-V600E) were incorporated into 2.0×10 4 In the corresponding wild-type plasmid (pWT-V600E) of the copy, real-time fluorescent PCR detection was performed, and the difference between th...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Embodiment 3, sensitivity
[0106] A total of 20 copies of the V600E site as a mutant plasmid (pMUT-V600E) were incorporated into 2.0×10 4 In the corresponding wild-type plasmid (pWT-V600E) of the copy, the incorporation ratio is shown in Table 9, and real-time fluorescent PCR detection was performed to investigate the sensitivity of the mutation detection system.
[0107] The specific primers, Block oligonucleotides, amplification primers on the other side, probe sequences, amplification reaction system and reaction procedures used in this example are the same as those in Example 2. The results are shown in Table 9.
[0108] Table 9. Sensitivity analysis results
[0109]
[0110] The above results show that, using the mutation detection system of the present invention, when the mutation ratio of the V600E site is 0.01%, there is still a good degree of discrimination from the wild-type plasmid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com