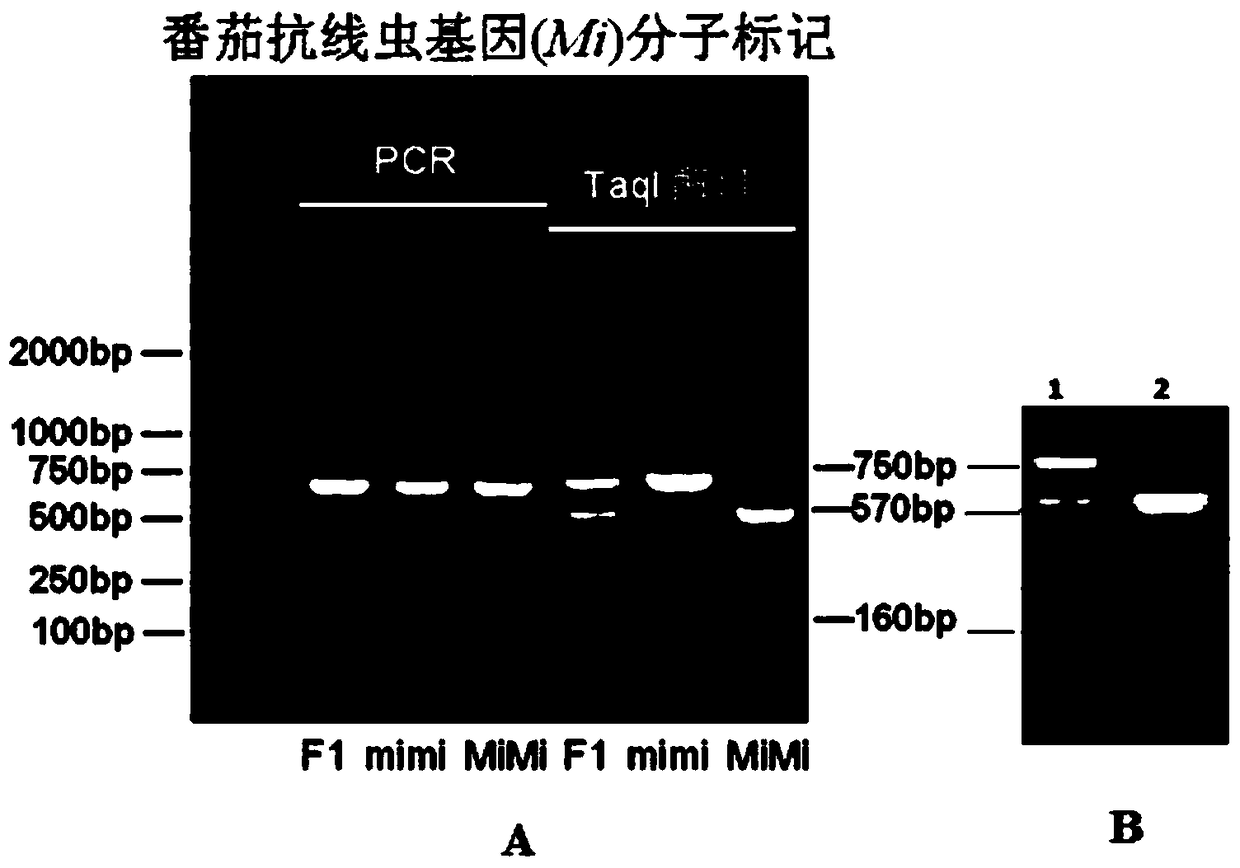
Method for cultivating tomato rootstocks with high compatibility and resistance to root knot nematode disease
A technology for resisting root-knot nematode disease and root-knot nematode is applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, fruit tree cultivation, plant genetic improvement, etc., and can solve the problems of tomato yield reduction, delayed grafting of rootstocks, incompatibility of rootstocks, and weak rootstocks, etc. Yield improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] The breeding of embodiment 1 anti-root-knot nematode tomato stock
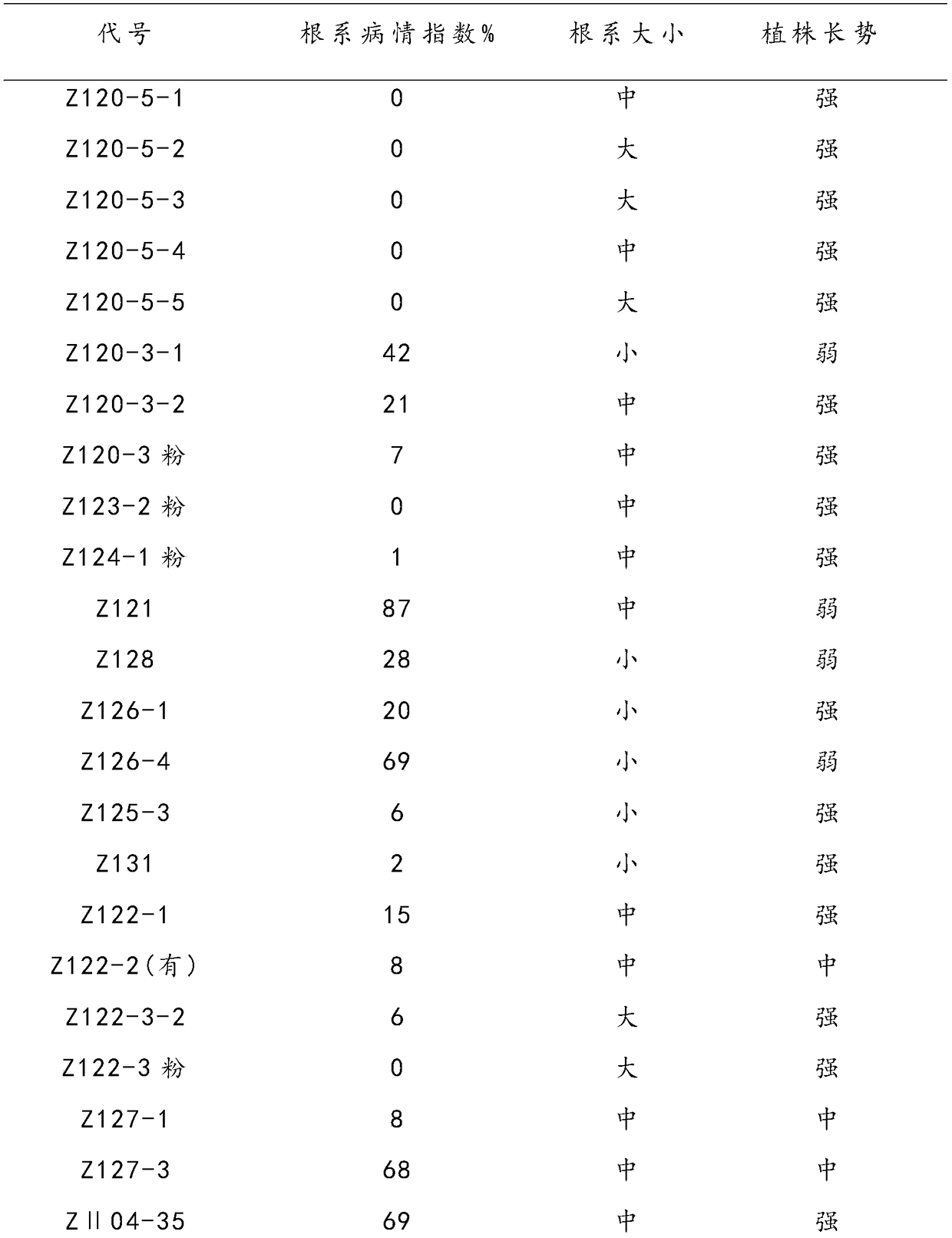
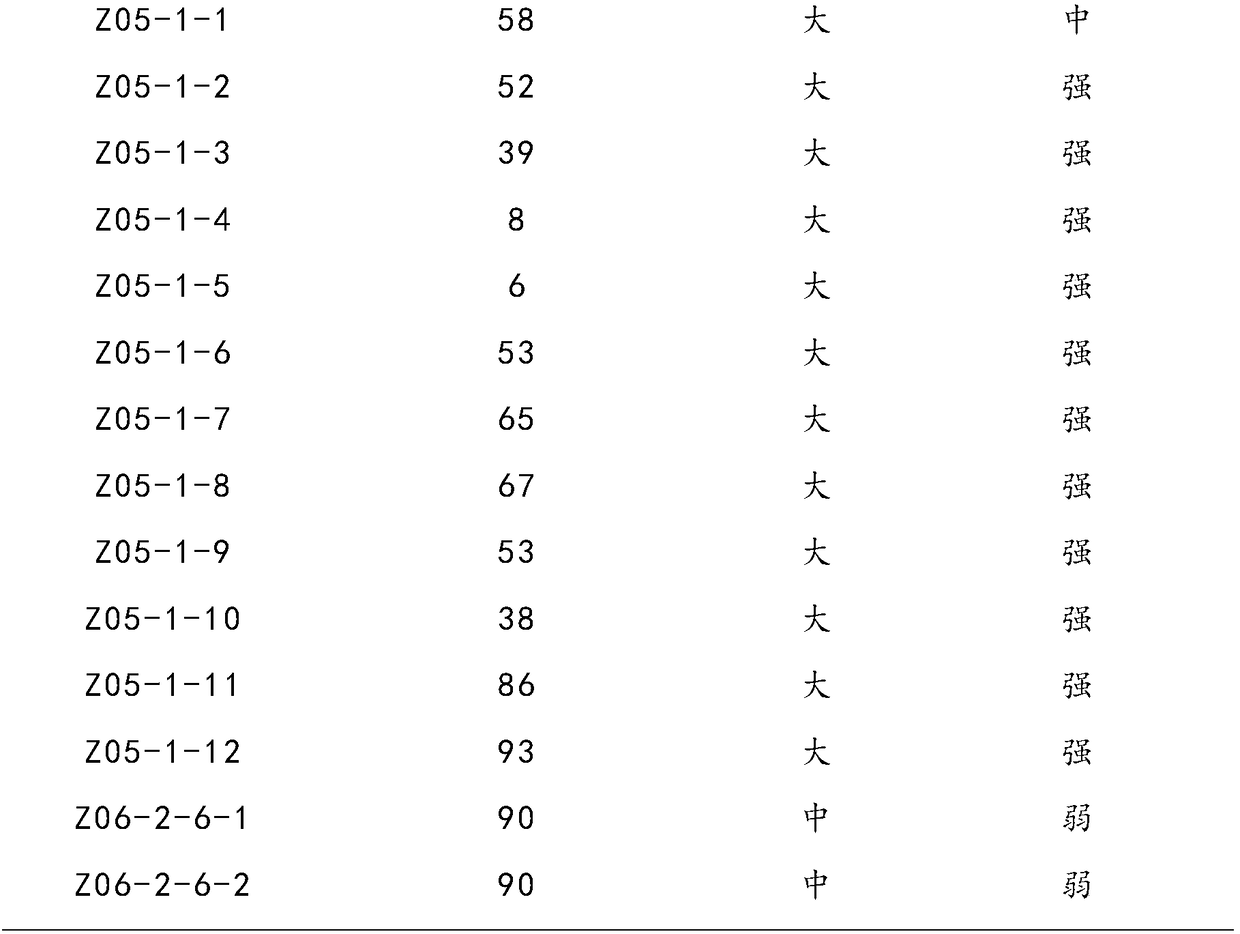
[0019] From 2008 to 2014, nematode-resistant rootstock materials were screened for many years in a field disease nursery where tomato had been planted continuously for more than 10 years and the root-knot nematode incidence rate was 100%. Among them, the disease-resistant lines 'Z120-5-3', 'Z120-5-5' and 'Z123-2' showed vigorous plants, dark green leaves, well-developed roots, and root nematode index was 0%; 'Z05-1- 4' and 'Z05-1-5' showed vigorous plants, dark green leaves, well-developed roots, and a root nematode index of 6%. The control 'Z121' showed yellow leaves, weak plants, and a root nematode index of 61.2%. Among them, 'Z05-1-5' was the most prominent among the 12 sown lines. The plants grew vigorously, with dark green leaves, well-developed root system, and were more resistant to nematodes, while the growth of other lines was obviously not as good as that of 'Z05-1- 5', the leaves are yellow...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The identification of embodiment 2 stock grafting affinity
[0042] Previous studies have found that when '72-69' is used as a scion to graft different rootstocks, the nutrient absorption rate of the root system of the rootstock will be slower than the development rate of the scion fruit, resulting in poor compatibility. It shows that the rootstocks with good grafting compatibility will grow normally after grafting; while the rootstocks with poor grafting compatibility will grow vigorously at the seedling stage and early fruit expansion stage after grafting, but the plants will wilt or even die in the late fruit expansion stage. Phenomenon.
[0043] 2.1 Materials and methods
[0044] In the spring of 2012, grafting compatibility tests were carried out on 48 rootstock hybrid combinations using '72-69' as scion. The experiment was arranged in Qingdao Academy of Agricultural Sciences. On February 4, tomato rootstock and scion varieties were sown in seedling trays. On Ma...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 verification test
[0053] Identification of Grafting Compatibility of Different Types of Scions to Rootstock ‘Z 05-1-5×Z 123-2’
[0054] 3.1 Materials and methods
[0055] In the spring and autumn of 2013, the rootstock 'Z 05-1-5×Z 123-2' was grafted with 'Qingyan Tomato No. 1' and 'Fensha No. 2' as scions respectively in the steel pipe shed of Qingdao Academy of Agricultural Sciences Product comparison test. 'Qingyan Tomato No. 1' matures early, and the fruit expands quickly. It is used as a scion. It has strict requirements on rootstocks, and rootstocks with strong compatibility can be selected. The area of the cultivated plot is 3.6 square meters, the distance between plants is 0.3 meters, and the distance between rows is 0.6 meters. 20 trees are planted in each border, and repeated three times.
[0056] 3.2 Test results
[0057] 3.2.1 'Qingyan Tomato No.1' as scion
[0058] In the spring of 2013, 'Qingyan tomato No. 3' was used as rootstock, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com