Organosilicon high-molecular fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorous acid and preparation method thereof
A technology for the detection of hypochlorous acid and silicon polymers, which is applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, chemical instruments and methods, analytical materials, etc., to achieve the effects of strong specificity, easy availability of raw materials, and simple synthesis steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Synthesis of Fluorescent Probes
[0039] (1) React 50g of 3-aminopropylmethyldimethoxysilane with 50g of dimethyldimethoxysilane to generate aminopropylpolysiloxane under the condition of water as solvent;
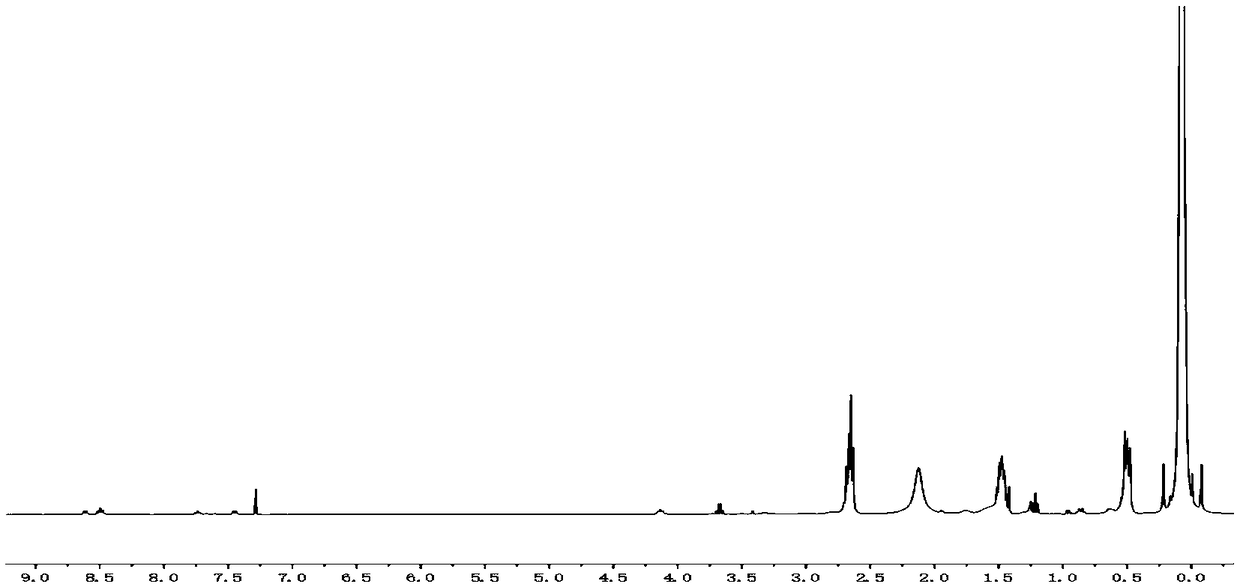
[0040] (2) In a 250 mL round bottom flask, add 2 g of aminopropyl polysiloxane, dissolve in 100 mL of ethanol, then add 0.10 g of 4-methylthio-1,8-naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride, dissolve in 100 mL of Ethanol, heated at 78°C with stirring and reflux for 24h. Rotary evaporation, drying to obtain the compound, i.e. fluorescent probe P-NS-ClO, its 1 H NMR spectrum as figure 1 shown. 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) :δ 8.63-8.59 (m, ArH), 8.52 -8.45(m, ArH), 7.76-7.70 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, ArH), 7.47-7.42(m, ArH), 6.46-6.26 (m, ArH), 3.70-3.64 (m, NCH 2 CH 3 ), 2.70-2.62 (t, J = 7.0Hz, NCH 2 ), 2.24-2.01(m, S-CH 3 ), 1.54-1.42 (m, NCH 2 CH 2 ), 1.29-1.19 (m, NCH 2 CH 3 ),0.59 -0.45 (m,Si-CH 2 ), 0.26-0.05 (m, Si-CH 3 ). Its number-average molecular...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 The selectivity of fluorescent probe P-NS-ClO to different molecules or ions
[0042] Prepare 5 mL of PBS aqueous solutions of various conventional ions and amino acids at a concentration of 40 mM and the fluorescent probe P-NS-ClO mother solution in Example 1 at a concentration of 1 mM as spares.
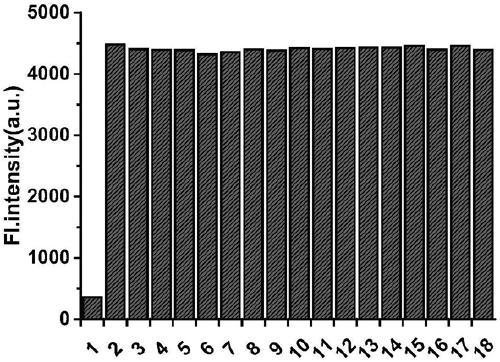
[0043] Add 25 μL of probe mother solution, 500 μL of ethanol and 500 equivalents of each ion (or amino acid) solution, and dilute to 3 mL with phosphate buffer solution PBS, so that the concentration of the probe is 10 μM, and the concentration of the test ion is 2.5 mM. The concentration of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species was 100 mM, and the concentration of aldehydes and ketones was 100 μM. Fluorescence detection was performed after shaking for 30 min (λ ex = 405nm,λ em = 485 nm), establish a histogram of fluorescence intensity and each ion (or amino acid, active oxygen, active nitrogen), the results are shown in figure 2 , wherein the ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Fluorescent detection of the fluorescent probe P-NS-ClO to different concentrations of hypochlorous acid
[0045] Prepare 10 mL of an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100 mM hypochlorous acid and a mother solution of the fluorescent probe P-NS-ClO in Example 1 with a concentration of 1 mM as backup.
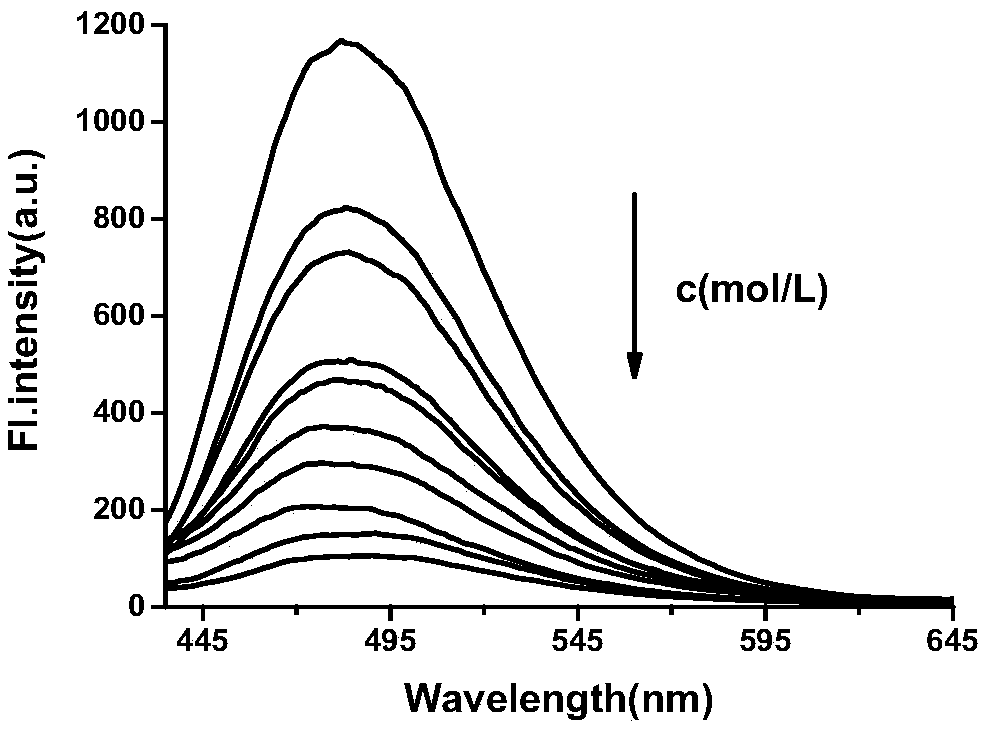
[0046] Prepare different concentrations of hypochlorous acid (0-20 μM) to react with the probe at a concentration of 10 μM, and perform fluorescence detection (λ ex = 405 nm), calculate the fluorescence intensity in each system, and establish the curve of fluorescence intensity and hypochlorous acid concentration, such as image 3 Shown: As the concentration of hypochlorous acid increases, the fluorescence intensity of the reaction system decreases rapidly, and when the concentration of hypochlorous acid reaches 20 μM, the fluorescence of the reaction system is completely quenched.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com