Multi-stator parallel pole type six-phase permanent magnet synchronous drive motor, application and method thereof
A permanent magnet synchronous driving motor technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuits, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the constant power operating range of the motor, the low utilization rate of the motor iron core material, and the poor adjustment ability of the motor magnetic flux and other problems, to achieve the effects of reducing the magnetic flux leakage effect at the end, low iron loss, and improving power density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
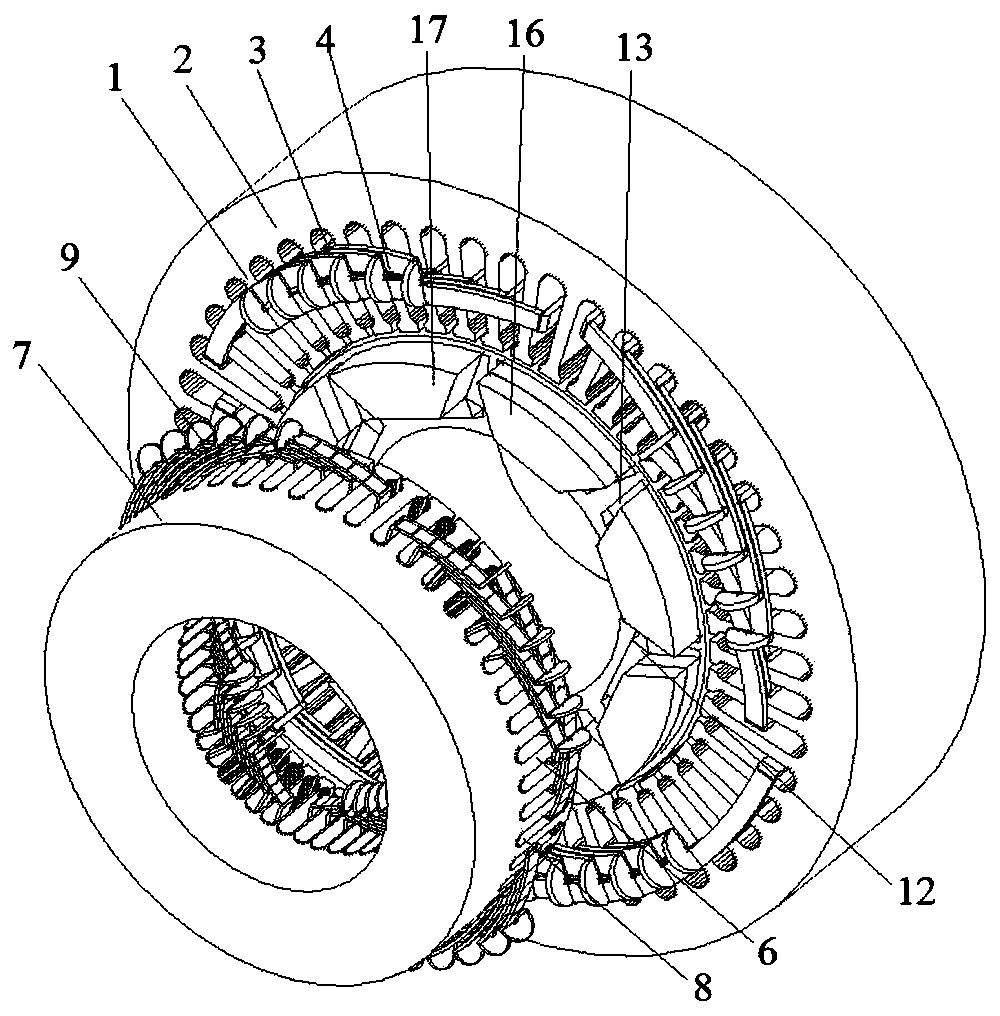
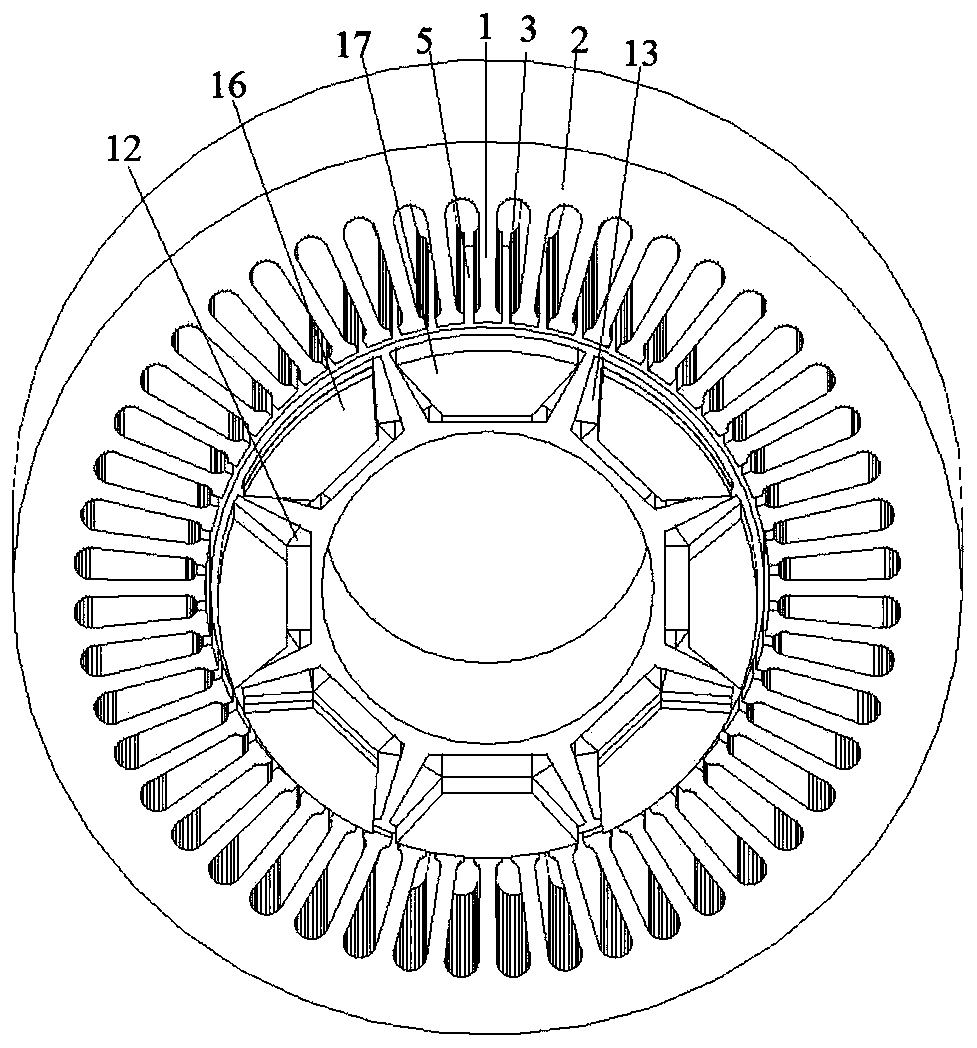
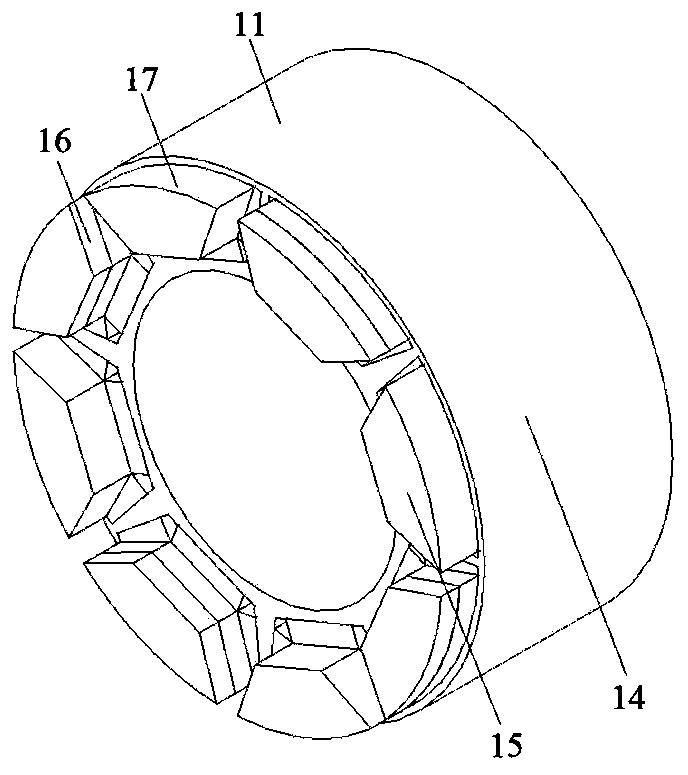
[0074] As shown in Figure 1(a)-Figure 1(e), the number of motor phases in this embodiment is 6, the number of radial stator teeth is 48, the number of axial stator teeth is 48, the number of rotor slots is 8, and the number of radial magnetic poles is 8 , the number of axial magnetic poles is 8, one end of the rotor has a fan ring structure, every other fan ring on the fan ring is placed with a permanent magnet in the form of parallel poles, and the permanent magnet on the fan ring is placed on the pole of the iron core side The polarity is opposite to the axial flux polarity formed by the permanent magnets in the rotor slots. This embodiment includes a radial stator, an axial stator and a rotor. The radial stator is made of laminated silicon steel sheets. The radial stator includes radial stator teeth 1, radial stator yokes 2 and radial stator slots 3. The radial stator A radial armature winding 4 is placed in the slot 3. The radial armature winding 4 can be divided into dist...
Embodiment 2
[0076] As shown in Figure 2(a)-Figure 2(e), the main difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that (1) there are axial stators at both ends of the motor in Embodiment 2, and the motor has soft magnetic The two ends of the composite rotor core are processed into the shape of the fan ring to form the axial magnetic poles, but in the first embodiment, only one end of the motor has an axial stator, and only one end of the motor rotor core is processed into a fan ring. The shape forms the axial magnetic poles. (2) In the second embodiment, since both ends of the rotor are processed into the shape of fan rings, permanent magnets are attached to every other fan ring at the two ends of the rotor in a parallel pole structure, and the two ends The permanent magnets at the top are at the same axial position, and the structure in the second embodiment can eliminate the unbalanced magnetic pulling force on the rotor because there are stators at both ends of the rotor. In this em...
Embodiment 3
[0079]As shown in Figure 3(a)-Figure 3(e), the main difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 2 is that there are fan ring structures on both ends of the rotor of the motor, and the permanent magnets on the fan ring structure are arranged every other fan ring structure. The rings are arranged in a parallel-pole manner, but the permanent magnet surfaces at both ends are attached to different axes, that is, they are staggered when viewed from the axial direction. In this embodiment, the number of motor phases is 6, and the number of radial stator teeth is 48. , the number of axial stator teeth is 48, the number of rotor slots is 8, the number of radial magnetic poles is 8, and the number of axial magnetic poles is 8. Both ends of the rotor are designed with fan ring structures, and the permanent magnets on the fan rings are separated by a fan ring. The rings are arranged in the form of parallel poles, and the permanent magnets on the fan rings at both ends of the rotor are o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com