Method for detecting antibiotics in drinking water
A technology for drinking water and antibiotics, applied in measuring devices, instruments, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve problems such as detection of difficult multiple targets, and achieve the effects of diverse selectivity, low detection concentration, and simple preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0063] Embodiment one: the method for detecting antibiotics in drinking water in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
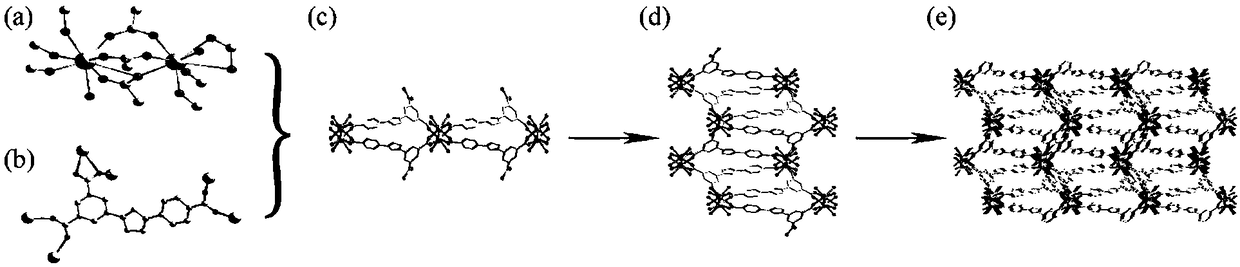
[0064] 1. Preparation of H 3 dcpcpt rare earth complexes:
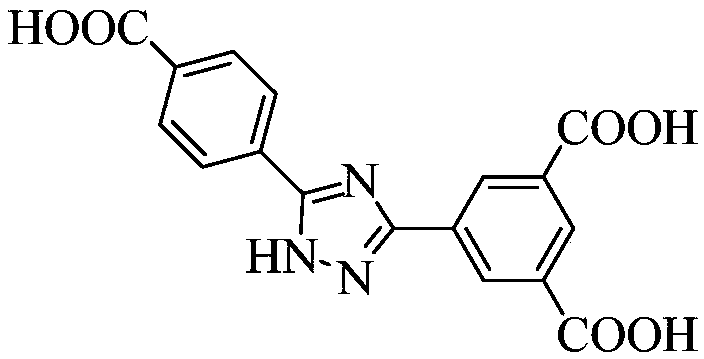
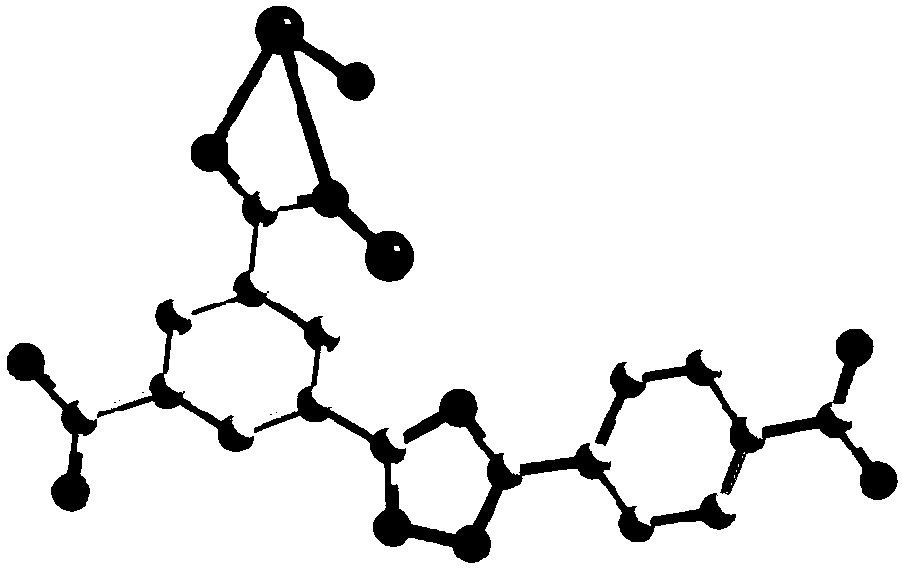
[0065]①. Add 3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-5-(4-carboxyphenyl)-1-hydrogen-1,2,4-triazole to N,N'-dimethylformaldehyde amide, and then add a solution of europium salt with a concentration of 0.01mol / L to 1mol / L, under the condition of a temperature of 140°C to 160°C, conduct a solvothermal reaction for 2h to 96h, filter after the reaction, and wash with water and methanol respectively, Vacuum drying at a temperature of 55°C to 65°C yields H 3 dcpcpt europium complex;
[0066] The mass of 3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-5-(4-carboxyphenyl)-1-hydrogen-1,2,4-triazole and N,N' -The volume ratio of dimethylformamide is 1g:(150~250)mL; the concentration described in step ① is the europium salt solution of 0.01mol / L~1mol / L and N,N'-dimethylformamide The volume ratio of amides is 1:(60~100)...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0094] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in step ①, 3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-5-(4-carboxyphenyl)-1-hydrogen-1, Add 2,4-triazole to N,N'-dimethylformamide, then add europium salt solution with a concentration of 0.01mol / L to 0.5mol / L, at a temperature of 150°C to 160°C , solvothermal reaction for 2h to 72h, filtered after the reaction, washed with water and methanol respectively, and dried under vacuum at a temperature of 60°C to 65°C to obtain H 3 dcpcpt europium complex;
[0095] The mass of 3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-5-(4-carboxyphenyl)-1-hydrogen-1,2,4-triazole and N,N' -The volume ratio of dimethylformamide is 1g:(150~200)mL; the concentration described in step 1. is the europium salt solution of 0.01mol / L~0.5mol / L and N,N'-dimethyl The volume ratio of formamide is 1:(60-80). Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0096]Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: in step one ②, 3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-5-(4-carboxyphenyl)-1 -Hydrogen-1,2,4-triazole is added to N,N'-dimethylformamide, and then gadolinium salt solution with a concentration of 0.01mol / L~0.5mol / L is added, and the temperature is 150℃~ Under the condition of 160°C, solvothermal reaction for 2h to 72h, after the reaction, filter, wash with water and methanol respectively, and dry under vacuum at a temperature of 60°C to 65°C to obtain H 3 dcpcpt gadolinium complex;
[0097] The mass of 3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-5-(4-carboxyphenyl)-1-hydrogen-1,2,4-triazole and N,N' -The volume ratio of dimethylformamide is 1g:(150~200)mL; the concentration described in step 1② is the gadolinium salt solution of 0.01mol / L~0.5mol / L and N,N'-dimethyl The volume ratio of formamide is 1:(60-80). Others are the same as those in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com